Cloud computing empowers organizations to access IT resources on demand, over the Internet, and on a pay-per-use basis. Thus, your company does not need to purchase, install, operate, and upgrade hardware for physical data centers.
Instead, you can rent resources as needed from cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS). For instance, AWS provides compute, storage, database, networking, machine learning, data lake, analytics, security, and IoT resources/services.
This means you can get to market faster, spend less money on owning computing hardware, and only pay for what you use once you use it.
What Are The Types Of Cloud Computing Tools Available?
Cloud computing tools support different service models: Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS). They also align with public, private, hybrid, and multicloud cloud environments.
We’ve covered the cloud computing services in more detail here.
Here are some of the best cloud computing tools organized into different categories:
Cloud Tools By Service Model
These tools provide the infrastructure, software, and other dependencies needed to do specific jobs in the cloud.
1. CloudZero – Cloud cost intelligence platform (SaaS)
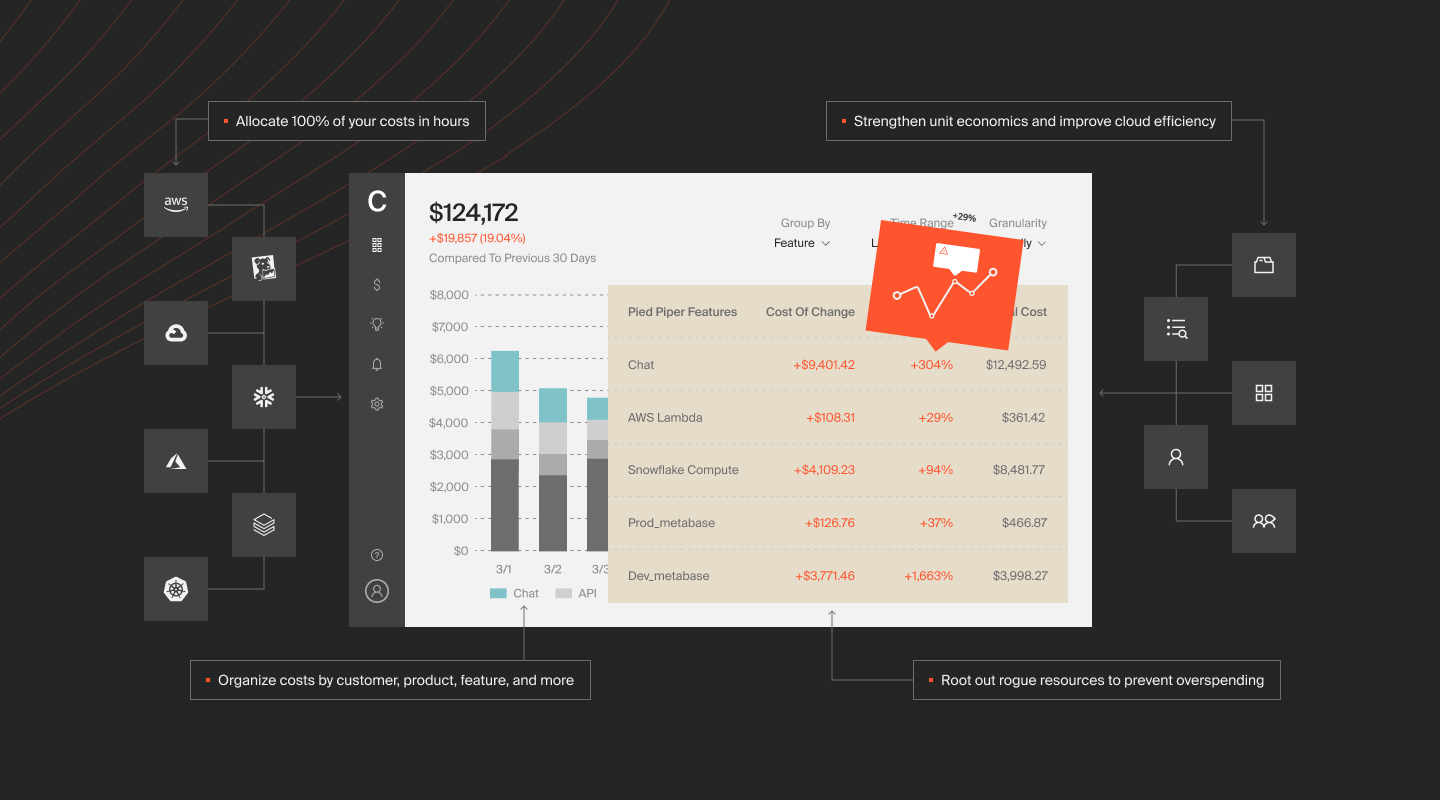
With CloudZero, SaaS companies can gain better visibility into cloud usage and costs, lower AWS costs, and increase their ROI. CloudZero helps them align cloud costs with the people, processes, and features that generate them.
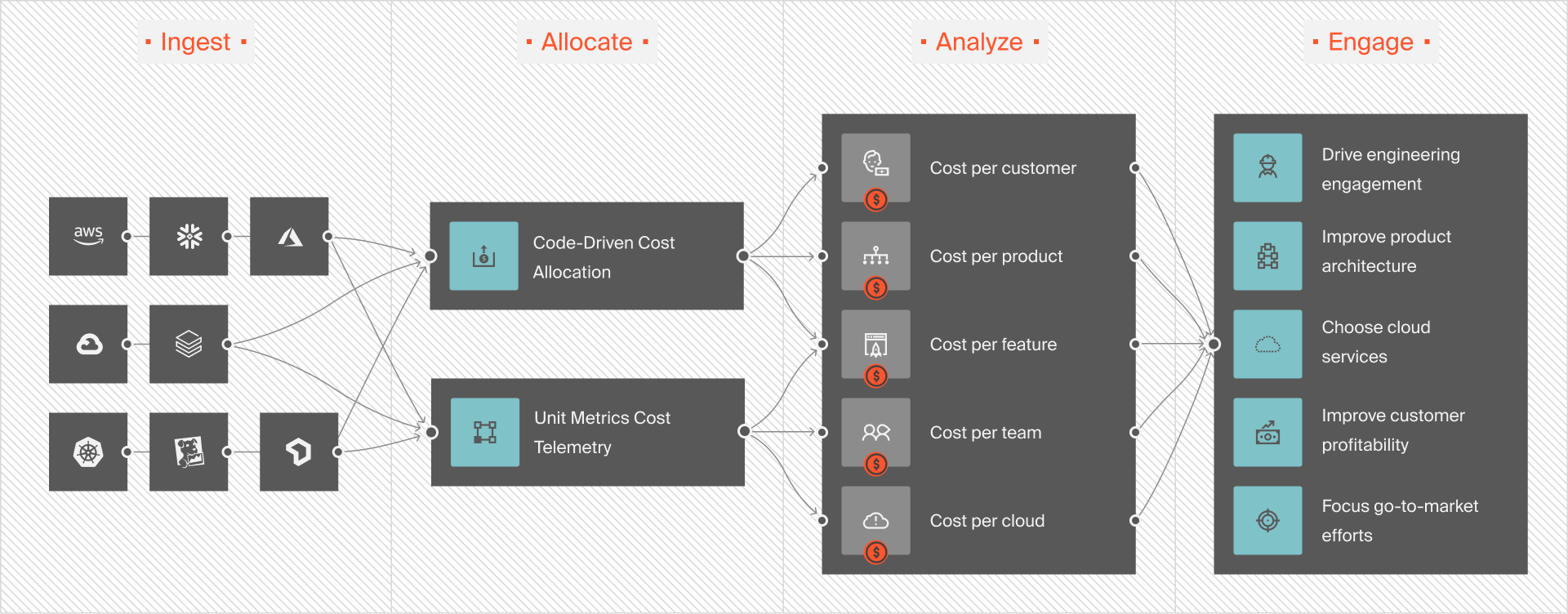
You can zoom in and view cost intelligence at a granular level, such as:
- Cost per customer – Find out how much each customer costs to support. With this intelligence, you can set your SaaS pricing to optimize profitability. In addition, you can use this insight to figure out what customer segments offer the highest ROI so that you can add similar clients to your portfolio.
