Imagine if you had a magic box where you could keep all your business information — sales numbers, customer feedback, everything — safe and sound, but also easy to look at whenever you needed.
That’s kind of what Snowflake does, but for big organizations and using the cloud. It’s a new way for companies to store and use their data without getting bogged down by the techy details. Think of Snowflake as a giant, smart library where businesses can easily store their books (data) and read them to make better decisions.
In this guide, we’ll explore why Snowflake is becoming the go-to choice for organizations wanting to be smarter about their data.
What Is Snowflake?
Snowflake is not just another cloud data warehouse; it’s a Software as a Service (SaaS) platform that revolutionizes data storage, processing, and analytics for modern enterprises. It offers a seamless, fully managed service that simplifies data warehousing, data lakes, data engineering, data science, and even the development of data-driven applications.
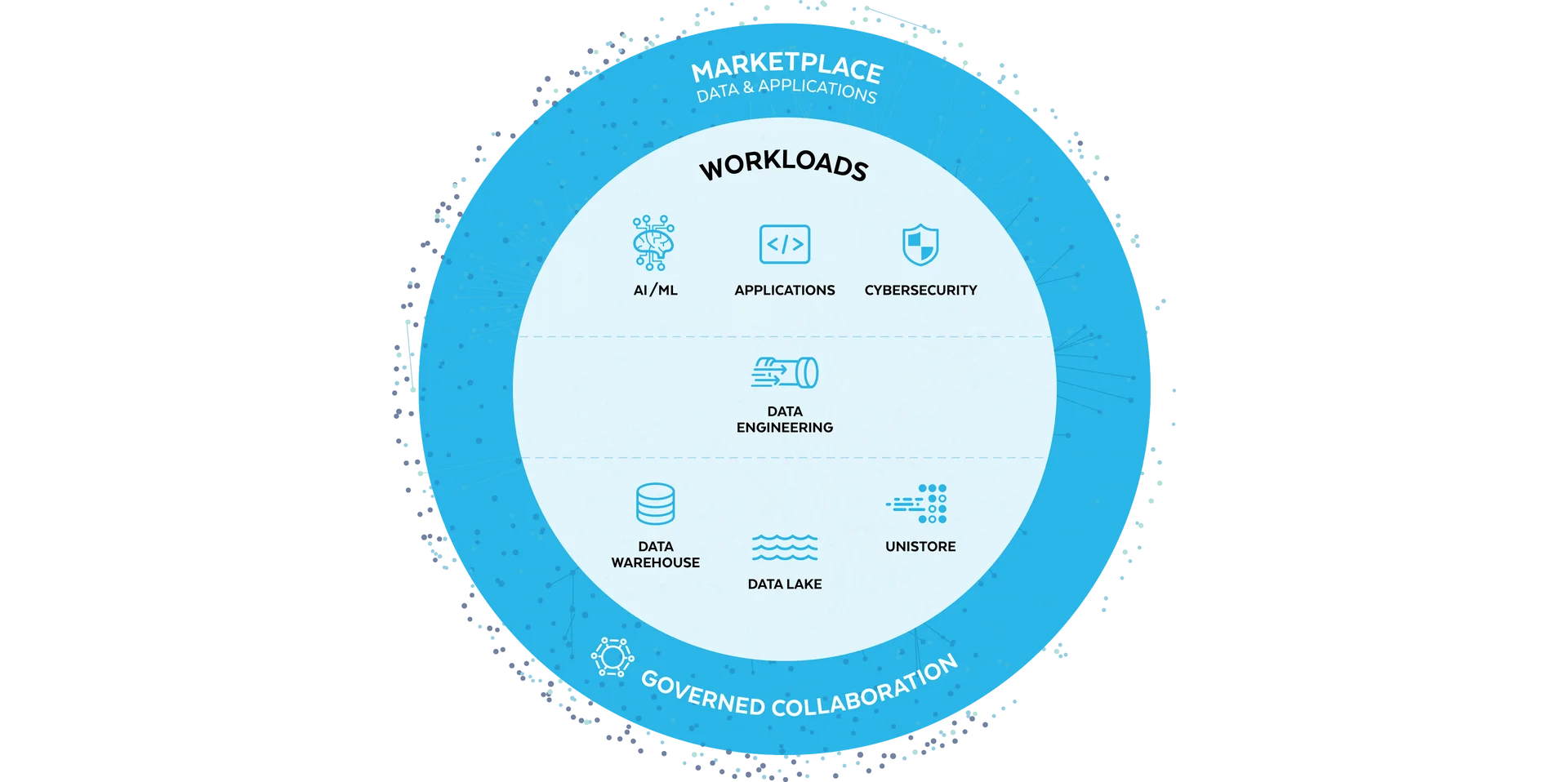
A One-Stop Data Management Solution Source: Snowflake
The core innovation behind Snowflake is its cloud architecture, which decouples storage from compute. This allows for unprecedented scalability and performance optimization.
