Yet, the same flexibility that makes EC2 so appealing can also make it complex, confusing, and unnecessarily costly.
A good way to understand the compute service is to familiarize yourself with EC2 instance types, and what the best use cases are for each. This guide will cover that and more.
We’ve also covered Amazon EC2 pricing in this article, featuring On-Demand Instances, Savings Plans, Reserved Instances, and Spot Instances.
What Is An Amazon EC2 Instance?
An EC2 instance is a virtual server in the AWS ecosystem that provides the processing, RAM memory, storage, and networking power to run applications. Compared to standard virtual machines (VMs), Amazon EC2 instances are unique in several ways, including:
- By activating Auto Scaling Groups, EC2 instances can automatically increase or decrease their compute capacity depending on demand.
- By enabling auto-scaling, you can prevent service interruptions caused by overloading.
- Instead of paying a minimum fee up front or provisioning capacity in advance, AWS bills EC2 instances based on a pay-as-you-go model.
- In addition, you can choose a longer term commitment (Savings Plans or Reserved Instances) to receive up to 72% off the regular On-Demand price.
- In addition, EC2 instances offer superior performance and availability because they don’t share memory among themselves.
- Yet, EC2 instances pair up with Amazon’s Elastic Block Storage (Amazon EBS) for greater durability.
- You can also use the Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) with EC2 as additional storage.
So, how do EC2 instances help?
What Are EC2 Instances Used For?
AWS offers five categories of Amazon EC2 instances for a variety of use cases. Here’s a quick overview of EC2 instances available today:
|
Amazon ECS Instances | ||||
|
General Purpose |
Compute Optimized |
Memory Optimized |
Storage Optimized |
Accelerated Computing |
- General Purpose instances provide balanced CPU, RAM, storage, and networking performance for a wide variety of workloads.
- Compute-optimized instances are suitable for workloads that require high-performance processing capacity, such as batch processing and high-traffic web servers.
- Memory-optimized instances are ideal for workloads that require processing large data sets in memory.
- Storage-optimized instances facilitate rapid, sequential read and write access to vastly large sets of data on local storage. They allow applications to perform tens of thousands of random I/O operations per second (IOPS) at low latency.
- Accelerated computing instances leverage co-processing or hardware accelerators to perform specific tasks, such as graphics processing.
Each of these instance classes divides further into different sizes and families of EC2 instances.
What Are The EC2 Instance Families?
The eight instance families available on Amazon EC2 are:
|
Amazon EC2 Instance Types | |||||||||
|
General Purpose |
Compute Optimized |
Memory Optimized |
Storage Optimized |
Accelerated Computing | |||||
|
Mac, T, M, A |
C, Hpc |
R, X, High Memory, Z |
I, D, H |
P, DL, Trn, Inf, G, F, VT | |||||
This table shows the different EC2 instance families under each Amazon EC2 instance class.
Each of these families was designed with a specific use case in mind, which we will explore in the sections that follow.
What Are The EC2 Instance Types Available Today?
An EC2 instance type describes the combination of CPU, RAM, storage, and networking capacity of a specific family of instances. Below is a handy table that highlights the various types of instances.
|
Amazon EC2 Instance Types | ||||
|
General Purpose |
Compute Optimized |
Memory Optimized |
Storage Optimized |
Accelerated Computing |
|
Mac, T, M, A |
C, Hpc |
R, X, High Memory, Z |
I, D, H |
P, DL, Trn, Inf, G, F, VT |
|
Mac T2 T3a T3 T4g M4 M5zn M5n M5a M5 M6a M6i M6g A1 |
C4 C5n C5a C5 Hpc6a C6a C6i C6gn C6g C7g |
R4 R5n R5b R5a R5 R6i R6g R6a X1 X1e X2iezn X2iedn X2idn X2gd High Memory z1d |
I3en 13 I4i Is4gen Im4gn D2 D3 D3en H1 |
P2 P3 P4 Inf1 Trn1 DL1 G3 G4ad G4dn G5g G5 F1 VT1 |
This table shows the different EC2 instance classes, families, and types.
Things get more interesting from there. Amazon EC2 offers different instance sizes for each instance family, so you can select the right one for your specific workload.
What Are The EC2 Instance Sizes?