- Cost per product feature – See what it costs to build, maintain, and run a feature and its usage statistics. This information can help you decide which features to add to which pricing tier, which ones to repurpose or decommission, and how to price the feature for profit.
- Cost per development team – View and test your development team’s efficiency (s) against others in your organization or industry.
- Cost per project – Know how much each project costs so you can allocate enough resources and send accurate quotes for similar projects.
- Cost anomaly detection – Get notified when costs spike with Slack, email, or your favorite incident reporting tool so you can take action to prevent overspending.
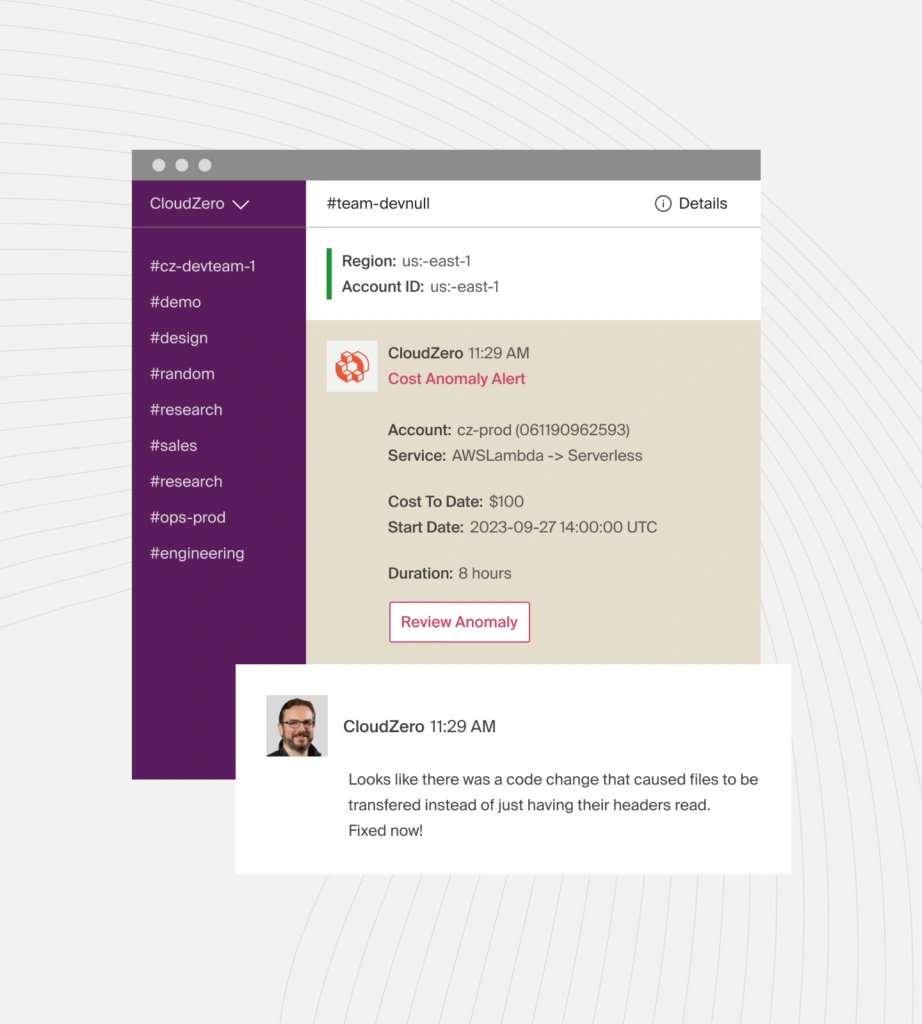
CloudZero also offers Budgets, a Migration Acceleration Program Dashboard for AWS MAP customers, and more, so it’s a complete cloud cost intelligence platform. See how CloudZero works in this demo.
If you want to optimize your AWS Reserved Instances and Savings Plans, we’ve teamed up with ProsperOps to help you save up to 40%. If you want to automate replacing On-Demand Instances with Spot Instances to save more, check out Xosphere Instance Orchestrator.
Pros
- Offers real-time insights to detect and fix cloud spending issues before they escalate.
- Tracks costs per customer or feature, making it easier to assess profitability and adjust pricing strategies for maximum ROI.
- Breaks down Kubernetes costs by clusters, namespaces, and pods. This granular view ensures better management of containerized workloads.
- Automatically alerts teams to unusual spending patterns, preventing budget overruns and enabling proactive cost control.
- Delivers customized cost data for engineering teams. This fosters cost-conscious development practices and ensures spending aligns with technical goals.
- It offers customizable dashboards that enable teams to track metrics relevant to their objectives.
- Supports collaboration between finance and engineering teams to ensure decisions align with financial goals and technical needs.
- Analyzes historical spending trends to help with budgeting and forecasting.
Cons
- CloudZero may not be the best choice for managing traditional cloud savings plans, such as committed use discounts. However, it makes up for this through its partnership with ProsperOps and Xosphere.
2. Amazon Web Services – Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
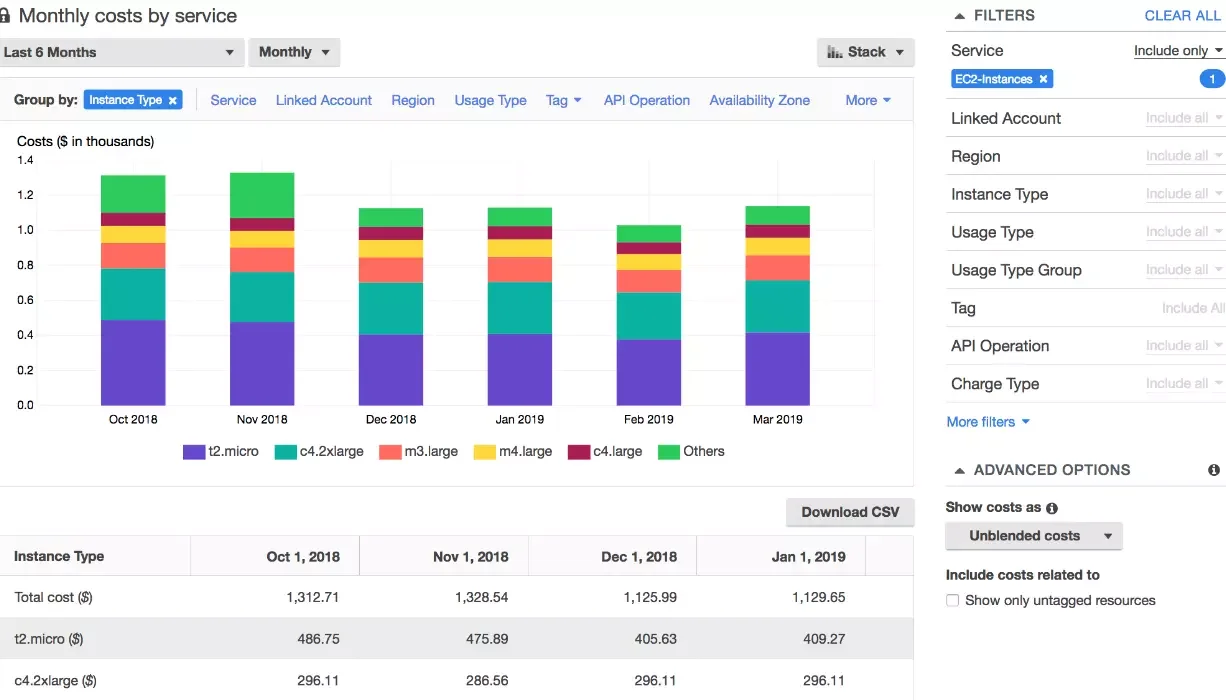
AWS provides over 200 cloud computing services, including compute, storage, analytics, IoT, AI/ML, and database services. With over 33% market share in cloud infrastructure services, AWS is the most popular IaaS today. It’s also popular because it offers infinite resources and services across the entire cloud spectrum.
