The Amazon Redshift data cloud provides a fast, secure, and widely accessible data warehouse solution. It is an ideal platform for performing complex analytics and processing large data sets. In addition to supporting multi-parallel processing (MPP), Redshift is also a type of Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) database.
Yet, one of Redshift’s main selling points is its cost-effectiveness over alternatives like Snowflake and BigQuery. Is this the case? What is the actual cost of Amazon Redshift?
This guide explores how Amazon Redshift pricing works. Furthermore, we’ll share how to understand, control, and optimize your Redshift costs like a pro.
How Does Amazon Redshift Billing Work?
Redshift charges on a pay-as-you-go model, so you only pay for what you consume. Yet, Amazon Redshift costs vary based on factors such as your AWS Region and the type and number of Redshift nodes you deploy.
For example, pricing for the current generation of Dense Compute (DC2) large begins at $0.25 per hour in the US East (Ohio) region. Here are the details for that entire setup:
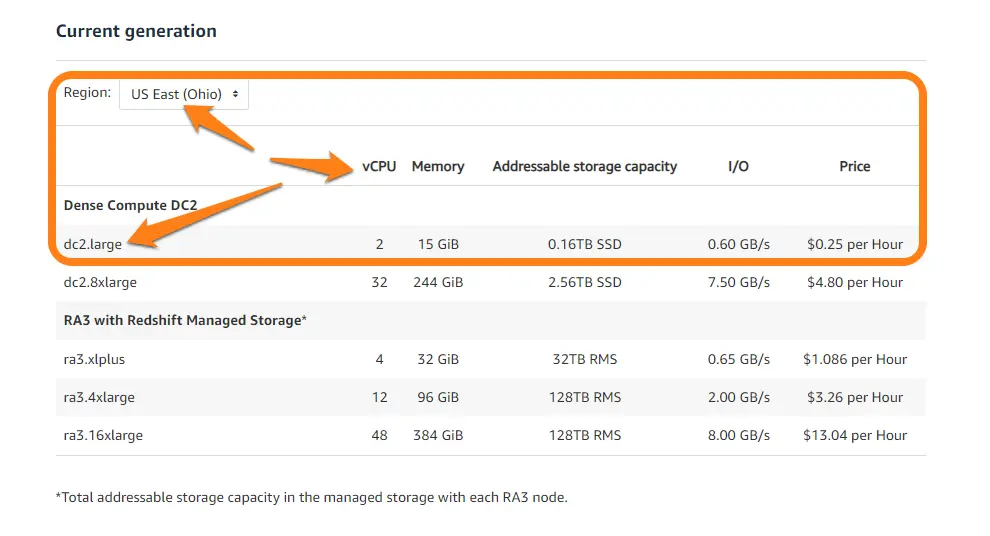
Credit: Amazon Redshift pricing for the US East – Ohio region
If you deploy your workload in the Europe – London Region, it would cost you $0.32 per hour for the same spec dc.large setup:
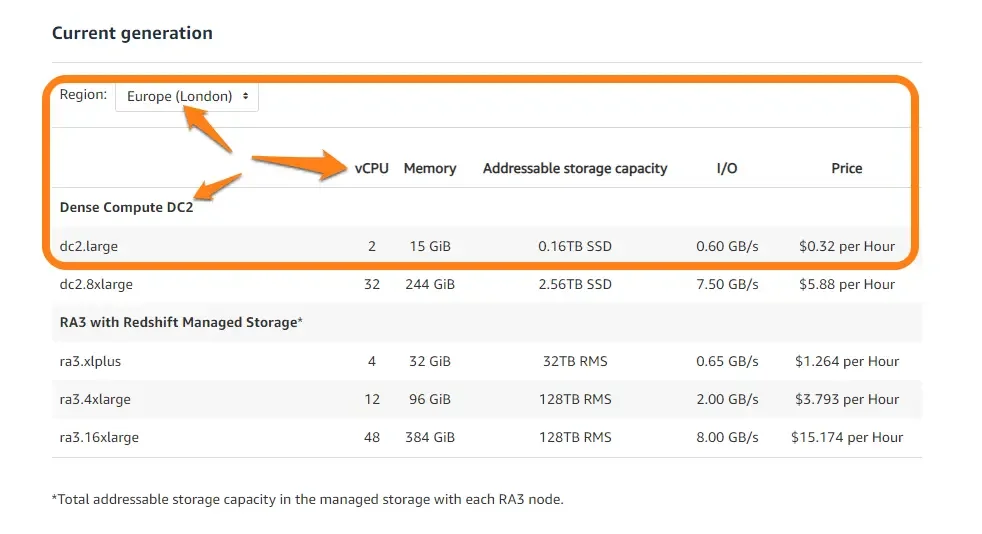
Yet this is only one pricing approach — the Redshift On-Demand billing approach, which kicks in after your free trial expires. Redshift offers several different pricing approaches.