Depending on your workload, you can scale compute resources up or down in real-time, without ever impacting your data storage. This separation ensures that you can manage and analyze data more efficiently, with the ability to run multiple workloads concurrently without contention.
Snowflake appeals to cloud engineers with its support for both structured and semi-structured data (such as JSON, Avro, XML). This flexibility means Snowflake can handle various data types natively, simplifying data integration and analysis processes.
The platform also introduces innovative capabilities like data sharing, which enables secure and easy access to shared data sets across different Snowflake accounts without duplicating data.
Additionally, Snowflake’s support for data cloning and on-the-fly scalable compute resources offers significant advantages in terms of cost-efficiency and operational agility.
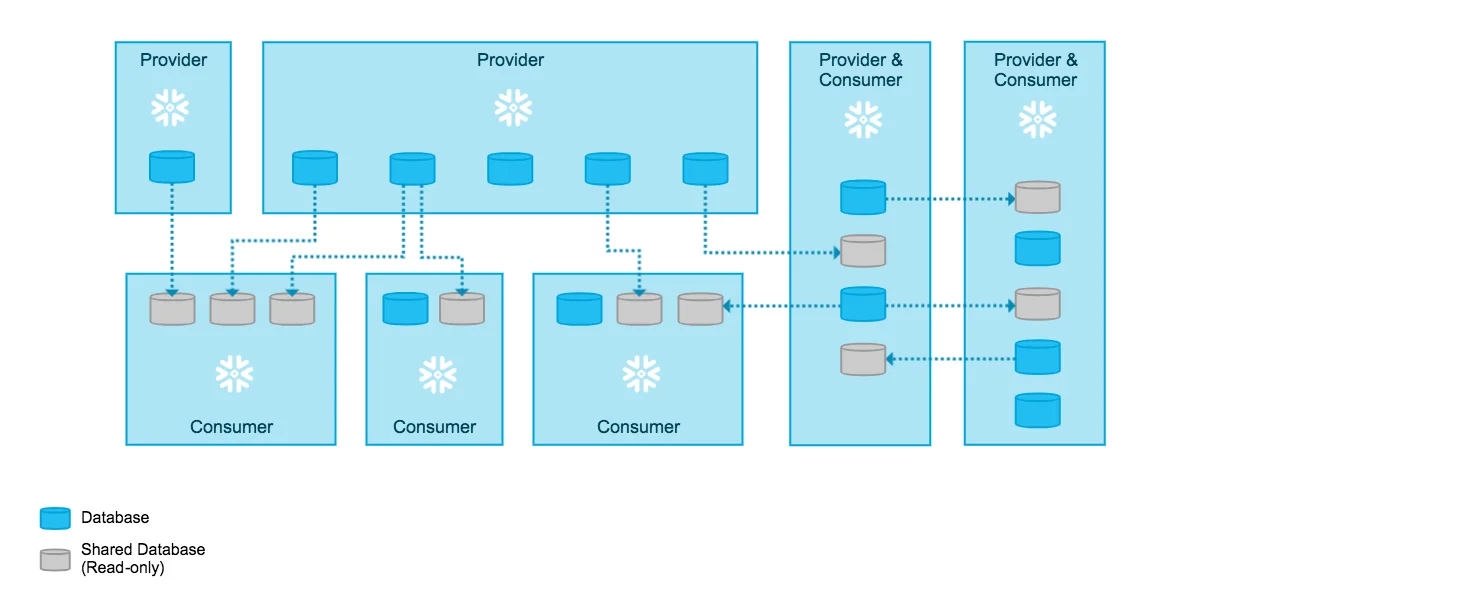
Snowflake data sharing overview
Snowflake’s compatibility with existing tools, alongside its security features, further cements its position as a highly effective solution for modern cloud engineering challenges.