Other Infrastructure-as-a-Service examples are Digital Ocean, Microsoft Azure, Alibaba Cloud, Google Compute Engine, Vultr, IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Linode, etc.
Pros
- Offers 200+ services for multiple business needs.
- Global infrastructure ensures low latency and high availability.
- Scales resources dynamically to match demand.
- Advanced security measures, including encryption and compliance.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing avoids upfront hardware costs.
Cons
- Complex pricing structures can lead to unexpected bills.
- The default service limits call for manual adjustments, leading to potential delays during scaling.
3. Google App Engine – Cloud application platform
Google’s App Engine offers organizations and developers a platform for building, running, and hosting web applications. As a fully managed environment, App Engine means zero configuration and server management for your developers. With App Engine, you can deploy in minutes and access an extremely scalable serverless PaaS environment.
More Platform-as-a-Service examples include Heroku, SAP Cloud, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Dokku, etc.
Pros
- Fully managed, serverless platform.
- Automatically scales resources with demand.
- Supports multiple programming languages.
- Built-in tools streamline testing and deployment.
- Secure environment with firewalls and encryption.
Cons
- Limited control over infrastructure customization.
- Predicting costs can be challenging due to the pricing model.
Infrastructure As Code (IaC) And Automation Tools
As cloud environments grow more complex, automating infrastructure setup and management becomes essential. IaC tools enable you to define, provision, and update your cloud infrastructure with code. This improves speed, consistency, and scalability across deployments. The best include:
4. Terraform – Scalable IaC tool
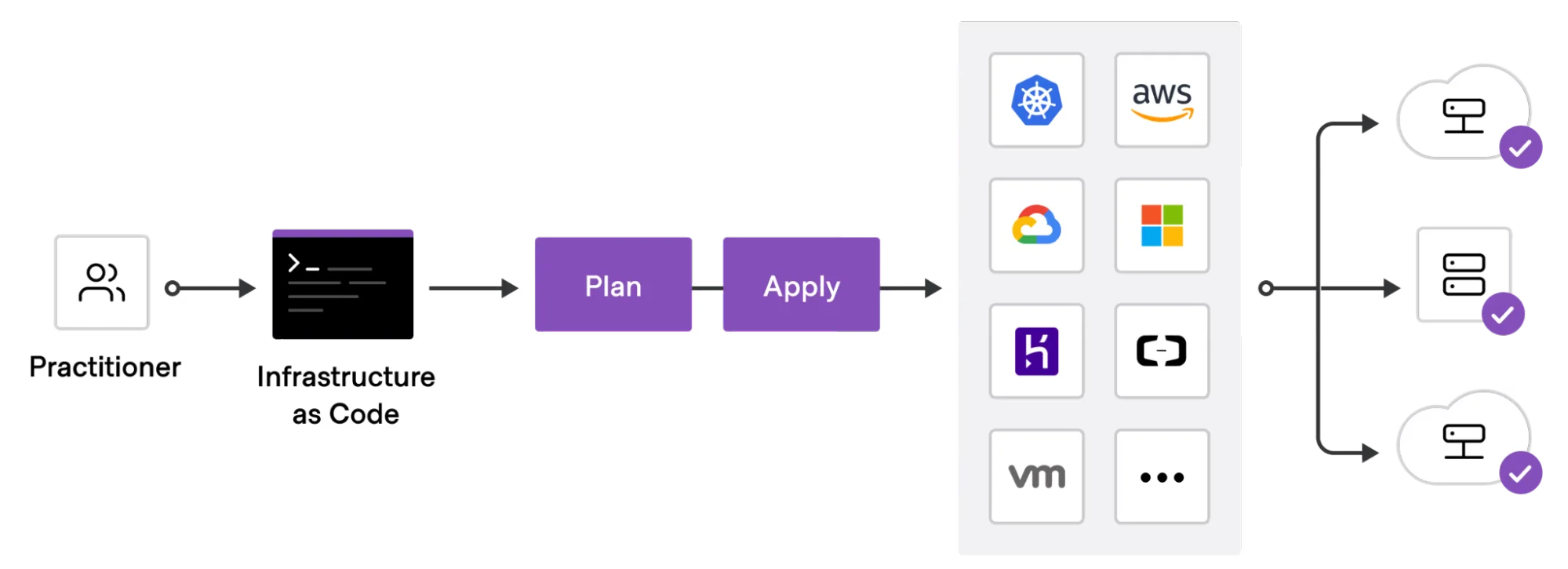
Terraform is an open-source IaC tool built by HashiCorp. It uses HCL — a simple, readable language — to describe what your cloud environment should look like. You write the code once, and Terraform applies it the same way every time, across any cloud.
It figures out the steps needed to match your environment to your code. Want to add servers? Rename a database? It plans and applies the changes for you. Teams love how consistent it is — and how easy it is to reuse setups with modules.
Terraform also tracks your current setup using a state file. That helps prevent mistakes and surprises. When your code lives in version control, your infrastructure becomes shareable, reviewable, and easy to roll back if something breaks.
Pros
- Works across all major cloud providers.
- Uses simple, readable HCL syntax.
- Enables repeatable, version-controlled deployments.
- Strong module support for reusable code.
- Large community and plugin ecosystem.
Cons
- Requires managing state files carefully.
- No built-in rollback if changes fail.
- Debugging can be time-consuming.
- Learning curve for new users.
- Limited support for imperative logic (by design).
5. Ansible – Cloud infrastructure automation
Red Hat’s Ansible suits organizations looking for a comprehensive platform that is also relatively easy to use. The platform lets you automate cloud provisioning, infrastructure configuration, container orchestration, application deployment, and security. Ansible is agentless, dependable, secure, and goal-oriented (no scripting required).
Ansible competitors include Jenkins, CFEngine, Puppet, Microsoft Azure Automation, Chef, and Google Cloud Deployment Manager.
Pros
- Operates without the need for agent installation on target nodes, simplifying management.
- Uses YAML for playbooks, ensuring automation tasks are more readable and maintainable.
- Extensive module library.
- Ensures repeated executions achieve the same result, preventing unintended changes.
- Compatible with different operating systems and environments.
Cons
- The licensing model for Ansible Tower can be expensive.
- Primarily command-line driven, with fewer graphical interface choices.
6. Pulumi – IaC platform for any programming language
With Pulumi, you can define and manage cloud infrastructure using popular programming languages such as Python, TypeScript, Go, C#, Java, and YAML.
The platform uses real programming constructs like loops, functions, and classes to create reusable and modular infrastructure components. This flexibility enables handling complex scenarios and promotes best practices in infrastructure management.
Pulumi also integrates with CI/CD pipelines, allowing for automated deployments and updates as part of your development workflow.
For advanced automation, Pulumi offers the Automation API, which exposes the Pulumi engine as an SDK. This feature enables you to create, update, and manage infrastructure programmatically. It is most suited for building custom cloud interfaces, self-service portals, and dynamic provisioning systems.
Pros
- Uses real programming languages (Python, TypeScript, Go, etc.).