Here are more details about each Amazon Redshift billing strategy.
1. Amazon Redshift On-Demand pricing
On-Demand billing allows you to use Redshift clusters without committing to long-term contracts or paying anything upfront. Instead, you pay hourly for the provisioned capacity of the particular node type and number you have running. Redshift bills partial hours per second you accumulate.
You can create, pause, delete, and resume these clusters. Redshift suspends On-Demand billing when you pause a cluster, but you still pay for its backup storage during that time.
A Redshift On-Demand plan is the most flexible data warehouse pricing option. You can seamlessly switch between node types, add or remove nodes to your cluster, and pause and resume it as your workload requires. A few clicks through the Amazon Redshift console or an API call will do the trick.
Yet, this method is the most costly. However, you can use Elastic Resize to adjust your provisioned compute capacity for steady-state processing promptly. Alternatively, using Resize Scheduler, you can scale your number of nodes up or down daily or weekly to optimize your costs and performance.
Still, On-Demand pricing can be up to 75% costlier than this next Redshift billing strategy.
2. Amazon Redshift Reserved Instances pricing
Redshift’s Reserved Instance costs follow a commitment-based pricing model. You commit to using Amazon Redshift for one or three years in return for up to 75% off of On-Demand pricing.
There are three types of reserved pricing available with Redshift:
- All Upfront – Saves up to 42% (1 year) or 75% (3 years) over On-Demand pricing when you pay 100% in advance.
- Partial Upfront – Saves up to 41% (1 year) or 71% (3 years) over On-Demand pricing depending upon the amount of upfront cost you put down (1% to 99%).
- No Upfront – Saves up to 20% compared to On-Demand pricing, is available only for one-year contracts, and requires no upfront payment.
Below is an example of Amazon Redshift’s reserved instance pricing with partial upfront payments:
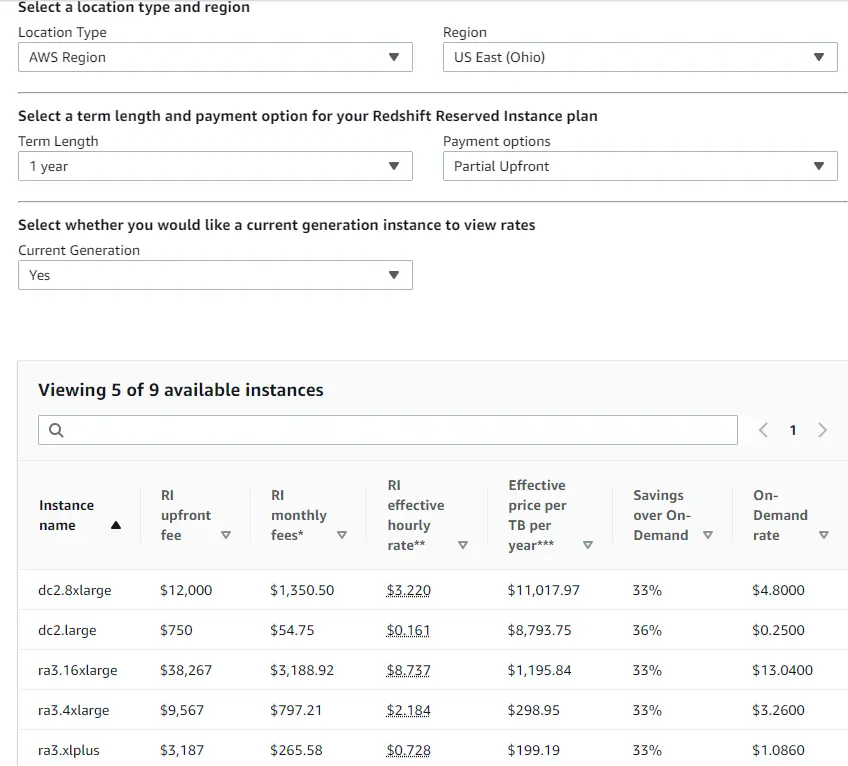
That’s quite a range.
