Google Cloud Platform (GCP) launched in April 2008 with Google App Engine. This developer-centric Platform as a Service (PaaS) offering allowed developers to build and host web applications on Google’s cloud infrastructure.
Initially, App Engine only supported Python, but in 2009, Google added Java support, offering more programming flexibility. In 2010, GCP expanded further with Cloud Storage, its second major cloud product.
Today, GCP is the world’s third-largest cloud provider, behind AWS and Microsoft Azure.
GCP has also maintained its focus, excelling in AI/ML and data analytics, web app hosting, and open-source contributions (such as Kubernetes). The platform offers a more transparent and less complex pricing model than its top competitors.
Now, these advantages might make GCP the right fit for your needs — but is it available in your region?
Let’s dive deeper into how GCP regions work and whether they support your specific workload and geographical requirements.
What Are GCP Regions?
A GCP region is a physical location that typically is composed of three geographically separate data centers. These data centers are referred to as zones.
- Each zone has its own power, cooling, and networking infrastructure, which ensures operational independence.
- Zones are logically connected within the same region for redundancy and high availability.
- They are also physically close, but not too close so that an outage in one doesn’t impact the others. Well, that is unless there’s a region-wide disaster like an earthquake or flood.
This setup helps improve fault tolerance while maintaining low-latency performance for workloads running in Google Cloud.
There’s more.
What Is The Scope Of GCP Regions?
As a global cloud provider, Google has built multiple regions across all continents except Antarctica. Google Cloud Platform services are available across 47 global regions and 127 zones (as of publishing this post).
That’s not all, though.
GCP also offers 202 network edge locations. An Edge Location refers to Google’s cloud infrastructure that’s closest to an end-user, like your organization.
GCP cloud services are also available across more than 200 countries and territories worldwide. Consider this:
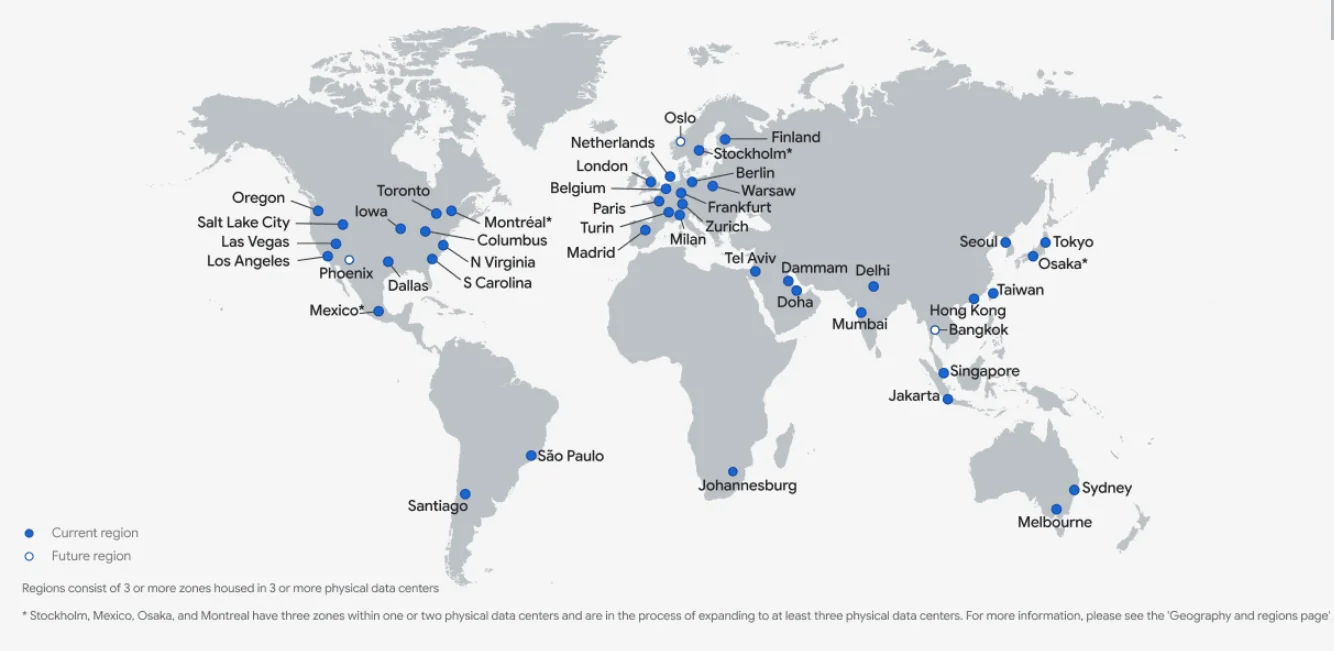
Image: GCP global regions map
These regions are strategically placed worldwide to provide low-latency, high-availability cloud services:
GCP Regions in North America:
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) has extensive coverage across the Americas, with multiple regions and zones across North and South America.