- Great for complex logic and reusable components.
- Supports AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes, and more.
- Strong CI/CD and GitOps integrations.
- Offers both open-source and enterprise options.
Cons
- Steeper learning curve for non-developers.
- Requires language-specific tooling and dependencies.
- Smaller community than Terraform.
- Can be overkill for simple infrastructure setups.
- Managing secrets securely needs setup (e.g., Pulumi Vault).
CI/CD And DevOps Platforms
Modern development teams rely on continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) to ship code faster and reliably. DevOps platforms help automate builds, run tests, and deploy changes with minimal manual effort. Here are some of the most trusted tools in this space.
7. GitHub – Source code management
GitHub is the most popular cloud-based version control, collaboration, and source code repository hosting for Git developers. Git’s distributed version control model enables distributed teams to build, deploy, and improve software from anywhere. The platform is also popular among developers as a social network, a repository for open-source projects, and a coding project management tool.
GitHub alternatives include GitLab, BitBucket, AWS CodeCommit, etc.
Pros
- Multiple integrated tools, CI/CD with GitHub Actions; hosting via GitHub Pages, etc.
- Robust cloud backup platform.
- Central platform for open-source contributions and knowledge sharing.
- Efficient collaboration with Git for branching and merging.
Cons
- Limited tracking features compared to dedicated tools.
- The learning curve is steep for beginners unfamiliar with Git commands.
8. PagerDuty
PagerDuty’s end-to-end incident response tools enable cross-functional teams to stay on top of incident management at scale. PagesDuty offers solutions, from DevOps and AIOps to security and customer service. The real-time on-call management and alerts make it easy for teams to schedule the right people for the right tasks at the right time.
Similar tools to PagerDuty include Big Panda, Splunk On-Call, Lightstep Incident Response by ServiceNow, etc.
Pros
- Facilitates scheduling and management of on-call duties.
- Integrates with a wide range of monitoring and collaboration tools.
- Offers insights into incident response performance.
- Enables management of incidents via mobile devices.
Cons
- Costs can escalate with additional features and integrations.
- Initial configuration can be complex.
9. Jenkins – CI/CD for complex workflows
Jenkins is a free, open-source automation server that helps teams build, test, and deploy code automatically. It supports multiple languages and tools, making it ideal for complex or custom workflows. You define pipelines using Groovy-based scripts or the visual editor. Jenkins then runs each step, from code checkout to deployment.
With over 1,800 plugins, Jenkins integrates with tools like Git, Docker, Kubernetes, Maven, and Slack. You can run it on any OS, cloud, or on-premises. It also supports distributed builds, letting you run jobs across multiple machines to speed things up.
Jenkins is also quite popular with DevOps and QA teams needing complete CI/CD process control. It’s not the easiest to set up, but once configured, it can handle almost any automation task you throw at it.
Pros
- Highly customizable with 1,800+ plugins.
- Supports complex, multi-step CI/CD pipelines.
- Works with any language or environment.
- Free and open source.
- Strong community support.
Cons
- UI feels outdated and cluttered.
- Plugins can conflict or break with updates.
- Not ideal for teams wanting a fully managed solution.
10. GitHub Actions – Native CI/CD built into GitHub
GitHub Actions is a CI/CD tool built right into GitHub. You can run tests, build code, or deploy apps automatically by pushing to your repository. Workflows are written in YAML, and everything lives inside your GitHub project.
Its biggest appeal? Simplicity. You never have to leave GitHub. It works out of the box, supports any language, runs on Linux, macOS, or Windows, and integrates with Docker. You can test multiple versions of your app using matrix builds.
GitHub Actions also has a vast library of prebuilt actions. Need to deploy to AWS, send a Slack message, or install dependencies? There’s probably already an action for it.
Pros
- Built into GitHub—no extra tools or configuration.
- Supports any language and platform (Linux, macOS, Windows).
- Huge library of prebuilt actions.
- Easy to trigger workflows with Git events.
Cons
- Limited UI for managing complex pipelines.
- Can get messy without structured workflow files.
- Usage limits apply to free plans.
11. CircleCI – Fast, flexible CI/CD platform
CircleCI is built for speed and automation. It helps teams run tests, create code, and deploy changes automatically. You write simple YAML files to define steps, and CircleCI takes care of the rest.
It supports Linux, macOS, Windows, and Docker. You can speed up builds with caching, run jobs in parallel, and reuse setups with orbs — small, shareable automation packages.
It also works with GitHub and Bitbucket. The Insights dashboard shows real-time build metrics, so you can catch slowdowns, fix issues fast, and keep your DevOps pipeline running smoothly.
Pros
- Fast builds with parallelism and caching.
- Supports Docker, Linux, macOS, and Windows.
- Easy YAML-based configuration.
- Strong GitHub and Bitbucket integration.
Cons
- Pricing can increase quickly at scale.
- Debugging failed jobs can be time-consuming.
- Limited functionality on the free tier.
Cloud Testing Tools
Cloud testing tools simulate traffic, test performance, and reveal system weaknesses before release. They let teams run large-scale tests without managing servers or hardware. Here are some of the best:
12. Gremlin – Chaos engineering platform
Chaos engineering is a proactive strategy to prevent system failures in cloud computing. Software developers use controlled experiments to identify weaknesses, study what could go wrong, and practice what to do if something does go wrong.
With Gremlin, you can use CPU spikes, server shutdowns, latency injections, process killers, and blocked DNS access to expose vulnerabilities in your system. Additionally, you can test your disaster recovery procedures to prevent a false sense of security.
Gremlin competitors include Chaos Toolkit, Litmus, ChaosMesh, etc.
Pros
- Conducts controlled experiments to test system resilience.
- Helps identify weaknesses and improve reliability.
- Offers pre-defined failure scenarios for efficient testing.
- Supports disaster recovery preparation.
- Integrates with DevOps tools for smooth operations.
Cons
- Implementing chaos engineering effectively demands specialized knowledge to design meaningful experiments and accurately interpret the results.
13. Apache JMeter – Open-source load testing for web and APIs

Apache JMeter helps teams simulate real-world traffic and measure how applications behave under stress. It supports testing for web apps, APIs, databases, and more, and runs on any system with Java.
You can simulate thousands of users by configuring thread groups and test plans. JMeter supports protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, JDBC, and SOAP. It also integrates with cloud services like AWS and Azure for distributed testing.
JMeter’s GUI lets you build tests visually, while its CLI mode supports automation and CI/CD pipelines. With plugins and dashboards, you can monitor performance metrics and identify bottlenecks. It’s a go-to choice for teams needing scalable, flexible testing without vendor lock-in.
Pros
- Open source and free.
- Supports multiple protocols (HTTP, FTP, JDBC, etc.).
- Runs large-scale performance tests.
- GUI for easy test creation; CLI for automation.
Cons
- High memory usage during large tests.
- Limited built-in analytics and reporting.
- Needs plugins for advanced features.
14. BlazeMeter – Scalable cloud-based load testing platform
With the ability to simulate over two million virtual users from 56 global locations, BlazeMeter helps identify performance issues and ensure application scalability. Its intuitive UI and real-time analytics provide insights into response times, error rates, and throughput.
BlazeMeter integrates with CI/CD tools like Jenkins and TeamCity to facilitate automated performance testing within development pipelines. Its compatibility with various protocols and support for distributed testing also make it an ideal choice for organizations aiming to improve their DevOps practices.
Pros
- Scales up to millions of virtual users.
- Easy-to-use UI with real-time analytics.
- Supports JMeter, Selenium, Gatling, and more.
- Integrates with CI/CD tools like Jenkins and TeamCity.
- Cloud-based—no local configuration needed.