For each instance type, EC2 offers up to seven instance sizes:
- Nano
- Micro
- Small
- Medium
- Large
- Xlarge
- 2Xlarge
Again, flexibility is the goal — to make sure you get just enough compute power for a workload (rightsizing) to save money without sacrificing performance. EC2 also automatically pairs each instance with an appropriate vCPU, RAM, storage, and networking capacity.
We’ve outlined each EC2 instance type’s characteristic, size, and best use case below.
1. T2 instance type
This general purpose instance type uses high-frequency Intel Xeon processors and Amazon EBS storage. T2 is designed to provide balanced performance in terms of processing, memory, storage, and networking for workloads requiring medium-performance most of the time.
Yet, T2 instances can burst higher performance in Unlimited Mode to match spikes in activity, such as a sharp increase in web traffic.
Also, a T2 EC2 instance accumulates credits as long as it performs at or below its baseline performance. The size of a T2 instance determines how many credits it generates each hour.
It then uses those credits in Unlimited Mode (burstable) without incurring additional charges. As soon as those credits run out, and the instance still needs to run in burstable mode, you will be charged $0.05 per hour for the extra resources it consumes.
|
T2 Instance Size |
vCPU |
Memory in GiB |
Networking Performance |
Credits Generated per hour of baseline performance |
|
t2.nano |
1 |
0.5 |
Low |
3 |
|
t2.micro |
1 |
1 |
Low to moderate |
6 |
|
t2.small |
1 |
2 |
Low to moderate |
12 |
|
t2.medium |
2 |
4 |
Low to moderate |
24 |
|
t2.large |
2 |
8 |
Low to moderate |
36 |
|
t2.xlarge |
4 |
16 |
moderate |
54 |
|
t2.2xlarge |
8 |
32 |
moderate |
81 |
When to use T2 instances:
Typical applications using T2 instances include small and medium line of business apps, web servers, web apps, and development environments.
2. T3 instance type
These General-purpose EC2 instances deliver balanced processing, memory, storage, and networking capabilities, with Unlimited Mode activated by default to provide high-performance bursts.
T3a instances use AMD EPYC 7000 series processors (2.5GHz), while T3 instances use Intel Xeon (Skylake or Cascade) cores (3.1GHz). Both support EBS temporary storage as well as Enhanced Networking.
T3 instances also generate credits when performing at or below baseline to use in burstable mode.
However, a T3 instance can continue to use credits even after it has consumed all accumulated credits. You won’t have to pay extra as long as the instance re-generates the credits owed within 24 hours. Otherwise, you need to pay $0.05 per instance per hour.
|
T3 Instance Size |
vCPU |
Memory in GiB |
Networking Performance |
Credits Generated per hour of baseline performance |
|
t3.nano |
2 |
0.5 |
Up to 5Ghz |
6 |
|
t3.micro |
2 |
1 |
Up to 5Ghz |
12 |
|
t3.small |
2 |
2 |
Up to 5Ghz |
24 |
|
t3.medium |
2 |
4 |
Up to 5Ghz |
24 |
|
t3.large |
2 |
8 |
Up to 5Ghz |
36 |
|
t3.xlarge |
4 |
16 |
Up to 5Ghz |
96 |
|
t3.2xlarge |
8 |
32 |
Up to 5Ghz |
192 |
When to use T3 instances:
According to AWS, T3 instances offer a 30% price-performance improvement over T2 instances. In addition, it recommends them for small/medium databases, development environments, virtual desktops, and low-latency apps.
3. T4g instance type
This is a newer generation of the T family instance that features AWS’s own, Arm-based Graviton 2 processors (64-bit), which deliver up to 40% better price-performance over T3 instances.
|
T4 Instance Size |
vCPU |
Memory in GiB |
Networking Performance |
Baseline performance to earn credits |
Credits Generated per hour of baseline performance |
|
t4.nano |
2 |
0.5 |
Up to 5Ghz |
5% |
6 |
|
t4.micro |
2 |
1 |
Up to 5Ghz |
10% |
12 |
|
t4.small |
2 |
2 |
Up to 5Ghz |
20% |
24 |
|
t4.medium |
2 |
4 |
Up to 5Ghz |
20% |
24 |
|
t4.large |
2 |
8 |
Up to 5Ghz |
30% |
36 |
|
t4.xlarge |
4 |
16 |
Up to 5Ghz |
40% |
96 |
|
t4.2xlarge |
8 |
32 |
Up to 5Ghz |
40% |
192 |
When to use T4g instances:
Business-critical applications, micro-services, small/medium databases and development environments, and virtual desktops.