Something else. When you reserve a Redshift node, you are not creating any nodes for yourself. Upon purchasing your reservation, specify which nodes you would like the reservation to apply to.
If you skip this step, Redshift will automatically bill for the Reserved Instance immediately after you purchase it — even if it’s not in use. The platform will bill you at the On-Demand rate after the Reserved Instance contract ends.
We also recommend you take the free trial to experiment before committing to a minimum one-year Reserved Instance plan. If you’ve never used Redshift before, you’ll get two months of free usage (up to 750 node hours) to see if it’s the right data warehouse solution.
Here’s the thing. You do not want to over or under-provision your storage. You’ll pay extra for unused capacity if you over-provision. Under-provision and your Redshift data warehouse performance may suffer.
If you are unsure what instances, nodes, or AWS services to use from the start, you can use a handy tool. For example, CloudZero Advisor helps you choose the best instance types for your workload, compare pricing, and get advice on AWS services like EC2, RDS, and ElastiCache.
Here’s a snapshot of CloudZero Advisor:
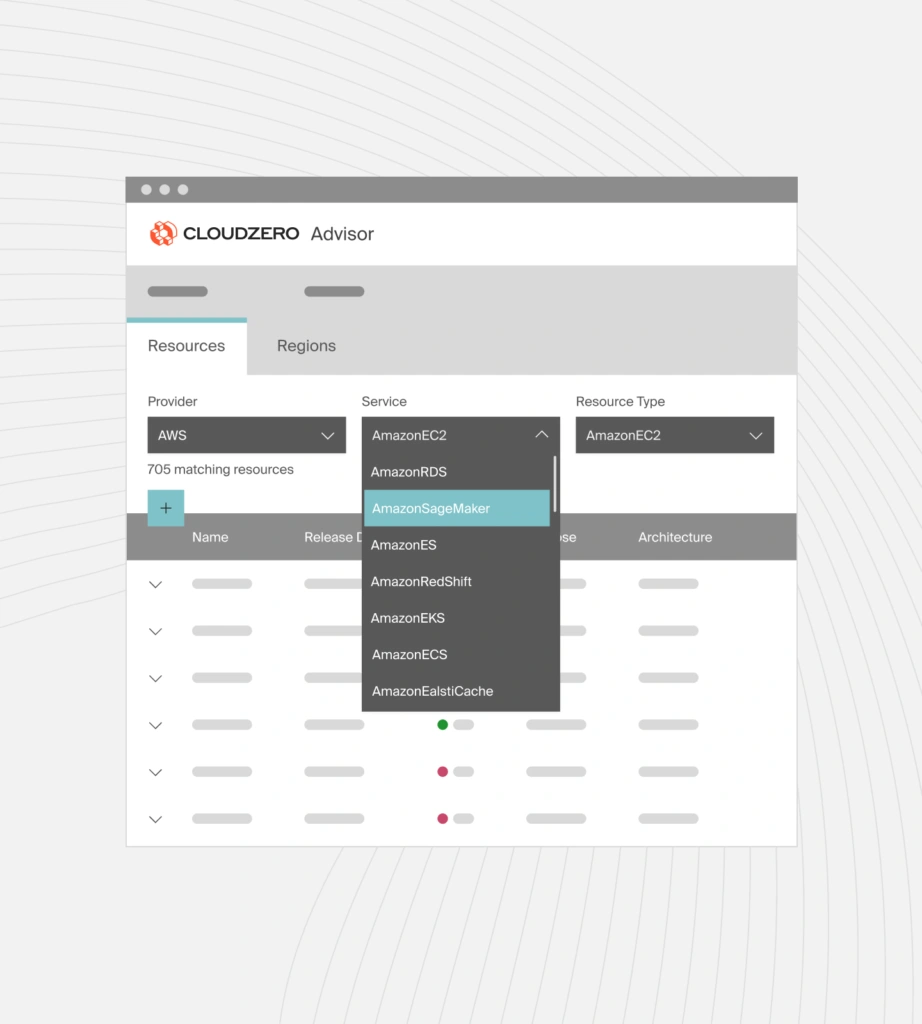
CloudZero Advisor compares instance types pricing and offers advice on various AWS services.
3. Amazon Redshift Serverless pricing
Redshift Serverless automatically starts up, shuts down, and scales capacity as your application needs to change. It charges only when it is actively processing workloads. This option is ideal for a dynamic workload with unpredictable requirements, such as those that can spike at any time.