Cons
- Can be expensive for large teams or tests.
- Some features are locked behind higher pricing tiers.
15. LoadRunner – Performance testing software tool
LoadRunner by OpenText is built for high-scale, complex testing. It simulates thousands of users from global locations to test how applications perform under heavy traffic, without needing to manage test infrastructure yourself.
What sets it apart is support for over 50+ protocols — far beyond most cloud testing tools. It handles web, mobile, SAP, Citrix, and legacy systems. That makes it ideal for large enterprises with diverse tech stacks or regulated environments.
LoadRunner also integrates with Jenkins and Azure DevOps, offers real-time dashboards, and supports shift-left testing for early-stage load validation.
Pros
- Supports 50+ protocols (web, mobile, SAP, Citrix, etc.).
- Handles high-scale, enterprise-grade performance testing.
- Real-time analytics and detailed reporting.
- Integrates with CI/CD and DevOps tools.
- Ideal for complex or legacy systems.
Cons
- Expensive, especially for smaller teams.
- Steep learning curve for new users.
- Requires powerful machines for local execution.
Cloud Provisioning Tools
Cloud provisioning tools help teams deploy infrastructure using code, automating resource setup, reducing errors, and keeping environments consistent. It’s important to note: provisioning is not the same as configuration. Provisioning prepares cloud resources; configuration defines how they behave after deployment.
Here’s our in-depth guide on provisioning and the difference between provisioning and configuration.
And here are the most commonly used tools across AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure.
16. AWS CloudFormation
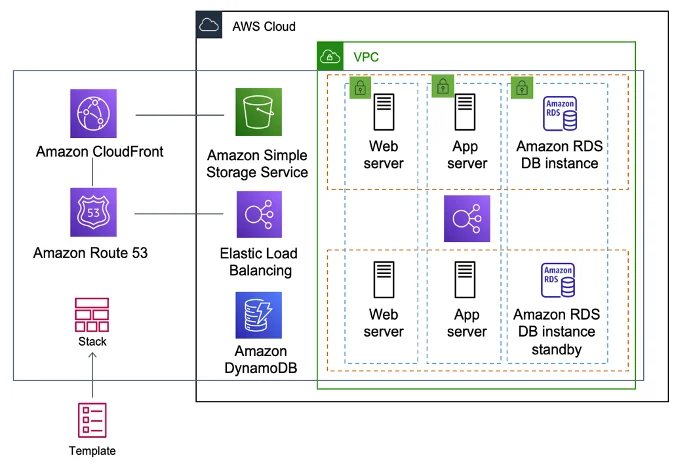
AWS CloudFormation enables you to model, provision, and manage AWS resources using infrastructure as code. By defining your infrastructure in JSON or YAML templates, you can automate the setup of AWS services such as EC2, RDS, and S3, ensuring consistent and repeatable deployments.
With CloudFormation, you can also manage resources as a single unit called a stack. This approach simplifies the orchestration of complex environments, enabling you to update or delete all related resources together. Additionally, features like change sets let you preview modifications before applying them, reducing the risk of unintended changes.
Pros
- Full AWS integration.
- Repeatable deployment, ensure a consistent setup every time.
- Stack management: manage related resources as a single unit.
Cons
- Limited to AWS, doesn’t support multi-cloud or hybrid setups.
17. Azure Resource Manager – Native Provisioning for Azure
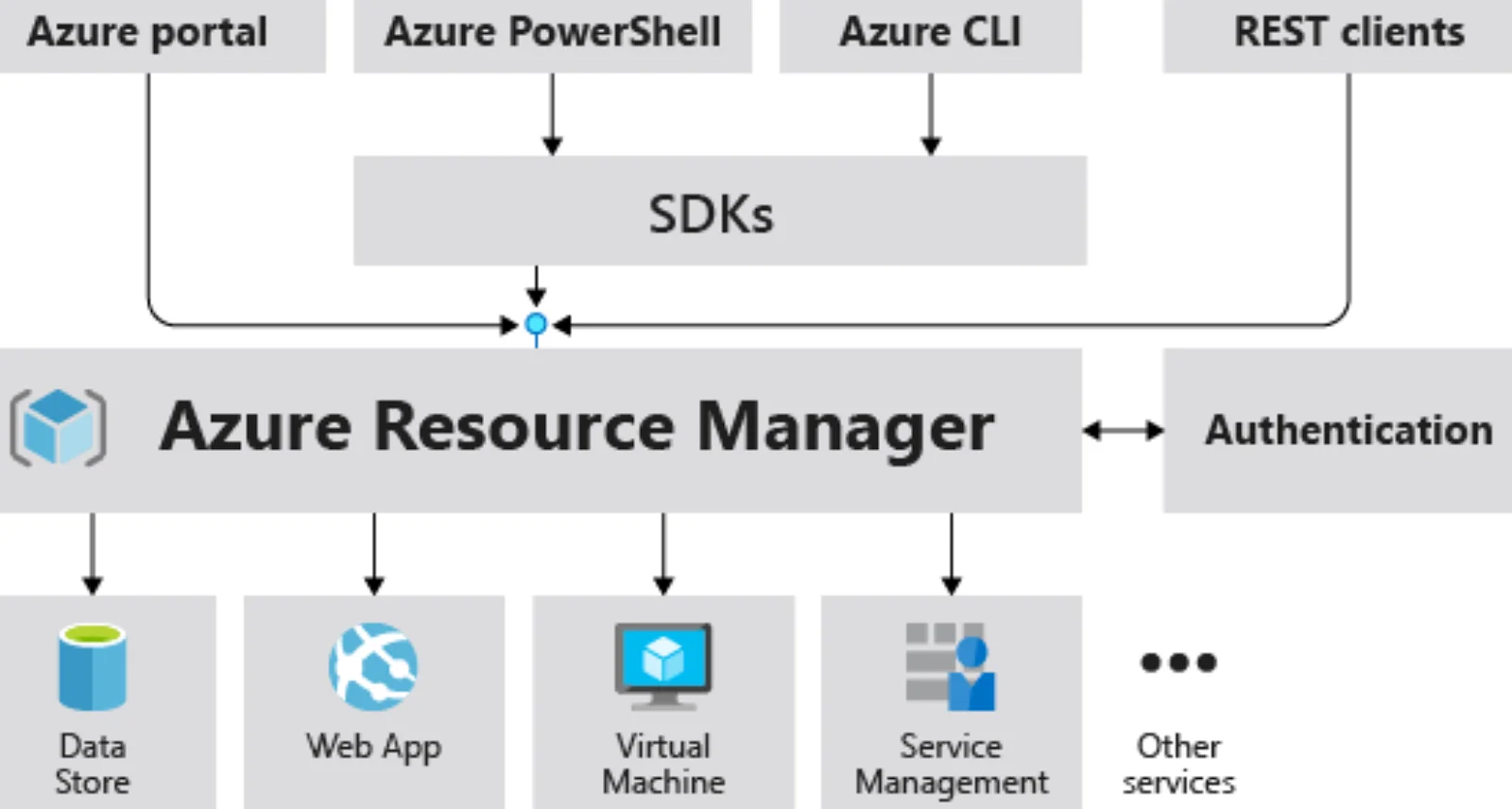
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) is Microsoft’s native IaC service for deploying and managing Azure resources. Using JSON-based templates, ARM enables you to define and provision infrastructure components such as virtual machines, storage accounts, and networks consistently and repeatedly.
ARM organizes resources into resource groups, enabling centralized management, access control, and monitoring. It integrates with Azure services, supporting RBAC, tagging, and policy enforcement to maintain governance and compliance across your deployments.
Pros
- Fully integrated with all Azure services.
- Automates infrastructure with repeatable JSON templates.