4. Amazon EC2 M instance types
With M family instances, you get balanced CPU, RAM, and networking capacity, as well as support for EBS and Enhanced Networking. Some instances, like M4, use Intel Xeon processors (scalable and clocked at 2.5GHz), while others, like M6g, use AWS’ Arm Graviton 2 processors.
Newer M instances also come in more sizes than older M4 instances, which only came in six.When to use M instances:
|
M4 Instance Type |
vCPU |
Memory in GiB |
Networking Performance |
|
m4.large |
2 |
8 |
Moderate |
|
m4.xlarge |
4 |
16 |
High |
|
m4.2xlarge |
8 |
32 |
High |
|
m4.4xlarge |
16 |
64 |
High |
|
m4.10xlarge |
40 |
160 |
10 Gbps |
|
m4.16xlarge |
64 |
256 |
25 Gbps |
For workloads that require mostly balanced resources but perform better with extra memory, like cluster computing, mid-size databases, and enterprise apps.
5. A1 instance type
This instance uses AWS Graviton processors, supports Enhanced Networking, EBS storage, and combines lightweight hypervisors and dedicated hardware. There are six sizes to choose from:
|
A1 Instance Type |
vCPU |
Memory in GiB |
Networking Performance |
|
a1.medium |
1 |
2 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
a1.large |
2 |
4 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
a1.xlarge |
4 |
8 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
a1.2xlarge |
8 |
16 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
a1.4xlarge |
16 |
32 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
a1.metal |
16 |
32 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
When to use A1 instances: Scale-out workloads like web servers, distributed development environments, and containerized apps.
6. Amazon EC2 C instance types
The C family of instances offers high-performance processing power for compute-intensive workloads. You can expect Intel Xeon (C4), AMD SYNC (C5), and AWS Graviton 3 (C7g) processors, enhanced networking, and EBS support. The baseline C4 instances have the following sizes:
|
C4 Instance Type |
vCPU |
Memory in GiB |
Networking Performance |
|
c4.large |
2 |
3.75 |
Moderate |
|
c4.xlarge |
4 |
7.5 |
High |
|
c4.2xlarge |
8 |
15 |
High |
|
c4.4xlarge |
16 |
30 |
High |
|
c4.8xlarge |
36 |
60 |
10 Gbps |
When to use Amazon EC2 C instances: Workloads that require high-performance, like batch processing, data analytics, and front-end fleets.
7. Amazon EC2 R instance types
These memory-optimized instances support DDR4 memory, Enhanced Networking, and high frequency processors for running memory-intensive applications.
R6a instances, powered by AMD EPYC processors, deliver up to 60% better price-performance than R4 instances, which are powered by Intel Xeon processors clocked at 2.3Ghz.
Between the two, R5 instances offer the following sizes:
|
R5 Instance Type |
vCPU |
Memory in GiB |
Networking Performance |
|
r5.large |
2 |
15.25 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
r5.xlarge |
4 |
30.5 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
r5.2xlarge |
8 |
61 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
r5.4xlarge |
16 |
122 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
r5.8xlarge |
32 |
244 |
10 Gbps |
|
r5.16xlarge |
64 |
488 |
25 Gbps |
When to use Amazon EC2 R instances: High-performance enterprise apps, databases, real-time big data analytics, and Hadoop clusters.
8. Amazon EC2 X instance types
Like R instances, these memory-optimized instances offer varying performance at varying sizes across the X1, X1e, and X2 series. As an example, X2gd instances offer a 55% better price-performance ratio, seven more sizes, and a higher network bandwidth than X1 instances.
As a middle ground, X2iezn instances are available in the following sizes:
|
X2iezn Instance Type |
vCPU |
Memory in GiB |
Networking Performance |
|
x2iezn.large |
8 |
256 |
Up to 25 Gbps |
|
x2iezn.xlarge |
16 |
512 |
Up to 25 Gbps |
|
x2iezn.2xlarge |
24 |
768 |
50 Gbps |
|
x2iezn.4xlarge |
32 |
1024 |
75 Gbps |
|
x2iezn.8xlarge |
48 |
1536 |
100 Gbps |
|
x2iezn.16xlarge |
48 |
1536 |
100 Gbps |
When to use Amazon EC2 X instances: Open-source databases, real-time caching servers, and in-memory cache workloads.