The United States has four regions (US East, US West, US Central, US South), covering nine zones:
- West: Oregon (us-west1), Los Angeles (us-west2), Salt Lake City (us-west3), and Las Vegas (us-west4)
- Central: Iowa (us-central1)
- East: South Carolina (us-east1), Northern Virginia (us-east4), and Columbus (us-east5)
- South: Dallas (us-south1)
Canada has one region (Northeast) and two zones: Montreal (northamerica-northeast1) and Toronto (northamerica-northeast2).
In Mexico, there is one zone: northamerica-south1.
GCP Regions in South America
There are two zones here, one in Santiago, Chile, and the other in São Paulo, Brazil.
GCP Regions in Europe
Expect five GCP regions here: West, Southwest, Central, East, and North. Currently, GCP offers 13 zones distributed across major hubs like London, Paris, Berlin, Belgium, Milan, Turin, Stockholm, Madrid, Warsaw, Frankfurt, Zurich, Finland, and the Netherlands.
GCP Regions in Africa
GCP has a single region in Africa, located in Johannesburg, South Africa, with the zone africa-south1.
GCP Regions in the Middle East
The Middle East is served from two regions, Central and West, with GCP zones available in Tel Aviv, Israel (me-west1), Doha (me-central1), and Dammam (me-central2).
GCP Regions in the Asian Pacific
Expect five regions here: South, Southeast, West, Northeast, and Central. These distribute across 11 zones in Mumbai, Delhi, Singapore, Jakarta, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Tokyo, Osaka, Seoul, Sydney, and Melbourne.
Now, here’s the thing.
While GCP strives for consistent reliability across all regions and zones, not all services are available everywhere, especially in newly established regions.
Some GCP products are always available by default, regardless of location. These include Compute Engine (compute), Cloud Storage (storage), and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
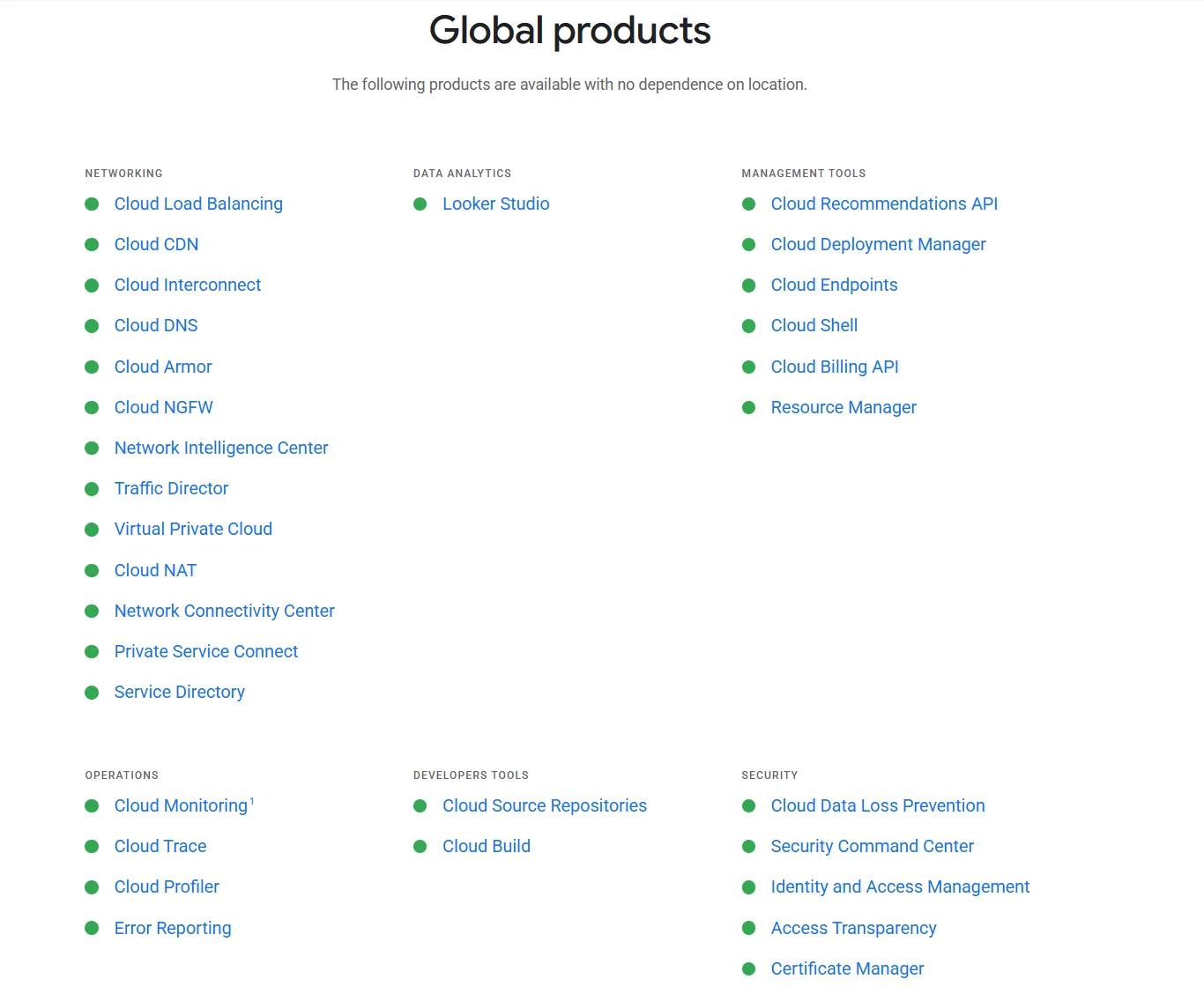
