As a provider of over 200 cloud products and services, Microsoft Azure provides most of the capabilities you need to manage your cloud workloads.
While this breadth of services can be beneficial, it can also create complexity issues, such as reducing cloud cost visibility and increasing security blind spots. Proper Azure cloud management can change this.
In this snackable guide, we’ll share what Azure cloud management is, the key tools you need to manage your Azure environment, and more.
What Is Azure Cloud Management?
Azure cloud management consists of the tasks and processes that are required to maintain your Azure infrastructure, applications, and services in optimal health and performance. It includes creating, deploying, and managing virtual machines, applications, and services.
It also involves monitoring, troubleshooting, and optimizing the performance of your Azure cloud environment.
Managing your Azure cloud involves a set of tools, services, and platforms. These enable you to configure, run, and optimize your infrastructure, applications, and services on Azure.
In addition, other areas of Azure cloud management involve automating processes, monitoring performance, and securing data.
Plus, it also includes providing support for users, troubleshooting issues, and responding to outages.
Microsoft Azure also provides a range of managed services, such as managed databases, managed storage, and managed applications. These services make it easier for users to manage and scale their cloud resources.
What Are The Benefits Of Azure Cloud Management?
Ultimately, you want to maximize the return on your Azure cloud investment. By practicing Azure cloud management, you can tweak things to meet your cloud performance, security, and cost goals.
Here are some advantages to managing your Azure cloud:
- Enhances security – Build, improve, and promote robust security measures to protect your data from unauthorized access and systems from degradation.
- Ensures availability – Maintain the health of your Azure cloud infrastructure, applications, and services to ensure high-quality user experiences.
- Facilitates disaster recovery – Provide redundancy, backup, and recovery for your Azure cloud assets.
- Helps improve performance – Monitoring performance helps to identify any potential issues before they affect other services.
- Improves cloud visibility – Be able to see your cloud components in a unified way, including infrastructure, apps, and services, allowing you to better integrate and configure them for optimal performance.
- Enables robust cloud cost management – Track and analyze resource usage to identify potential cost savings and maximize efficiency.
- Implement hybrid cloud and multi-cloud deployments – This practice can help you take advantage of different cloud providers’ strengths without leading to operational chaos.
In addition, Microsoft has increasingly introduced automation to help Azure cloud users handle repetitive tasks that can be time-consuming.
These include auto-scalability, which ensures your cloud resources can increase and decrease on demand to meet workload requirements.
Yet, there are some limitations you’ll want to keep an eye on.
What Are The Limitations Of Azure Cloud Management?
Managing an Azure Cloud environment does have its fair share of challenges. These include:
- Complexity – The broader the cloud components, such as the number of services running, the more complex the environment gets to manage effectively.
- Requires advanced expertise – It requires a deep understanding of not only general cloud computing concepts and technologies but also Azure-specific best practices. Organizations that do not have the expertise to manage their Azure Cloud may need to hire consultants or staff with the necessary skills.
- Azure Cloud Management can be expensive – Continuously monitoring your Azure cloud environment can require you to invest in people, tools, and services, which can quickly rack up your cloud bill. This is especially true for organizations that use a lot of resources.
- Security risk – Organizations that store data in the cloud are responsible for securing it. That means you need to have the proper security and compliance measures in place. Otherwise, your data could be compromised.
- Personalized support – This can be difficult to get, especially for organizations that have complex issues, such as operating across clouds (hybrid cloud and multi-cloud). You may need to wait a long time for support or hire consultants to help you.
Despite these challenges, practicing Azure cloud management can help your organization to more effectively use your Azure cloud resources.
That said if you want to simplify your Azure management work, consider investing your time, effort, and talent in the following areas.
What Is A Microsoft Azure Management Area?
This refers to the groupings of tasks and processes required to maintain your Azure applications and the resources that support them.
According to Microsoft, there are six Azure management areas you’ll want to track:
- Migration
- Configuration
- Security
- Protection
- Monitoring
- Governance
Picture this:
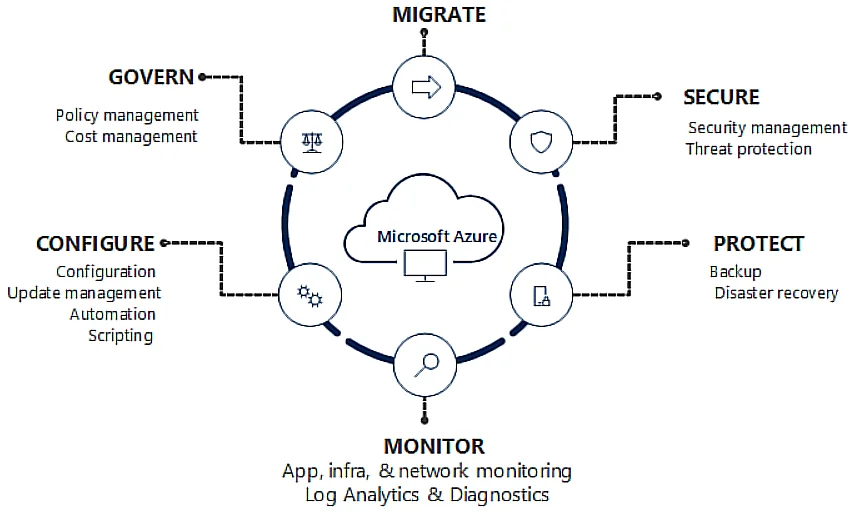
Credit: Microsoft Azure management areas
What Are The Six Azure Management Areas To Keep Track Of Today?