9. Amazon EC2 Z1d instances
If you need both high compute and memory performance, Z1d instances deliver the fastest instance types in the AWS cloud (up to 4.0Ghz in all Intel Xeon cores), up to 384 GiB RAM, and up to 1.8TB storage for each instance. The following sizes are available:
|
Z1d Instance Type |
vCPU |
Memory in GiB |
Networking Performance |
|
z1d.large |
2 |
16 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
z1d.xlarge |
4 |
32 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
z1d.2xlarge |
8 |
64 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
z1d.3xlarge |
12 |
96 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
z1d.6xlarge |
24 |
192 |
10 Gbps |
|
z1d.12xlarge |
48 |
384 |
10 Gbps |
|
z1d.metal |
48 |
384 |
25 Gbps |
When to use Amazon EC2 z1d instance types: relational database use cases with high per core license costs and electronic design automation workloads.
10. Amazon EC2 P instance type
These Accelerated Computing instances provide high performance graphics processing.
P2 instances are ideal for general-purpose GPU workloads, P3 are suitable for high performance compute, while P3 are the latest-generation instances, supporting the highest-performance amongst GPU-based instances.
Here are the size options for P3 instances, as an example:
|
P3 Instance Type |
GPU |
GPU Memory |
vCPU |
Memory in GiB |
Networking Performance |
|
p3.2xlarge |
1 |
16 |
8 |
61 |
Up to 10 Gbps |
|
p3.8xlarge |
4 |
64 |
32 |
244 |
10 Gbps |
|
p3.16xlarge |
8 |
128 |
64 |
488 |
25 Gbps |
|
p3.24xlarge |
8 |
256 |
96 |
768 |
100 Gbps |
When to use Amazon EC2 P instances: Machine Learning, high performance computing, and more.
Like P instances, G, F1, VT1, DL1, Trn1, and Inf1 instance types are all optimized for GPU-intensive applications. The best thing to do is to check out each instance type individually to see if it suits your needs perfectly.
Speaking of choosing the right EC2 instance type, you can do that either manually or automate the process.
How To Choose The Best EC2 Instances For Your Needs
More than any other AWS service, Amazon EC2 gives you the most choice in the type of instances you choose to launch, run, and maintain your applications.
However, configuring EC2 instance types can be time-consuming, error-prone, and waste a massive amount of resources. For example, by setting just one instance size larger than you require, you can:
- Drain your cloud budget faster than what you planned.
- Reduce funds for engineering innovation, limiting feature updates.
- Be forced to pass on your heavy costs to your customers, increasing the price of your services.
- In turn, this can lead to customer churn, revenue loss, slow adoption, and debt accumulation.
It’s a downward spiral that no company wants to experience. You can avoid that with intelligent tools, like CloudZero Advisor.
CloudZero Advisor is a free tool that offers recommendations on the best Amazon EC2 instances for a specific workload by compute instance, pricing, name, release date, architecture, region, compute capacity, and more filters. You can even add a custom filter for even more personalized results.
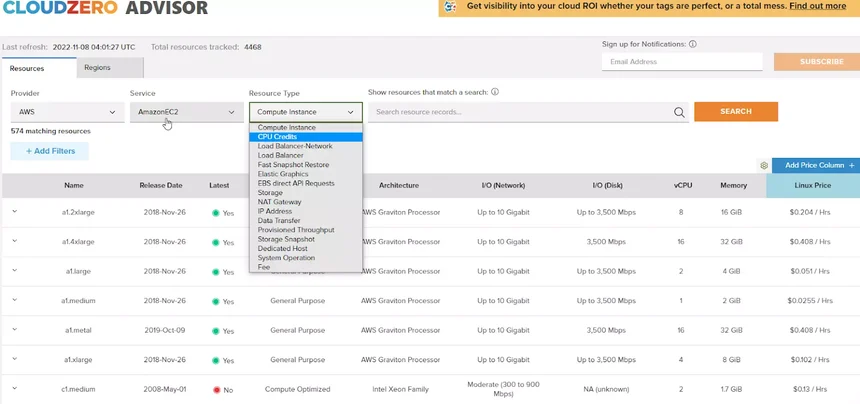
You can also track Amazon EC2 costs by customer, service, feature, team, project, and more with CloudZero — down to the hour.
Therefore, you can tell who, what, and why your Amazon EC2 costs are changing. This empowers you to tell exactly where to cut costs — or increase investment to maximize ROI.