This Redshift pricing strategy bills you per second based on Redshift Processing Unit Hours (RPU-hours). There is a minimum billing requirement of 60 seconds. Additionally, you pay for queries to open file formats in Amazon S3.
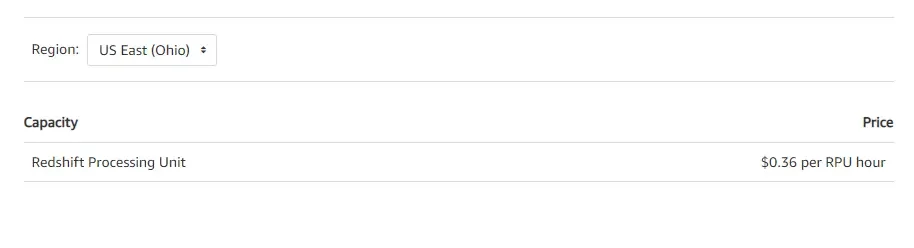
Credit: Redshift Serverless pricing for the US East – Ohio region
Redshift Serverless does not charge additional fees for auto-scaling, data warehouse startup time, or security features.
One more thing. Redshift Serverless pricing includes concurrency scaling and Redshift Spectrum.
So, what’s concurrency scaling and Redshift Spectrum, you ask?
4. Concurrency scaling in Amazon Redshift
Concurrency scaling automatically launches additional, short-lived clusters during high usage periods. The feature removes them as soon as they are no longer needed to save costs.
Redshift lets you use one hour of Concurrency Scaling for free every 24 hours and charges you by the second once you go over it. Your cluster earns credits for every hour it operates, and you can accumulate a maximum of 30 free hours. As long as you don’t terminate the cluster, these credits will not expire.
When you activate concurrency scaling for a cluster, there’s a 60-second minimum charge. The rate is based on Redshift’s On-Demand rate.
5. Redshift Spectrum pricing
With Redshift Spectrum, you can query your data lake directly without importing it to Redshift. It charges based on the number of bytes it scans (rounded off to the next gigabyte). There’s also a 10 MB minimum charge per query.
Note: Redshift Spectrum costs are reduced when you store your data in a compressed, columnar, partitioned format.
Prices for Redshift Spectrum vary by location. In the US West – Northern California – region, it costs $5 per terabyte (TB) of data scanned, but in the Asia Pacific – Hong Kong – region, it costs $5.75 per TB.