When Google launches a new region, it’ll often include additional services, such as BigQuery and Cloud Run, within the following six months.
Wondering how GCP Regions stack up against AWS Regions? Here’s a quick comparison to help you determine which provider best fits your geographic needs.
GCP Regions Vs. AWS Regions: What Are The Notable Differences?
GCP is rapidly expanding. But AWS remains the most globally distributed cloud provider. The difference isn’t just about the number of regions and zones; It’s also about the depth of reach.
Here are some examples to consider:
- AWS has significantly more edge locations than GCP. So AWS ensures peak performance for applications that demand single-digit milliseconds latency.
- Using multiple zones in GCP can generally be more cost-effective than using multiple regions in AWS. This is due to GCP’s lower data transfer fees and uniform pricing within regions.
See more about pricing differences in our AWS vs GCP pricing comparison here.
- However, AWS’s multi-region setup offers broader geographic reach and stronger disaster recovery capabilities, albeit at a higher cost and complexity level. For example, AWS also offers multiple regions and zones in Africa and South America, while GCP currently has just one region in each.
This broader infrastructure makes AWS a stronger choice for businesses needing deeper global coverage, even in emerging markets.
However, the ultimate choice depends on your business priorities — cost efficiency versus global reach and compliance needs.
Related read: Measuring The Scale Of AWS Data Center Locations Worldwide
Still, GCP holds its own in networking:
- GCP’s global Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) architecture simplifies cross-region networking compared to AWS’s region-specific VPCs.
- GCP subnets span all zones in a region automatically. When creating a VM, you pick both the subnet and a specific zone. On AWS, you need to explicitly tie subnets to individual Availability Zones, forcing more granular network planning.