For a detailed breakdown of how Snowflake’s pricing works and how to maximize its cost-effectiveness based on your usage, we invite you to explore our in-depth article on Snowflake pricing here: Understanding Snowflake Pricing.
How Does Snowflake Work?
Snowflake’s Data Cloud revolutionizes data storage, processing, and analysis, offering a solution that’s faster and easier to use than traditional models and highly adaptable to modern data management needs.
Distinct from legacy databases or big data frameworks like Hadoop, Snowflake melds a brand-new SQL query engine with an architecture ingeniously crafted for the cloud.
Data platform as a self-managed service
Snowflake redefines simplicity in data management by eliminating the hardware and software overhead traditionally associated with data platforms.
It operates entirely on cloud infrastructure, making it a purely self-managed service where Snowflake handles the installation, configuration, maintenance, upgrades, and tuning. This means cloud engineers can focus more on strategic tasks rather than the operational upkeep of their data platform.
Snowflake Architecture
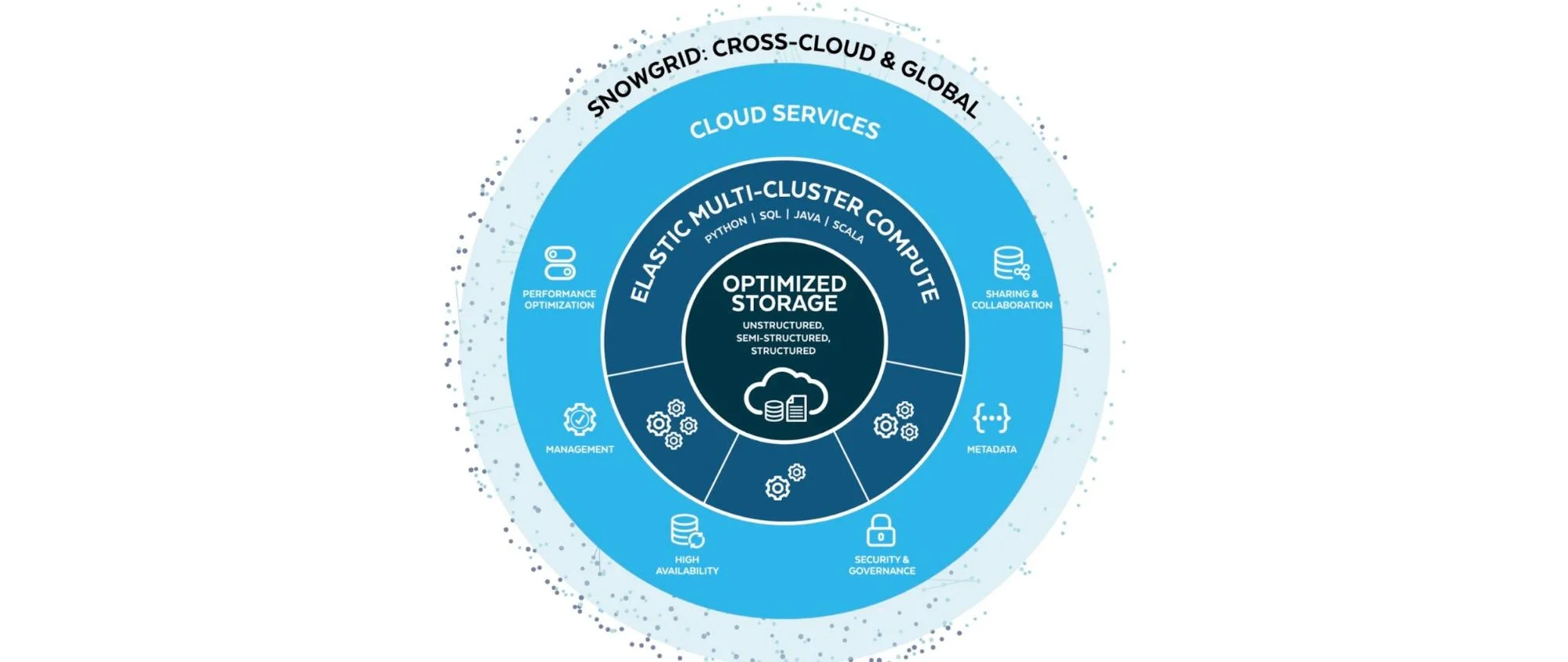
Snowflake Architecture
The Snowflake architecture ingeniously combines the best of shared-disk and shared-nothing architectures. It utilizes a central data repository, making persisted data accessible across compute nodes — similar to shared-disk architectures.
