A good chunk of your Amazon Web Services (AWS) public cloud spending goes to the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) service. Amazon EC2 is the default compute service on AWS, so it’s is key to building, running, and scaling your AWS-based applications.
That also means Amazon EC2 pricing has a tremendous impact on your AWS budget. Understanding how the EC2 billing model works will help you control and optimize your AWS spending.
We’ve compiled this handy EC2 pricing guide to cover exactly what EC2 does, how EC2 pricing works, and how you can choose the best AWS services for your product or software.
What Does Amazon EC2 Do?
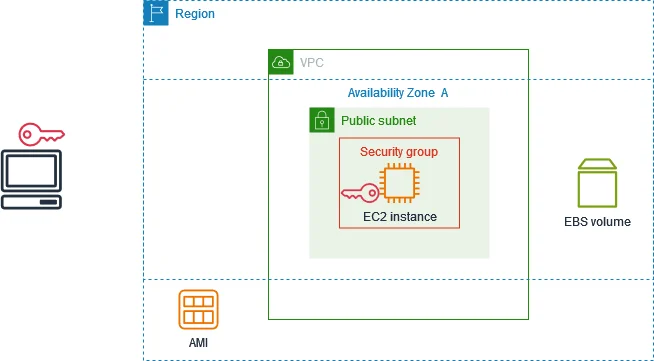
Amazon EC2 provides scalable compute capacity whenever your workload requires it. It also offers a variety of CPU, RAM, storage, and networking configurations (instance types) for your virtual servers (instances).
EC2 enables you to rent nearly unlimited virtual server capacity on demand rather than provisioning excess resources in anticipation of unexpected spikes in traffic or workload.
EC2 Cost Explained: How Does Amazon EC2 Pricing Work?
The EC2 pricing model prevents you from buying and configuring your own hardware. Instead, Amazon lets you pay-as-you-go for only the resources you’ve used within a billing cycle. Often, that cycle is monthly.
This enables you to convert capital expenditures (CapEx) into operating expenditures (OpEx) when you pay your Amazon EC2 bill monthly.
That’s straightforward enough. But things can get complex pretty quickly.
Here’s why.
- Amazon EC2 instances are available in different sizes, too — not just different types. This flexibility empowers you to choose the most suitable EC2 instance sizes and types for your specific workload.
- There’s a term for that: rightsizing. Rightsizing minimizes the computing power you use while providing just enough power to run your workload smoothly.
- Inefficient rightsizing leads to wasted cloud spending. A 2024 Stacklet survey found that 78% of organizations waste 21-50% of their cloud budgets due to poor resource sizing and outdated instance types. Some enterprises even lose over $50,000 per month due to this inefficiency.
- Manually choosing the best EC2 instance type and size for your needs can be daunting. Fortunately, you can use tools like CloudZero Advisor to help you with this.
These insights make navigating AWS EC2 instance pricing easier by recommending the most cost-efficient instance types based on your workload needs.
Yet, to maximize ROI from your cloud budget, you’ll need to understand how Amazon EC2 pricing works.
Here’s how.
What Is The EC2 Billing Model?
AWS provides five Amazon EC2 billing methods:
- EC2 On-Demand Pricing
- EC2 Savings Plans
- EC2 Reserved Pricing
- EC2 Spot Pricing
- Dedicated Hosts Pricing
Also, EC2 pricing is either hourly or per second. EC2 per second billing has a 60-second minimum commitment and is ideal for workloads that do not always require full hours, like testing and staging.
Here’s a breakdown of each EC2 billing method.
1. Amazon EC2 On-Demand pricing
EC2 On-Demand pricing lets you choose any instance type or size, scale up or down as needed, and pay only for what you use — with no upfront payment or long-term commitment.
You control when instances start, stop, reboot, or hibernate, and billing is hourly or per-second. On-Demand is available across all Regions, Availability Zones, and operating systems, including Linux, Windows, and RHEL.
This default pricing model offers maximum flexibility, but it is more expensive than other EC2 pricing options.