- Supports governance.
Cons
- Limited to Azure, doesn’t support multi-cloud environments.
- Not as readable or flexible as YAML.
- Demand deep knowledge of Azure and ARM syntax.
18. Google Cloud Infrastructure Manager – Native Terraform provisioning for GCP
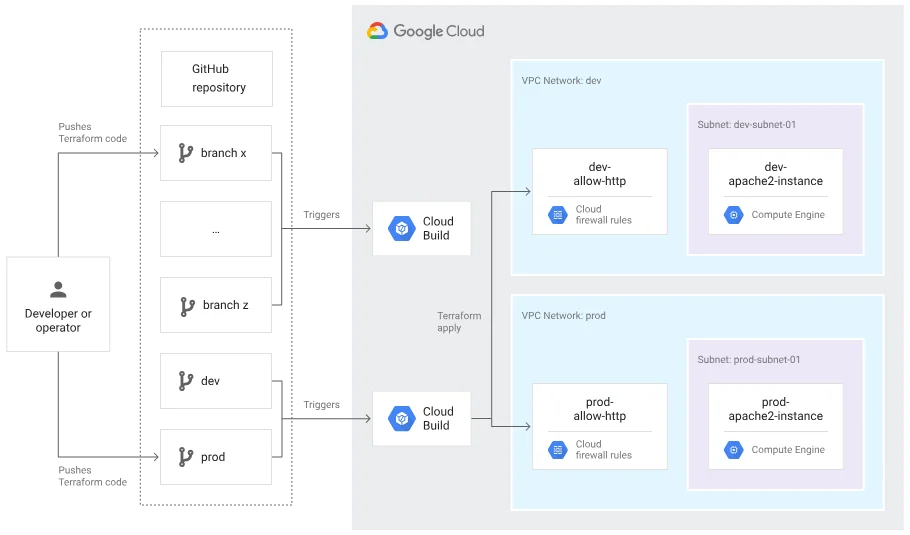
Google Cloud Infrastructure Manager (Infra Manager) is a managed service that automates the deployment and management of Google Cloud resources using Terraform. It enables users to define IaC and deploy resources programmatically. This eliminates the need for a separate Terraform toolchain.
Infra Manager works with Cloud Build to run Terraform commands in a temporary, clean environment. This helps keep deployments consistent. You can store your configs in Git or Cloud Storage for easy version control and teamwork. It also offers previews, auto-retries, and detailed logs for every deployment.
Pros
- Uses standard Terraform syntax with full GCP support.
- Managed by Google, no need to install Terraform manually.
- Works with Git and Cloud Storage for safer deployments.
- Supports preview and rollback, users can see planned changes before applying them.
- CI/CD friendly.
Cons
- Native to GCP.
- Requires Terraform knowledge.
- Most control is via CLI or API, not a complete dashboard experience.
If you’re looking for tools that support multi-cloud provisioning, Morpheus Data, Scalr, CloudBolt, Rundeck, Apache CloudStack, and Ansible are some of the best candidates.
19. Cloudsfer – Cloud migration tool

If you are planning to move to the cloud, check out our complete guide to cloud migration here. Cloudsfer offers on-premises-to-cloud and cloud-to-cloud migration services. You can migrate data from multiple sources to 20+ cloud storage services. The backup tool lets you sync cloud services, and the archiving tool enables you to copy data from cloud storage and replicate it locally.
Whether you need a cloud-to-cloud, on-premise-to-cloud migration, or a tool that supports both, see more cloud migration services here. Here are seven AWS migration strategies if you want to learn specific methods for migrating to the AWS public cloud.
Pros
- Supports on-premises-to-cloud and cloud-to-cloud migrations.
- Intuitive interface simplifies the migration process.
- Syncs and backs up data between platforms.
- Flexible scheduling minimizes disruption during migration.
- Offers detailed migration reports for tracking progress.
Cons
- Large data transfers can face speed issues based on network conditions.
- It may be expensive for small businesses with tight budgets.
Kubernetes cost optimization
Kubernetes is robust, but without cost visibility, it can quietly drain your cloud budget. As clusters scale, so do inefficiencies: overprovisioned nodes, idle pods, and underused resources.
Here are the tools leading the way in keeping Kubernetes efficient and cost-aware.
20. Kubernetes – Container orchestration and management

Kubernetes, or K8s, is an open-source, production-grade platform for orchestrating containers. You can use it as a platform and tool to deploy, scale, and manage containerized applications. Its self-healing, automated rollbacks and rollouts, load balancing, and batch execution capabilities make Kubernetes particularly well-suited to managing container orchestration at a massive scale.
Kubernetes alternatives include Docker, Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), Red Hat OpenShift, and Rancher.
Pros
- Facilitates automated deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- Supports deployment across various environments, including on-premises, public clouds, and hybrid setups.
- Automatically restarts failed containers and replaces them, ensuring application resilience.
- Distributes network traffic effectively, maintaining application stability.
- Enables automatic mounting of storage systems such as local or public cloud providers.
- Supports custom controllers and APIs, enabling customized functionalities.
Cons
- Initial setup and configuration can be highly complex.
- It can consume substantial system resources.
21. Harness – Kubernetes Cost Control With Built-In Intelligence
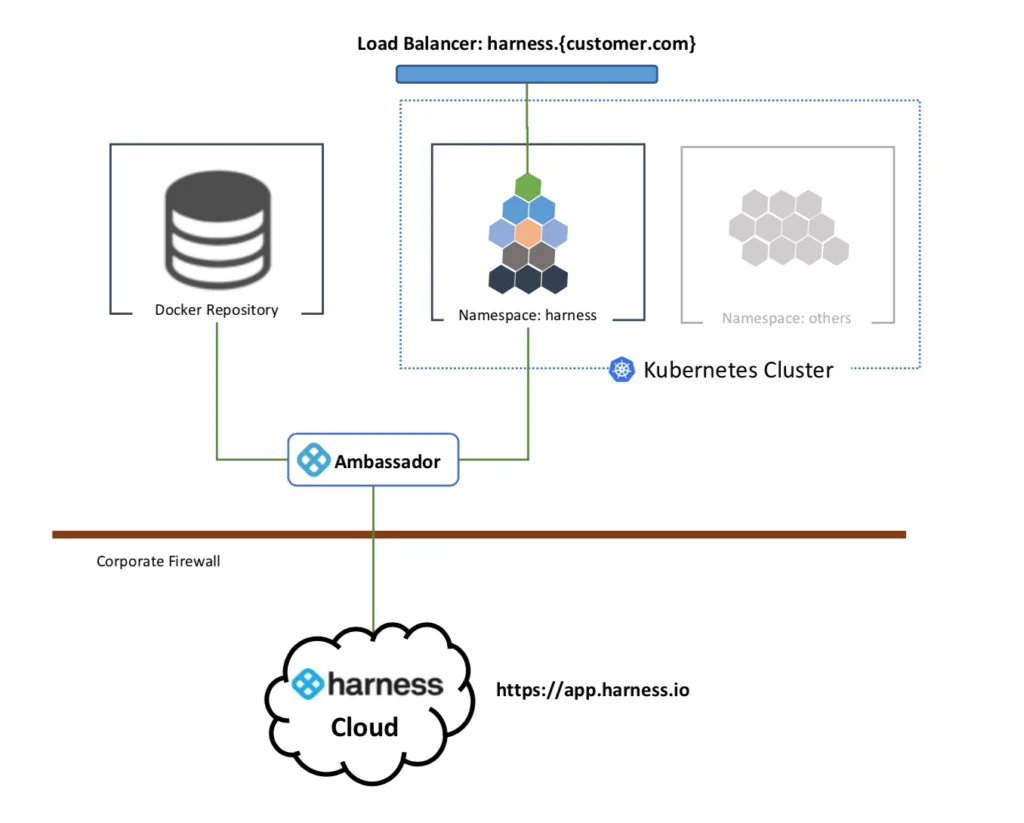
Harness Cloud Cost Management helps teams monitor and reduce Kubernetes spend across clusters. It breaks down costs by pod, namespace, workload, and environment, so you can see exactly where waste is hiding — and address it fast.