- In AWS, subnets are designated as public or private. GCP uses a simpler approach: any instance can toggle public IP access without subnet changes, using Cloud NAT for private connectivity.
- Also, GCP offers Premium and Standard network tiers. This means you can choose between Google’s premium backbone or standard ISPs. AWS doesn’t have an equivalent tiered network service.
Additionally, if you prefer GCP for its strong open-source focus, AI/ML capabilities, and Kubernetes expertise, it still offers multiple regions where you can leverage its strengths.
How GCP Regions Affect Your Costs
If you’ve read our guide on How AWS Regions Affect Cloud Costs (And How To Reduce Fees), you already know that where you run your workloads, applications, and data can significantly impact cloud costs.
The GCP region you choose directly affects pricing for virtual machines, data transfer (egress), and other cost factors that vary by location.
Understanding these regional pricing differences can help you optimize costs while maintaining performance.
Here’s what you’ll want to consider:
- Resource pricing variations: VM and storage costs vary by region due to differences in infrastructure and operational expenses. For example, running resources in us-central1 is generally cheaper than in southamerica-east1, where cloud infrastructure costs are higher.
Consider this:
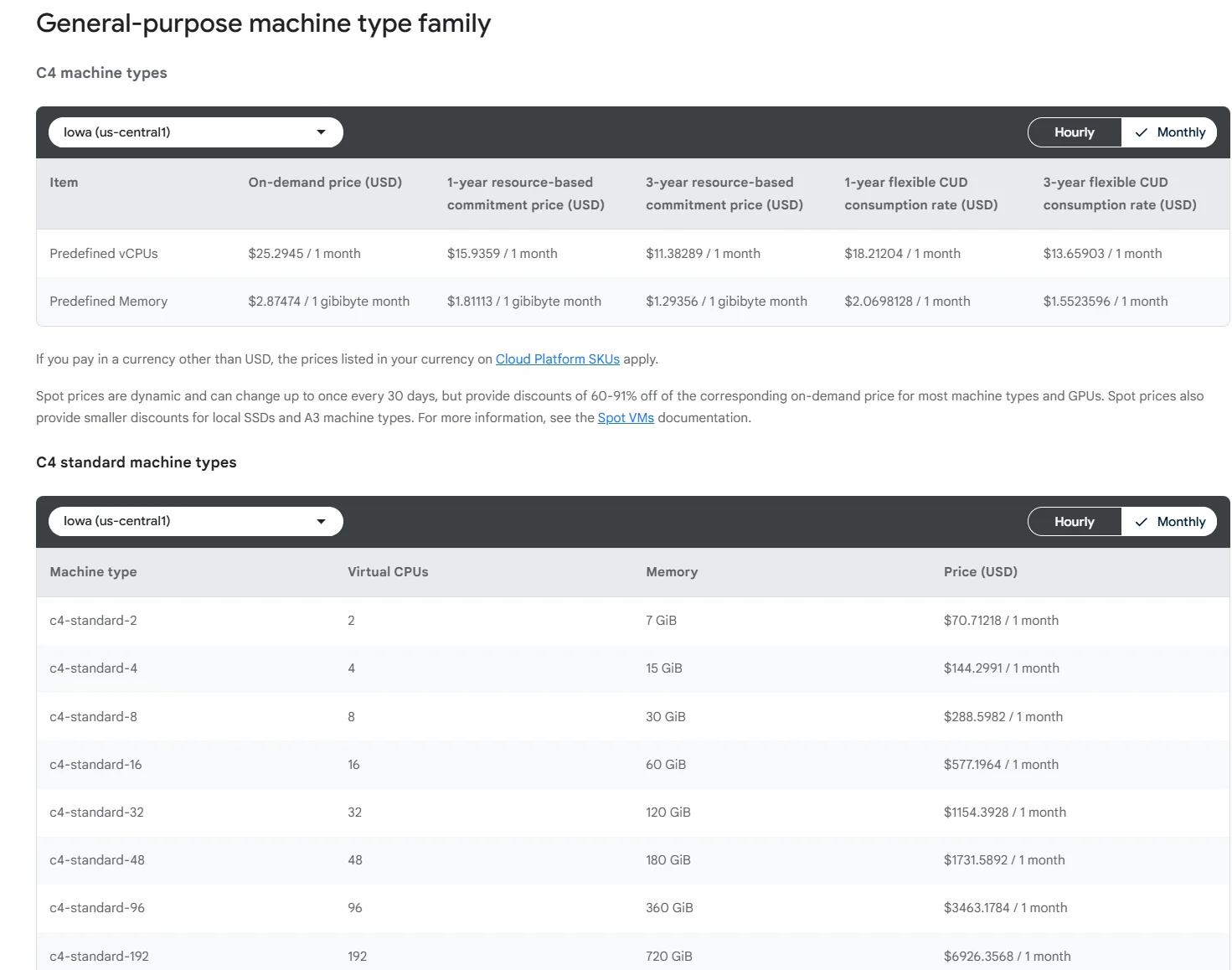
Image: Google Cloud Compute pricing in Iowa (us-central1)
Now compare that to prices in Sao Paulo:
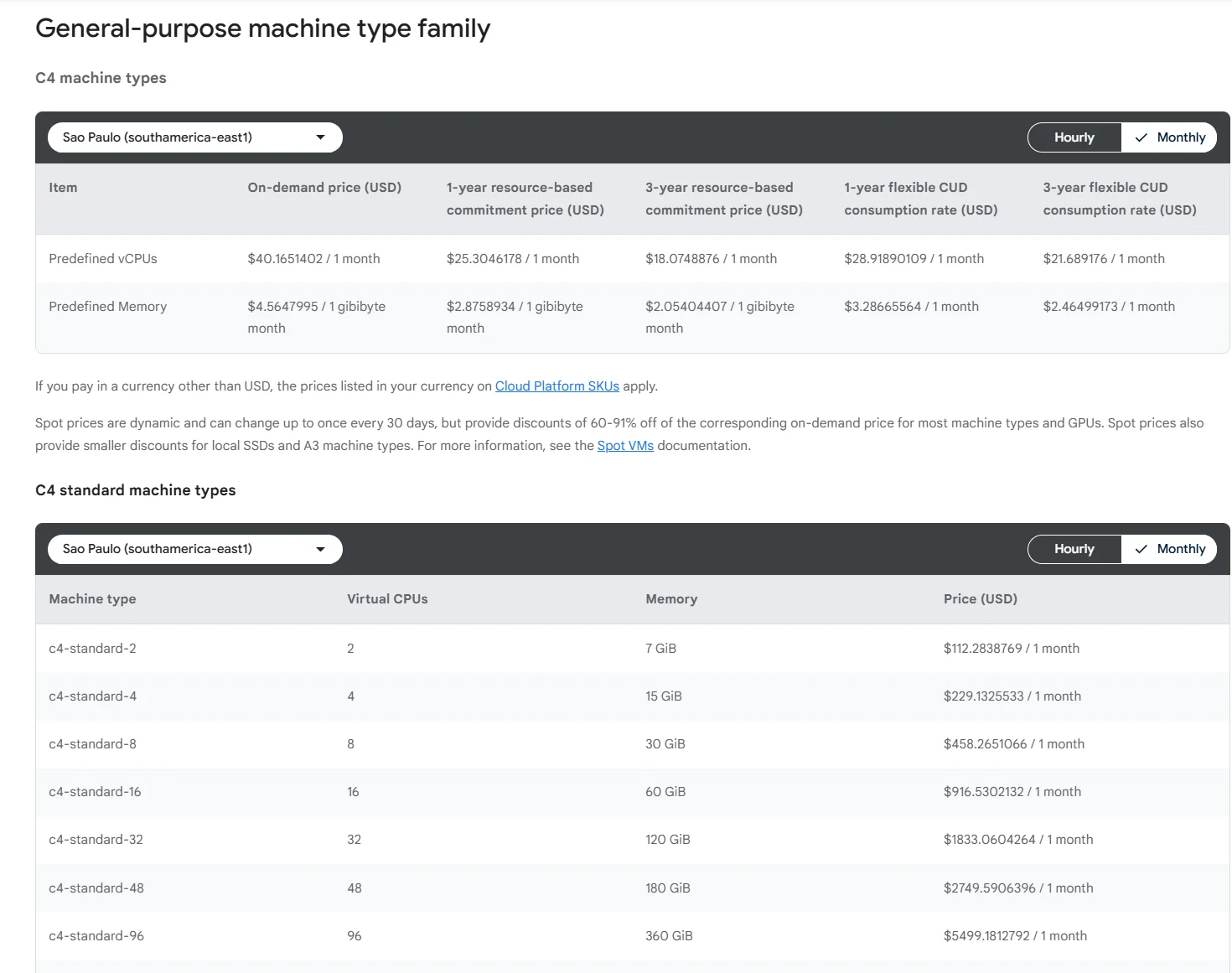
Image: Google Cloud Compute pricing in Sao Paulo (southamerica-east1)
- Data transfer costs: Transferring data between GCP regions is more expensive than within a single region. Syncing data between asia-south1 (India) and asia-east1 (Taiwan) can cost up to 5x more than transfers between us-east1 and us-west1, which are geographically closer.