Also, On-Demand pricing is highly variable and depends on your choice of region/availability zone, OS, instance type, and instance size. Here’s an example.
|
Location |
Instance type |
Instance size |
vCPU |
Memory |
Operating system |
On-Demand pricing per hour |
|
US West (North California) |
General purpose – T3 |
Large |
2 |
8 GiB |
Linux Windows RHEL |
$0.0992 $0.1268 $0.128 |
|
EU (Ireland) |
General purpose – T3 |
Large |
2 |
8 GiB |
Linux Windows RHEL |
$0.0912 $0.1188 $0.12 |
An example of how different operating systems affect EC2 pricing
We’ve covered more on On-Demand instances and when to use them here.
2. Amazon EC2 Savings Plans pricing
EC2 Savings Plans offer up to 72% savings when you commit to consistent usage for 1 or 3 years, paying per hour (e.g., $8/hour).
Instance Savings Plans allow you to switch between instance sizes and operating systems within the same instance family and Region. For example, you can move from an M5.xlarge running Windows to an M5.2xlarge running Linux in the same Region, but not to another family or Region.
Compute Savings Plans offer up to 66% savings and apply across EC2, AWS Fargate, and AWS Lambda, providing more flexibility across services, Regions, and instance families.
You can choose all upfront, partial upfront, or no upfront payments — and the more you pay upfront, the more you save.
3. Amazon EC2 Reserved Instances pricing
Reserved Instances (RIs) offer savings of up to 72% when you commit to consistent usage for one or three years. They also reserve capacity in a specific Availability Zone, ensuring you can launch instances when needed.
Standard Reserved Instances provide up to 72% savings and let you change the Availability Zone, instance size, and networking settings during the term.
Convertible Reserved Instances offer up to 66% discounts and allow you to switch instance types, tenancy options, and operating systems.
Like Savings Plans, you can pay all upfront, partially upfront, or monthly — with higher upfront payments delivering greater savings.
See the differences between AWS Savings Plans and Reserved Instances here.
Tip: If you want to optimize your RIs and Savings Plans automatically, tools like ProsperOps can help you do that continuously.
Check out this chart by ProsperOps showing an overview of the differences between AWS SPs and RIs:
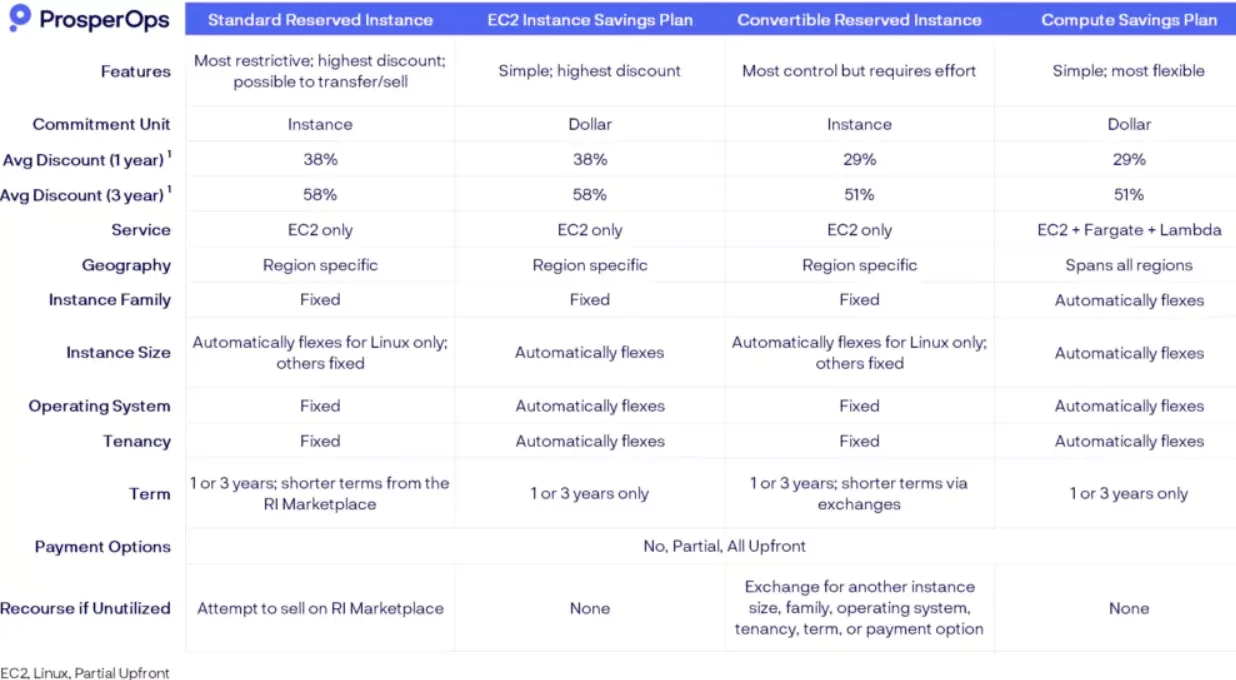
Also, AWS offers Reserved Instance volume discounts when you purchase many EC2 RIs in a specific AWS Region (e.g., 5% for $500,000 to $4M and 10% for $4M to $10M).
You can learn more about when to use Reserved Instances pricing and best practices for optimizing AWS RIs here.
4. Amazon EC2 Spot Instances pricing