Additional costs may apply sometimes, such as when requests are made against an S3 bucket. Depending on your usage patterns, you may continue to incur other costs.
These five factors are not the only ones that affect Amazon Redshift costs. Charges also apply for data transfers, machine learning features, and managed storage. Your payment will also vary depending on how much you use each factor.
Certainly, that’s some flexibility – but it’s also a lot of complexity.
What Is The Pricing Difference Between Redshift RA3 And DC2 Nodes?
DC2 nodes charge storage and compute together, but RA3 nodes charge storage and compute separately.
Also, RA3 node types offer better price-performance value for data sets larger than 1 TB compared to DC2 nodes, which are ideal for smaller data sets.
In addition, DC2 nodes use Solid State Disks (SSDs), which make them fast yet affordable.
There are two more types of DC2 nodes:
- Dense Compute nodes (Up to 60% more cost-effective than Dense Storage and ideal for data that’s less than 500 GB) and
- Dense Storage nodes (optimized to store data sets of over 500 GB but are costlier than Dense Compute nodes).
You cannot mix-match these DC2 node types. You can check out CloudZero’s free tool to compare the best AWS tools, resources, and services for that job – including the best compute or storage instances.
Further DC2 node options include Dense Compute Large (dc2.large from $0.33 per hour) versus Dense Compute Extra Large (dc2.8xlarge from $6.40 per hour) or Dense Storage Large versus Dense Storage Extra Large.
Note: A node type’s computing power and storage capacity do not differ by region; this only applies to the price.
RA3 nodes, on the other hand, use Redshift Managed Storage (RMS), which automatically stores frequently used data on SSDs and moves infrequently used data to Amazon S3. RMS uses RA3 nodes by default.
Redshift charges you a flat $0.024 per GB per month of data present in the managed storage. You will not be charged for data transfers between your RA3 nodes and managed storage, but data transfers to and from Amazon S3 may incur fees. In addition, RA3 manual backup charges continue to accrue after terminating the cluster.
You’re right; calculating Redshift costs can be challenging, so let’s get done with it.
So, How Much Does Redshift Really Cost?
There are several factors that influence Redshift pricing, including the type of nodes, the number of nodes in a cluster, and the features you use. You can pay as you go for the computing and storage you consume. Or, you can sign up for a one- or three-year subscription for greater savings.
Taking advantage of those discounts requires thoroughly understanding your Amazon Redshift usage patterns. Only then can you choose the best Redshift reserved instance pricing strategy for your needs (all upfront, partial upfront, or no upfront).
So, how can you immediately improve your Redshift usage and cost visibility?
How can you spot the warning signs that your Redshift costs are about to run out of control?
How can you pinpoint who, why, and what drives your Amazon Redshift costs?
How To Understand And Control Redshift Costs With Cloud Cost Intelligence
You can monitor your data warehouse logs and usage patterns using Amazon CloudWatch. However, AWS Redshift integrates with over 170 AWS services. These include Amazon S3, AWS Glue, Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose, and Amazon Quicksight. When analyzing your CloudWatch data, it’s hard to tell how each service impacts your Redshift bill and why.
Another thing: Most cloud cost management tools don’t accurately map data-related costs to the specific people, processes, and products that produced them.
You can now organize your Amazon Redshift costs with CloudZero, normalize them, and then view them by customer, software feature, tenant, team, product, environment, etc. No manual tagging is required.