At the same time, it adopts the massively parallel processing (MPP) approach for handling query processing, similar to shared-nothing architectures, where each node locally stores a portion of the data set.
This combination offers the simplicity of data management of shared-disk systems with the performance and scalability of shared-nothing systems. The three key players in snowflake architecture include:
Database storage
Snowflake transforms data into an optimized, compressed, columnar format upon loading. It meticulously manages the storage — handling the organization, compression, and other crucial aspects — making the data accessible solely through SQL queries. This optimization is key to Snowflake’s fast data retrieval and query performance.
Query processing
This occurs in virtual warehouses, each an MPP compute cluster consisting of multiple compute nodes allocated from a cloud provider.
These virtual warehouses operate independently, ensuring that the workload of one does not affect the performance of others. This design principle allows for concurrent, high-performance data processing across different parts of an organization without resource contention.
Cloud services
Snowflake’s backbone, the cloud services layer, orchestrates the platform’s components to process user requests efficiently. It features various services from authentication, metadata management, query optimization, to access control, all running on compute instances provisioned by Snowflake.
Connecting to Snowflake
Snowflake supports versatile connectivity options — from a web UI for management and usage, command-line clients like SnowSQL, to ODBC/JDBC drivers and native connectors for application development.
These options ensure smooth integration with various tools and platforms, enhancing Snowflake’s utility across different data engineering and analytics scenarios.
Snowflake Use Cases
Snowflake’s versatility shines across various data management and analytic scenarios:
Data ingestion
With Snowpipe, Snowflake offers a robust solution for continuous data ingestion. It allows real-time data availability from sources like S3 and Azure Blob, and its integration facilitates uninterrupted data flow into Snowflake tables.
Business intelligence and analytics
Snowflake enhances decision-making by integrating with leading BI tools (QuickSight, Looker, Power BI, Tableau), providing deep insights from complex data sets.
Data sharing and collaboration
Through the Snowflake Marketplace, it fosters a collaborative ecosystem, enabling secure and easy data exchange between different entities, thereby enhancing data-driven strategies across businesses.
Machine Learning
Snowflake supports machine learning workflow within its platform, accommodating data preparation, model building, and deployment, streamlined by its integration with TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Apache Spark, and support for popular programming languages.
When Would You Use Snowflake?
Choosing Snowflake is particularly advantageous when your organization faces:
Rapid data growth
When your organization experiences or anticipates rapid data growth, Snowflake’s scalable architecture ensures that your data handling capabilities can grow consistently with your needs, without the overhead of managing physical infrastructure.
Complex data analytics needs
For organizations diving deep into data analytics and requiring fast and complex query executions across large datasets, Snowflake’s performance and concurrency are unmatched, especially when coupled with its dynamic scaling.
Data silos and integration challenges
If your organization struggles with data silos and seeks a unified platform to consolidate various data sources for cohesive analysis, Snowflake’s data sharing capabilities and broad ecosystem of connectors simplify data integration and accessibility.