- Networking costs: Multi-region architectures incur additional networking costs since inter-region traffic is subject to egress fees. This can be costly for applications that require frequent data synchronization or replication across regions.
- Redundancy costs: Building redundancy across regions means duplicating VMs, storage, and other resources, effectively doubling costs.
- Cross-region disaster recovery setups further increase operational expenses due to ongoing data replication fees.
- Sustained Use Discounts: GCP offers sustained use discounts for VMs running consistently within a region for a full month. However, deploying VMs across multiple regions may lead to fragmented usage, making it harder to qualify for discounts.
These are just a few ways your choice of GCP Region impacts your cloud bill.
Yet, deciding to use a single region for your applications or target markets isn’t always straightforward. For example, you‘ll likely need multi-region redundancy for disaster recovery and low-latency access to users in different locations.
Then again, running workloads closer to end users can improve performance. But, it can also inflate costs. Unexpected costs can mean diverting funds from innovation to paying a surprise cloud bill.
So, how do you ensure smarter cloud spending, stronger margins, and greater financial control without compromising performance?
Understanding, Controlling, And Optimizing Your GCP Cloud Costs Just Got Smarter
To keep your GCP costs under control while maintaining peak performance, you need deep visibility into your cloud spend. This empowers you to pinpoint exactly what’s driving costs so you can trim, pause, and optimize as needed.
The challenge? Most cloud cost tools provide basic data and lack immediately actionable insights to help you make smarter decisions.
With CloudZero, you can:
- Allocate 100% of your GCP cloud costs in no time. And prevent cost blindspots that often turn into surprise costs.
- Instantly see which teams, products, and processes drive your cloud costs with granular insights like Cost per Feature, Cost per Deployment, and Cost per Customer.
- Track costs in real-time and identify areas for optimization. Catch cost issues before they escalate with timely, noise-free alerts delivered straight to your inbox.
- Increase cloud efficiency and cost savings without slowing down innovation.
Companies like Coinbase and Wise use CloudZero to control and optimize their GCP costs without sacrificing engineering velocity. You can, too, risk-free.  to experience CloudZero for yourself.
to experience CloudZero for yourself.
GCP Regions FAQs
What is a cloud region?
Cloud service providers like GCP and AWS define a cloud region as a geographic location containing multiple logically linked, physically close data centers. These data centers provide the public cloud resources needed to run workloads efficiently in the cloud.
How many GCP regions and zones are there today?
GCP is currently available in 47 regions worldwide, with more set to launch soon. To support this network, GCP operates 29 physical data centers across 11 countries and offers 127+ zones distributed within those regions.
What is the cheapest GCP region?
On average, the cheapest GCP region for running instances is currently Iowa (us-central1).
How do I find my GCP region?
Try these three ways: 1) Use the Google Cloud Console under the Compute Engine section, 2) view your resource metadata Compute Engine dashboard, and 3) run this gcloud CLI:
command gcloud compute zones list
Is GCP more available than AWS?
AWS has a more extensive global reach than GCP, especially in terms of edge locations.