It uses AI to spot idle resources and overprovisioned workloads, then recommends rightsizing actions. You can automate these changes or review them manually. Harness also supports showback and chargeback, making aligning costs with teams or products easier.
For DevOps and FinOps teams, Harness adds auto-governance, budget alerts, and forecasting. You can set policies and stop overspending before it starts. It works across AWS, GCP, Azure, and hybrid Kubernetes environments — all from one platform.
Pros
- Kubernetes-native.
- Multi-cloud support.
- DevOps-friendly, integrates with CI/CD workflows.
Cons
- Limited support for non-cloud K8s, best results come from cloud-native environments.
Related read: 5 Powerful Harness.io Alternatives For CI/CD, Security, And Cloud Cost Optimization
22. Densify – Kubernetes resource optimization
Densify uses machine learning to analyze Kubernetes workloads and recommends precise resource settings. It helps you rightsize pod CPU and memory requests so you’re not overpaying for unused capacity or under-resourcing critical services.
It continuously monitors your clusters and suggests adjustments to avoid waste and performance issues. These recommendations are tailored to your usage patterns and can be integrated into CI/CD pipelines for automated efficiency.
Densify also helps with node optimization and bin-packing, making better use of available compute. It’s a strong fit for platform teams managing large-scale, cost-sensitive Kubernetes environments.
Pros
- Supports CI/CD integration.
- Supports multi-cloud.
- Improves compute efficiency at the node level.
Pod-level precision – Rightsizes CPU and memory for each workload.
Cons
- Can be complex to tune.
Data And Analytics Platforms
Modern cloud environments generate massive amounts of data, but raw data isn’t enough. Data and analytics platforms help teams centralize, clean, model, and analyze that data to drive decisions. Here is the best:
23. Civis Analytics – Big data and analytics tool

If you are looking for a service to help your data team centralize, clean, enrich, and apply data at scale, Civis Analytics may be a good choice. This service lets you collect data from trusted third parties to fill knowledge gaps in your data, share it across your organization, and inform decision-making. You can also work with data in your favorite language, from SQL to Ruby to Python.
More Big Data analytics tools include Apache Hadoop, OpenRefine, RapidMiner, Amazon EMR, etc.
Pros
- Aggregates data from multiple sources for comprehensive analysis.
- Provides tools for advanced data analysis and visualization.
- Supports team collaboration on data projects.
Cons
- It may offer fewer customization options than some open-source tools.
- Dependence on the platform could impact control over certain processes and the timeline.
Multi-Cloud Management Solutions
Multi-cloud tools help unify management across providers. They simplify operations, boost visibility, and enforce security and governance, no matter where your workloads run. Below are some of the leading platforms built for multi-cloud control.
24. Lacework FortiCNAPP – Cloud security tool

Lacework FortiCNAPP provides continuous cloud security and compliance management at scale. You can collect, analyze, and correlate security threats across multiple cloud platforms, such as AWS, Google Cloud Platform, and Azure, so you can prioritize addressing them.
This Infrastructure-as-a-Code security service provides vulnerability, security posture, and compliance management for all your environment’s apps, workloads, containers, processes, machines, accounts, and users.
Lacework alternatives include Fugue, Orca Security, Synk, Threat Stack, etc.
Pros
- Real-time security monitoring for multiple cloud platforms.
- Automates compliance management for industry standards.
- Scales to secure large cloud environments.
- Provides deep insights into apps, containers, and workloads.
Cons
- Requires effort to integrate with existing tools.
- Complex features may take time to utilize fully.
25. Cloudify – Open-source, multi-cloud orchestration platform
With Cloudify, users leverage YAML blueprints to define full-stack environments — then deploy, scale, and update them from a single control layer.
One of Cloudify’s standout features is that it acts as an “orchestrator of orchestrators.” This means it integrates with existing tools such as Terraform, Ansible, and Kubernetes to facilitate automation across different platforms.
DevOps and platform teams use it to build self-service environments or manage hybrid infrastructure. It also supports role-based access control, identity integration, and monitoring via Prometheus for enterprise governance.
Pros
- Open source.
- Reusable blueprints – define setups once and use them anywhere.
- Supports AWS, Azure, GCP, and more.
- Smooth integration with multiple platforms.
- Self-service environments enable teams to launch what they need, fast.
Cons
- It can be buggy; some blueprint errors require manual fixes.
- Its GUI may lack some advanced features.
26. CoreStack – Next-gen cloud business accelerator
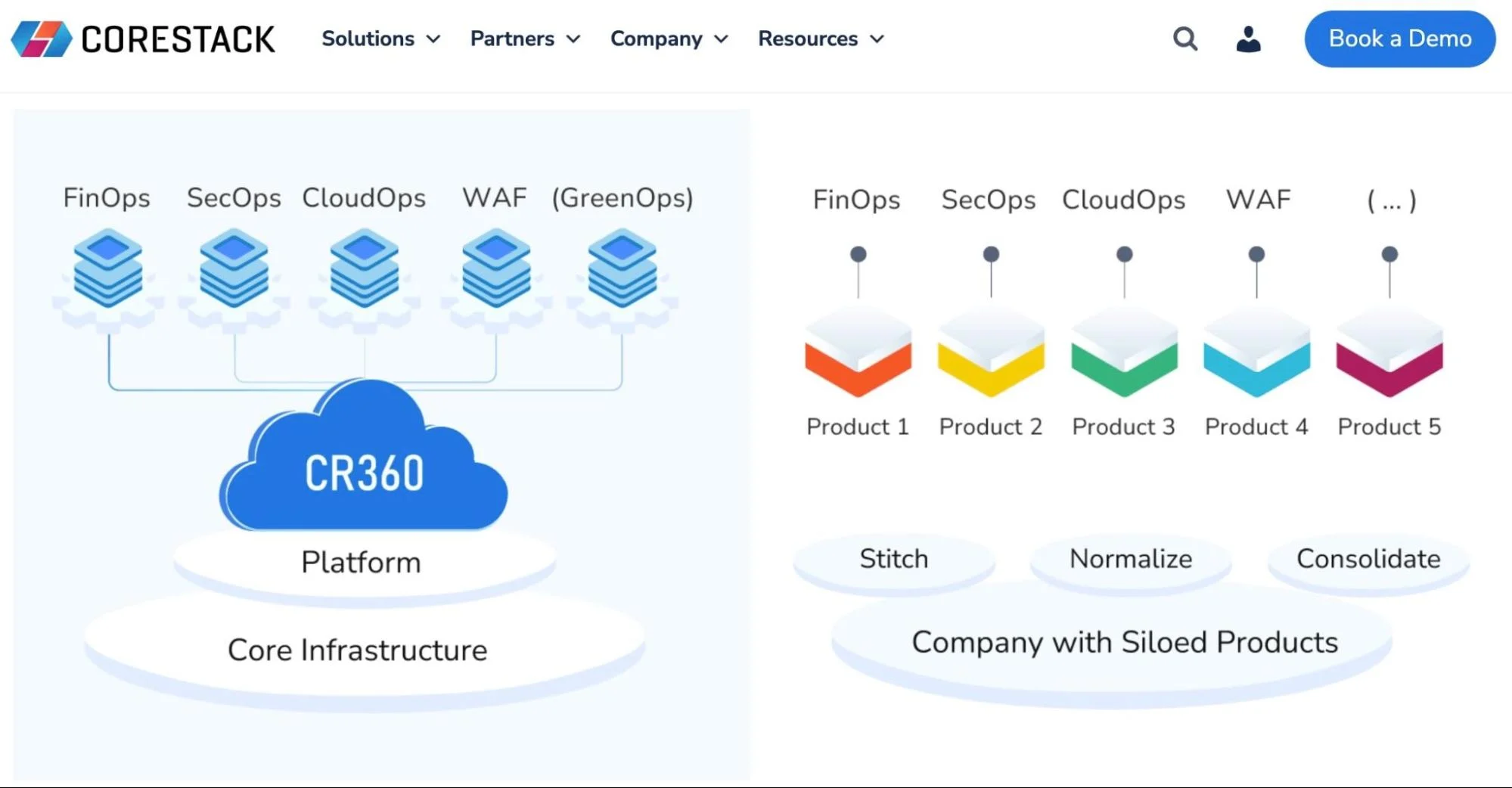
CoreStack aggregates cost, security, operations, and compliance into one clean dashboard. You can manage AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and more without juggling different tools.