Developing data-driven applications
When building applications that rely heavily on real-time data processing and analytics, Snowflake’s support for machine learning and its ability to handle diverse data workloads make it an ideal backend service.
Need for stringent data security and governance
Organizations that operate in regulated industries or have strict data security and governance requirements will find Snowflake’s comprehensive security features, including encryption, Time Travel, and Fail-safe, crucial for compliance and data protection.
Seeking operational efficiency
For teams aiming to reduce the operational burden of data management and focus more on strategic initiatives, Snowflake’s self-managing and serverless options present a compelling case by removing the complexities of traditional data warehouse maintenance.
Cost-effective data strategy
Lastly, for organizations looking for a cost-effective way to manage their data infrastructure, Snowflake’s on-demand pricing model provides a flexible approach to managing costs, paying only for the resources used, which is particularly advantageous for varying workloads.
The Pros Of Snowflake
Advanced security and data protection
Snowflake ensures top-tier data security, offering features like Time Travel and Fail-safe for robust data recovery and historical data protection, alongside compliance with major regulatory standards.
Impressive performance and scalability
Its architecture allows for concurrent workloads with minimal latency, supporting both vertical and horizontal scaling effectively, which translates to high performance across diverse queries and workloads.
Data caching and micro-partitions
These features highly boost query performance, with Snowflake’s intelligent caching and efficient data storage in micro-partitions facilitating faster data retrieval and processing.
User-friendly experience
Snowflake’s SQL-based interface caters to both beginners and seasoned users, offering an intuitive UI and a gentle learning curve, simplifying data warehouse operations.
Zero management overhead
Emphasizing a serverless experience, Snowflake abstracts the complexity of management and maintenance, providing a hassle-free environment for users to focus on deriving insights from their data.
Rich ecosystem of connectors and integrations
Snowflake boasts extensive connectivity options, including native connectors for Python, Java, C++, and popular data integration tools, enhancing its adaptability within diverse tech stacks.
The Cons Of Snowflake
While Snowflake offers numerous advantages, it’s essential to be mindful of:
Cost management
The on-demand pricing model, while flexible, requires careful management to optimize spending, particularly for compute-intensive operations.
Cloud-agnostic nature
While offering freedom from vendor lock-in, Snowflake’s cloud-agnostic approach means companies need to consider how it fits into their cloud strategy, especially when comparing it with native cloud data warehouse solutions.
How Does Snowflake Compare To Other Data Warehouses?
In comparing Snowflake to other data warehouses, it’s crucial to look at how its features and architecture match up against some of the major alternatives in the market.
Let’s delve into how Snowflake stands against some of its major competitors, Apache Hadoop, Databricks, and Amazon Redshift, focusing on key aspects like architecture, scalability, ease of use, and integration with existing tech stacks.
Snowflake vs. Apache Hadoop
Architecture and scalability
Snowflake’s architecture, separating storage and compute, provides flexibility and scalability without compromising performance. Apache Hadoop, while powerful for distributed processing across clusters, requires more complex management and lacks the straightforward scalability of Snowflake, especially in terms of on-the-fly computational adjustments.
Ease of use and security
Snowflake offers a more user-friendly experience with SQL support and built-in security features. Hadoop, though highly customizable, demands deeper technical expertise to manage its ecosystem and implement security measures effectively.
Suitability
Snowflake is ideal for organizations looking for a managed, scalable cloud data warehouse with minimal administrative overhead. Hadoop suits organizations that need a customizable, open-source framework for big data processing and have the capability to manage its complexity.
Snowflake vs. Databricks
Architecture
Databricks provides a lakehouse architecture that merges the benefits of data lakes and warehouses. Snowflake, with its cloud data warehouse approach, excels in data management and analytics without requiring extensive setup or management.
Ease of Use
While both platforms are powerful for data analytics and machine learning, Databricks demands more specialized knowledge for managing and optimizing Spark and its associated data pipelines. Snowflake’s simplicity and serverless model make it accessible to more users.