Here’s what each area is all about.
1. Migration
This refers to the process of moving your on-premises workloads to an Azure cloud environment. The migration can also be from another cloud service provider, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Alibaba Cloud.
An Azure cloud migration involves quite a bit of planning (known as pre-migration) rather than merely moving your physical servers, Hyper-V VMs, and VMware VMs to Azure.
On Azure, these pre-migration steps include discovery, assessment, and right-sizing resources. The cloud provider offers one primary platform to help with this: Azure Migrate
Azure Migrate is a suite of cloud migration tools, including Discovery and Assessment, Data Migration Assistant, and Movere. It also provides a unified portal for starting your Azure migration process and tracking its progress.
2. Configuration
Configuration refers to the process of defining dependencies, allocating resources, and maintaining an IT system’s components in a desired state, enabling it to handle certain workloads.
This is a very involving process because it not only comes before deployments, it is also an ongoing process. It is also why Azure provides Azure Automation.
With Azure Automation, you get a service that provides cloud-based automation, updates to your operating system, and a configuration service that enables uniform management across your Azure (and non-Azure) environments.
There is also this:
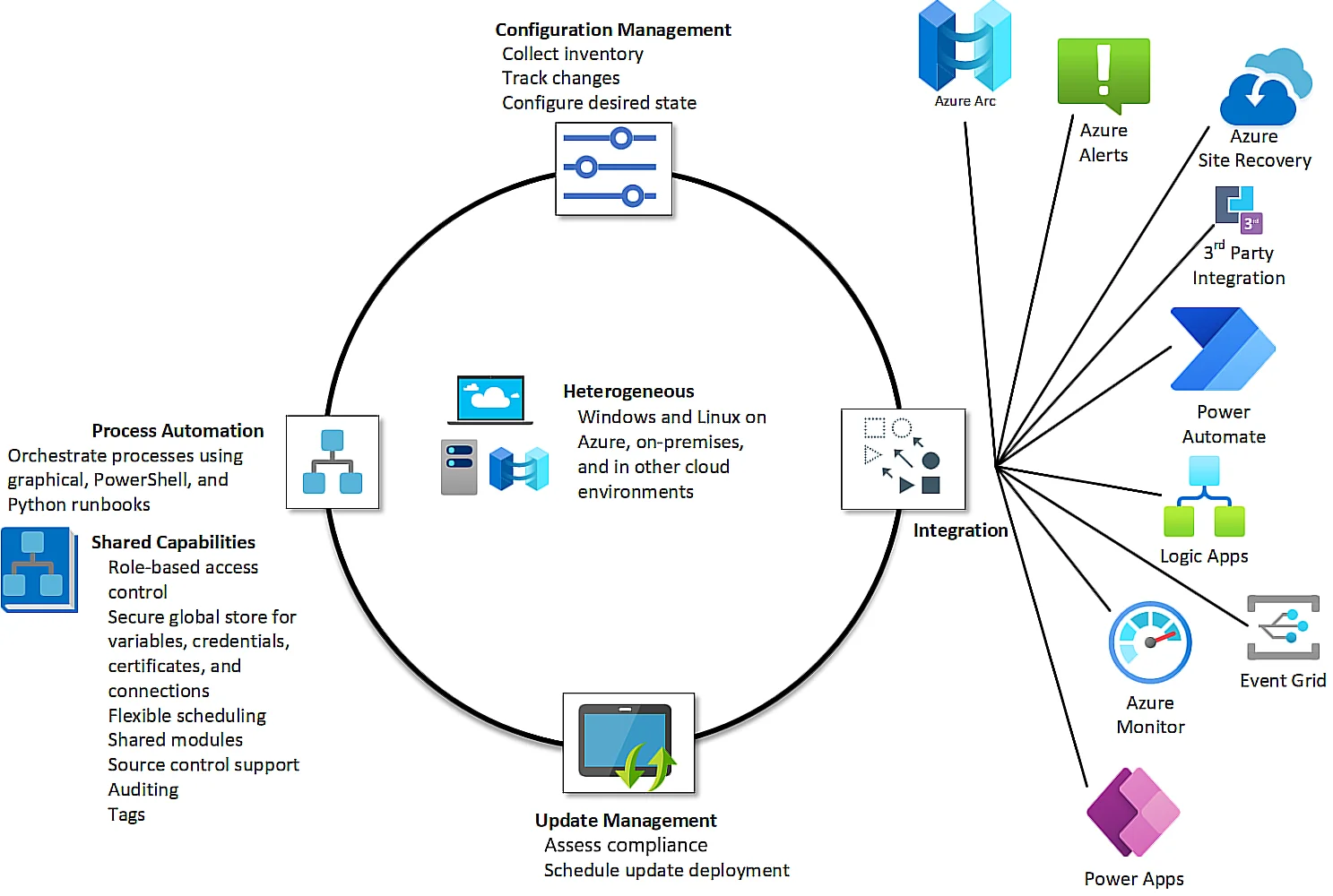
As shown here, you can also use Azure Automation for configuration management, process automation, update management, and shared capabilities.