EC2 Spot pricing offers the biggest savings — up to 90% off standard rates — by using surplus AWS capacity until it’s needed elsewhere.
Spot prices fluctuate based on bidding and market demand across Availability Zones. If demand increases or you are outbid, AWS can interrupt your Spot Instances, potentially disrupting fault-intolerant workloads.
If reclaimed, AWS automatically switches those workloads to On-Demand pricing, which can quickly increase costs. While you can configure Hibernate or Pause-Stop manually, managing this at scale is complex.
Tools like Xosphere help automate switching between Spot and other capacities so you can safely maximize Spot pricing benefits.
See the best use cases for Spot pricing here.
5. Dedicated Hosts pricing
A dedicated host is a physical server allocated only to you. This EC2 pricing option combines public cloud flexibility with the ability to use your own licenses (such as your Windows SQL Server license).
Billing is based on the On-Demand hourly rate, but committing for one or three years can save up to 70%. With Savings Plans, you can save up to 72% on Dedicated Hosts.
This model is ideal for companies that need strict compliance, dedicated hardware, or minimal resource sharing.
6. Related costs to consider
Yes, there are more variables to compute into your Amazon EC2 pricing scheme. AWS bills for additional related services, like block storage, egress traffic, premium support, load balancing, and IP addresses.
So, how do you understand, control, and optimize your Amazon EC2 costs with all these variables to consider?
Key Factors That Influence Amazon EC2 Costs
These cost drivers help you estimate workloads accurately and avoid surprises:
- Instance family and size. More CPU and memory increase cost; choose based on workload needs, not defaults.
- Region and availability zone. Pricing varies by location due to demand and resource availability.
- Operating system and licensing. Windows, RHEL, and enterprise software licenses increase compute spend.
- Tenancy model. Shared, dedicated, and host tenancy pricing differ based on isolation and compliance needs.
- Networking and data transfer. Traffic between regions, AZs, or the public internet can add up quickly.
- Storage and I/O. EBS volumes, snapshot usage, and high-performance storage impact total compute cost.
- Usage patterns. Consistent workloads benefit from commitment models; variable workloads don’t.
So, how do you understand, control, and optimize your Amazon EC2 costs with all these variables to consider?
How To Understand, Control, And Reduce Amazon EC2 Costs Immediately
Start with visibility. Break down your AWS bill to see exactly how much goes to EC2 — and why it changes. Totals aren’t enough; you need cost context tied to usage, teams, and services.