CoreStack is also built around a smart, modular approach. It offers FinOps to cut waste, ecOps for security and compliance, and CloudOps for operational efficiency. These modules provide real-time insights, automate routine tasks, and enforce policies across diverse cloud environments.
Pros
- Built-in compliance automates HIPAA, ISO, and PCI-DSS checks.
- Self-service access.
- Unified multi-cloud governance.
Cons
- Users have reported that the initial configuration can be complex .
IT System Monitoring Tools For DevOps
Monitoring and observability tools give teams real-time visibility into system health, performance, and uptime. They help detect issues early, reduce downtime, and keep services running smoothly. T
27. Sematext – Cloud monitoring service
There are dozens of cloud monitoring tools, but Sematext provides an all-in-one monitoring platform.
You can monitor front-end and back-end logs, APIs, applications, and multiple cloud environments from one place. Sematext lets DevOps teams monitor everything from networks, containers, microservices, databases, and servers.
Pros
- Combines logs, metrics, and real user monitoring in a single platform.
- Offers both cloud-based and on-premises deployment options.
- Flexible integration.
Cons
- Some users find Sematext’s pricing relatively high, especially for log management.
- Applications may be deleted after 31 days of inactivity without sufficient warning.
Data Protection And Backup Tools
In the cloud, protecting your data is as important as storing it. These tools help prevent data loss, enable fast recovery, and ensure business continuity, whether from accidental deletion, system failure, or cyber threats.
28. Carbonite by OpenText – Data governance platform

Carbonite offers data protection, migration, and backup services for homes, small businesses (professionals), and enterprises (business solutions).
The service replicates virtual, cloud, and physical workloads with push-button failover to ensure that business-critical systems are always available. Carbonite’s automatic cloud backup service supports various environments, devices, and cloud platforms, such as MySQL, Hyper-V, and Oracle.
Other Data protection, backup, and recovery services include Zscaler, Google Cloud Storage, Forcepoint, Dropbox, and OneDrive.
Pros
- Offers data protection for environments, including physical, virtual, and cloud.
- Disaster recovery.
- Seamless data migration across platforms.
- User-friendly interface.
Cons
- No file-sharing or folder-syncing features.
- No backup to local media.
Collaboration And Productivity Tools
Cloud-native collaboration tools help teams stay organized, share knowledge, and work together in real time, no matter where they are.
29. Notion – Document collaboration and file-sharing
Notion provides a workspace, collaboration tool, knowledge base, and file-sharing platform in one. Teams can easily share knowledge, workflows, schedules, project progress, etc., and get work done without putting together multiple tools. Instead of starting from scratch, you can choose and modify a template.
Notion is also well-known for its note-taking capabilities. It enables you to record insights, ideas, and progress statuses from meetings, brainstorming sessions, etc., and share them with others or edit them later.
Some Notion alternatives include Confluence, Bit.ai, Google Workspace, ProofHub, etc.
Pros
- All-in-one workspace, notes, tasks, databases, etc.
- Real-time collaboration.
- Customizable templates.
- Accessible on various devices and operating systems.
- Multiple integrations.
Cons
- Lacks built-in features for goal tracking.
- Performance issues with large databases.
Data Integration And Management Platforms
These platforms help organizations unify data from multiple sources, clean it, and prepare it for analytics and reporting. They support ETL/ELT workflows, ensure data quality, and power modern business intelligence in the cloud.
30. Informatica – Cloud data integration platform
Informatica can combine data from multiple sources for analysis and business intelligence with ELT, ETL, Spark processing, or a fully managed serverless solution. It’s also available on-premises. The platform also features application integration, data cleansing/quality, API management, etc., in one platform and usage-based pricing.
More data integration tools include Talend Cloud Integration, Oracle Integration Cloud Service, SnapLogic, etc.
Pros
- Smooth data integration across multiple sources.
- Ensures high-quality data through cleansing and validation features.
- Provides AI-driven recommendations for data integration processes through its CLAIRE® engine.
- Scalability with serverless computing.
Cons
- Its data quality tools may lack real-time processing capabilities.
- Multiple tools for a single workflow.
Related read: 30+ Essential ETL Tools For Data Pipelines
Now that you know the top tools by category, here’s how to pick the one that fits your cloud strategy.
How To Choose The Right Cloud Computing Tool
Choosing a cloud tool isn’t about finding the most features but finding the right fit. Here are key things to consider before you decide:
- Cloud environment: Is your setup single-cloud, multi-cloud, or hybrid? Some tools are cloud-specific (like CloudFormation or ARM), while others work across platforms (like Terraform or Pulumi).
- Use case: Do you need cost visibility, automation, provisioning, migration, or security? Ensure the tool focuses on what matters most to your team.
- Team skills: Does your team prefer YAML, Python, UI dashboards, or CLI? Tools like Pulumi support dev languages, while others like Terraform use declarative syntax.
- Integration and automation: Check if the tool works with your CI/CD pipeline, tagging standards, or IAM setup. Smooth integration reduces friction.
- Cost and scalability. Some tools are open-source, others require licenses. Think about long-term value, not just sticker price.
- Support and documentation. Strong docs, a helpful community, or responsive support can make or break your experience with any tool.
What next?
Optimize Your Cloud Computing Usage And Costs With CloudZero
Cloud computing is one of the best developments in modern business. Cloud users can leverage IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS to get to market quickly, utilize managed cloud services, and enjoy pay-per-use pricing.
- You’ll pay only for the services you use when you use them.
- You won’t need to purchase hardware for a physical data center.
- You can also ensure continuity by backing up and syncing business-critical workloads, apps, and data.
But while the cloud offers nearly limitless elasticity, it can quickly become a complex maze with little visibility into costs and usage. Unless you can see which specific features, customers, environments, teams, projects, etc., are driving those costs, you won’t know how to optimize them without hurting customer experiences.
- Engineering, finance, and the C-suite can tell precisely what’s driving their cloud computing costs with CloudZero’s Cloud Cost Intelligence approach.
- We align cloud spend with the people, product features, and processes that create it.
- CloudZero also delivers cost intelligence for Snowflake and Kubernetes environments.
- Whether you have untagged, untaggable, or shared resources, CloudZero can map those costs accurately. It does not require tags to do this.
- Finally, if you are tired of juggling multiple tools to manage, analyze, and report your cloud computing costs and usage, CloudZero has the budgeting, migration, cost forecasting, and allocation solutions you need in one place.
 to see how to reduce your cloud computing costs within a week or two, not months.
to see how to reduce your cloud computing costs within a week or two, not months.