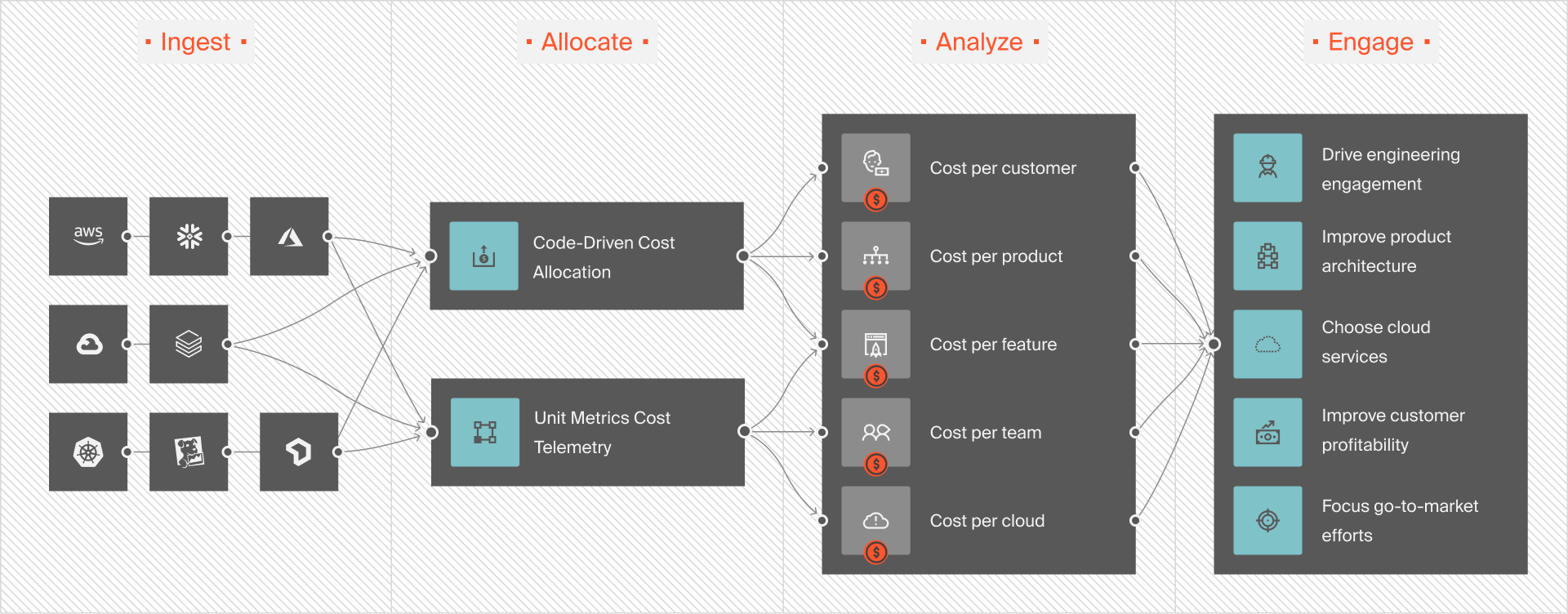
With this granularity, you can precisely identify what parts of Redshift need to be optimized to reduce costs without compromising performance.
You can also combine Snowflake and Amazon Redshift cost data in CloudZero to analyze and act on it in one place.
Have you seen CloudZero in action yet?  ! One of our Cloud Cost Analysts is waiting to help you get started.
! One of our Cloud Cost Analysts is waiting to help you get started.
Amazon Redshift Pricing FAQs
Does Amazon Redshift have a free plan?
Yes. If you’re new to Redshift, you can try the DC2 large node for two months for free.
You’ll get 750 free monthly hours with 160 GB of compressed SSD storage. You can then continuously run one DC2 large node or more for as long as this capacity lasts.
After your free trial expires or usage exceeds 750 hours monthly, you can shut down your cluster to avoid charges. Or, you can keep it running at Redshift’s On-Demand Rate.
Is Redshift cheaper than Snowflake?
Amazon Redshift is more cost-effective than Snowflake in several use cases. For a more precise comparison, check out our Redshift vs. Snowflake guide here.
Is Amazon Redshift better than Amazon S3?
Despite both being AWS cloud storage options, they serve different purposes. Most organizations find it more practical to use both than to choose one over the other.
What is RA3 in Amazon Redshift?
Redshift RA3 nodes are optimized for handling large data sets and separate compute and storage functions. They are the default nodes for Redshift Managed Storage (RMS).