Suitability
Databricks is well-suited for organizations deeply invested in Spark and looking for a platform that bridges the gap between data lakes and warehouses. Snowflake appeals to those prioritizing ease of scaling, security, and simplified data management.
Snowflake vs. AWS Amazon Redshift
Architecture and performance
Both Snowflake and Redshift offer cloud-based data warehousing solutions with strong performance metrics. Redshift’s architecture is optimized for AWS, offering deep integration with its ecosystem, while Snowflake’s independent architecture allows for cross-cloud flexibility.
Serverless and scalability
Redshift provides managed services with options for serverless computing, aiming for a balance of performance and convenience. Snowflake’s distinct advantage lies in its dynamic scalability and the separation of storage and compute, allowing for more granular control over resources and costs.
Integration and optimization
For AWS users, Redshift may offer a smoother integration with existing AWS services. However, additional optimization efforts might be required to achieve optimal performance. Snowflake’s design minimizes the need for such optimizations, offering out-of-the-box performance efficiency.
Introducing Snowflake Cost Intelligence By CloudZero
CloudZero is proud to present Snowflake Cost Intelligence, a pioneering solution designed to bridge the gap between Snowflake and AWS cost data, offering unparalleled insights into the true cost of building and running your products.
This intelligence platform empowers engineering teams to map costs to specific architectural decisions, nurturing a culture of cost-conscious engineering and autonomy. By breaking down costs related to storage, compute resources, and beyond, Cloudzero helps pinpoint exactly where your costs are flowing and how to optimize them.
Why CloudZero?
- Unified Cost Insights: Get a holistic view of your costs across AWS and Snowflake, eliminating blind spots in your cost of goods sold (COGS).
- Actionable Intelligence: Understand the impact of architectural and technical decisions on your spending with detailed cost mapping.
- Proactive Cost Management: Leverage AI-driven anomaly alerting and weekly cost trend updates to stay ahead of unexpected expenses.
- Full-Feature Support: Enjoy all the benefits and features of CloudZero, now extended to include Snowflake, ensuring a comprehensive and cohesive cost management experience.
Don’t let cost complexity slow down your growth. Discover how CloudZero’s Snowflake Cost Intelligence can illuminate your path to efficient and effective cloud usage. Ready to see the difference for yourself?  and step into a new era of cloud cost management with CloudZero.
and step into a new era of cloud cost management with CloudZero.
FAQ: Understanding Snowflake
What is Snowflake used for?
Snowflake primarily serves as a data warehouse for storing and analyzing large volumes of data. It also supports data lakes, data engineering, data science, and the development of data-driven applications. Its architecture is built to handle diverse data workloads and analytics needs, making it an all-inclusive solution for data management.
Why is Snowflake so popular?
Several key factors contribute to Snowflake’s popularity:
- Cloud-Native Approach: It’s built for the cloud from the ground up, offering flexibility and scalability.
- Scalability: It can easily scale resources up or down based on demand, allowing businesses to manage data more efficiently.
- Ease of Use: Snowflake provides a user-friendly interface and supports SQL for data querying, making it accessible to users with various skill levels.
- Performance: Its unique architecture ensures high-speed data processing and analytics, simplifying data storage, processing, and analysis.
Is Snowflake the same as SQL?
Snowflake and SQL are not the same, but Snowflake uses SQL as its query language.
While SQL (Structured Query Language) is a standard language for accessing and manipulating databases, Snowflake is a cloud-based data warehousing solution that offers a broader range of data management and analytics capabilities.
Snowflake’s support for SQL means that it’s compatible with SQL queries, allowing users familiar with SQL to work with Snowflake effectively.
Is Snowflake an ETL tool?
No, Snowflake itself is not an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tool. Instead, it’s a data warehouse solution that can integrate with ETL tools.
ETL tools are used to extract data from various sources, transform it into a usable format, and then load it into a data warehouse for analysis. Snowflake can work alongside ETL tools to manage and process data, serving as the end destination where transformed data is stored and analyzed for business intelligence purposes.