Native AWS tools (Cost Explorer and CUR) give surface-level trends and massive raw data, but they don’t explain allocation drivers. They also require heavy tagging before you get clarity, slowing cost decisions.
That’s why you need to…
Get Unit Cost Intelligence With CloudZero
CloudZero links EC2 spend directly to your business — customers, features, teams, deployments, and environments — so you can see who drives cost, what changed, and why.
You can:
- View AWS costs by customer, product, team, and workload
- Pinpoint expensive features and environments
- Identify unprofitable usage (e.g., free plans costing margin)
- Forecast EC2 cost changes based on growth
- Compare Savings Plans, RIs, and Spot effectiveness
- Get real-time alerts before spend spikes
CloudZero also combines data from AWS, Azure, GCP, Snowflake, and Kubernetes, giving one unified cost source — including for modern AI + GPU workloads.
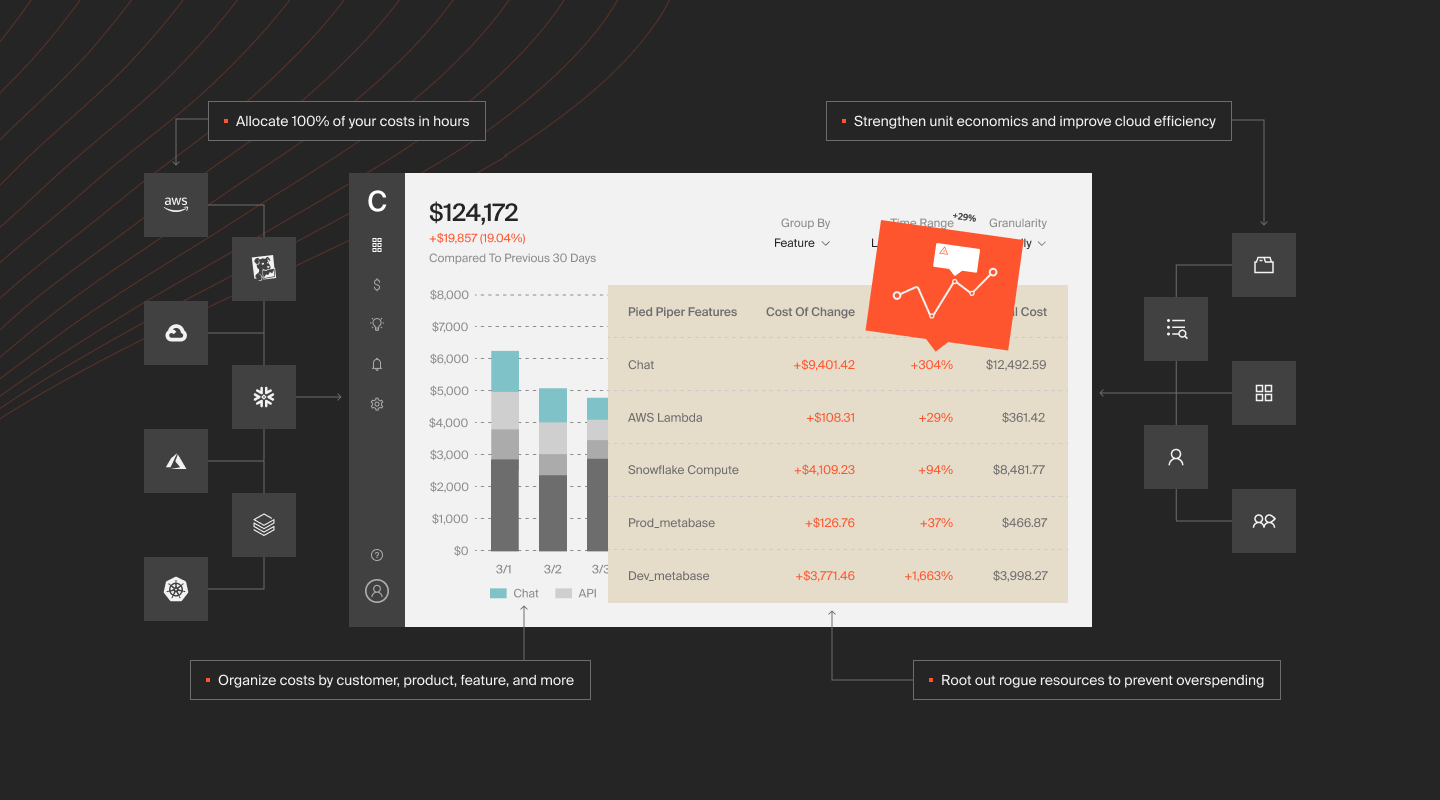
See every dollar, assign it to a business driver, and act fast — without waiting on tags
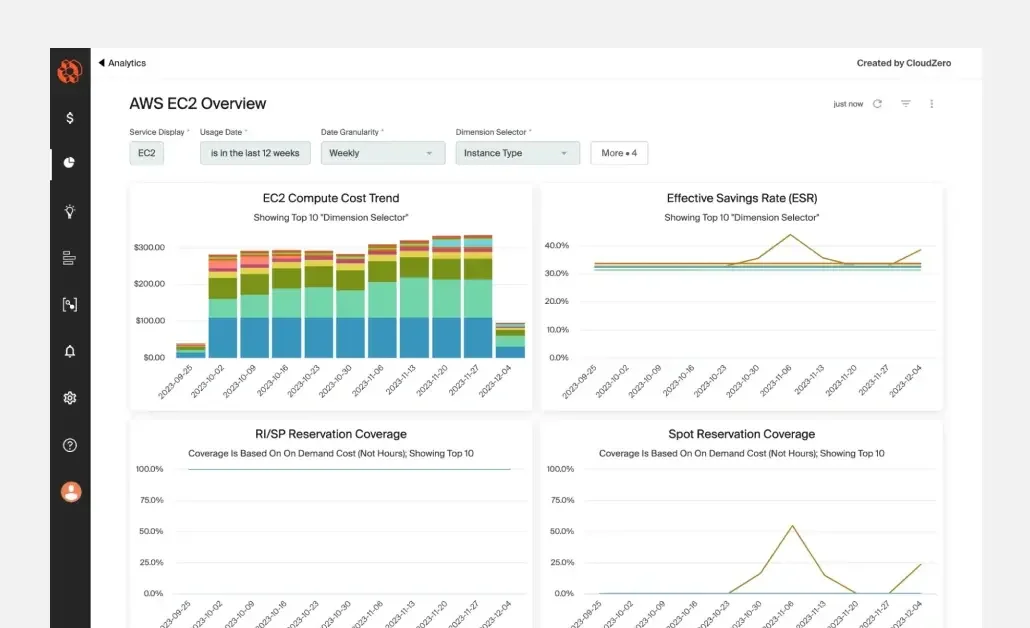
CloudZero’s dashboards also show compute cost trends, reservation coverage, and effective savings rate to help you evaluate and tune your EC2 spend strategy in one place.
Will CloudZero save you $2.4 million annually as we did for our customer, Drift?  to find out.
to find out.
Amazon EC2 Pricing FAQs
How much does EC2 cost per month?
It depends on the pricing model, instance type and size, operating system, tenancy, and Region. AWS EC2 instance pricing also varies with usage patterns and whether you use features like load balancing or premium support.
What are the main pricing options for Amazon EC2 instances?
EC2 offers five pricing options: On-Demand, Savings Plans, Reserved Instances, Spot Pricing, and Dedicated Hosts. Other costs include egress data transfers, premium support, and block storage costs.
Is Amazon EC2 free?
EC2 pricing includes a free tier that offers 750 hours of Linux or Windows t2.micro instances (or t3.micro where the t2 instance family is unavailable) per month for a year.
What is the cheapest EC2 instance type in AWS?
Compared to other instance types, General Purpose T2 instances are relatively inexpensive. Your specific use case may change this.