3. Security
This area refers to the different aspects of securing your infrastructure, applications, services, and data.
As part of the process, you assess and detect threats, collect and analyze risk data, and report the data to the most relevant professionals for threat analysis, interpretation, and further action.
Azure provides several tools to help you secure your resources, including Microsoft Defender for Cloud, Azure Firewall, and Microsoft Sentinel. These are a few examples of customer-facing controls you can use to tailor and improve security for your Azure apps and services.
4. Protection
In Azure, the Protect management area involves maintaining the availability of your system, which helps prevent service disruptions. This happens through a suite of disaster recovery tools and best practices.
The two Azure tools involved here are:
- Azure Backup Service – Provides an intuitive, secure, and cost-effective platform to store your data and recover it from the Azure cloud in case of an incident.
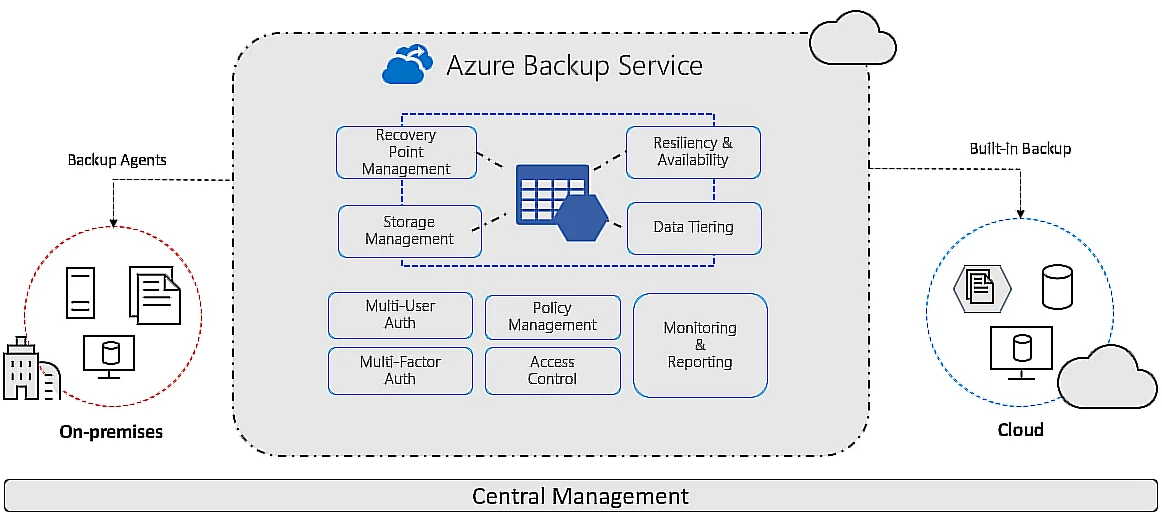
You can use it to back up many components, including VMs, file shares, managed disks, etc.
- Azure Site Recovery – Replicates services running on your Azure cloud or on-premises from their primary site to a secondary destination. This ensures you can still run your apps and services on the secondary location if the primary site is down, ensuring business continuity.
There are more areas of Azure cloud management below.
5. Monitoring
This refers to the continuous process of collecting your cloud metrics, logs, traces, and events data and analyzing them to get actionable insights. Depending on the Azure service, you can track your performance in real time, enabling you to detect issues before they become large problems.
Yet, monitoring also covers security, cloud costs, and compliance with your industry’s requirements.
With Azure Monitor, for example, you can also programmatically and manually respond to your system’s events. It aggregates monitoring data from every level and component of your system, whether it be on Azure or non-Azure tenants and subscriptions.
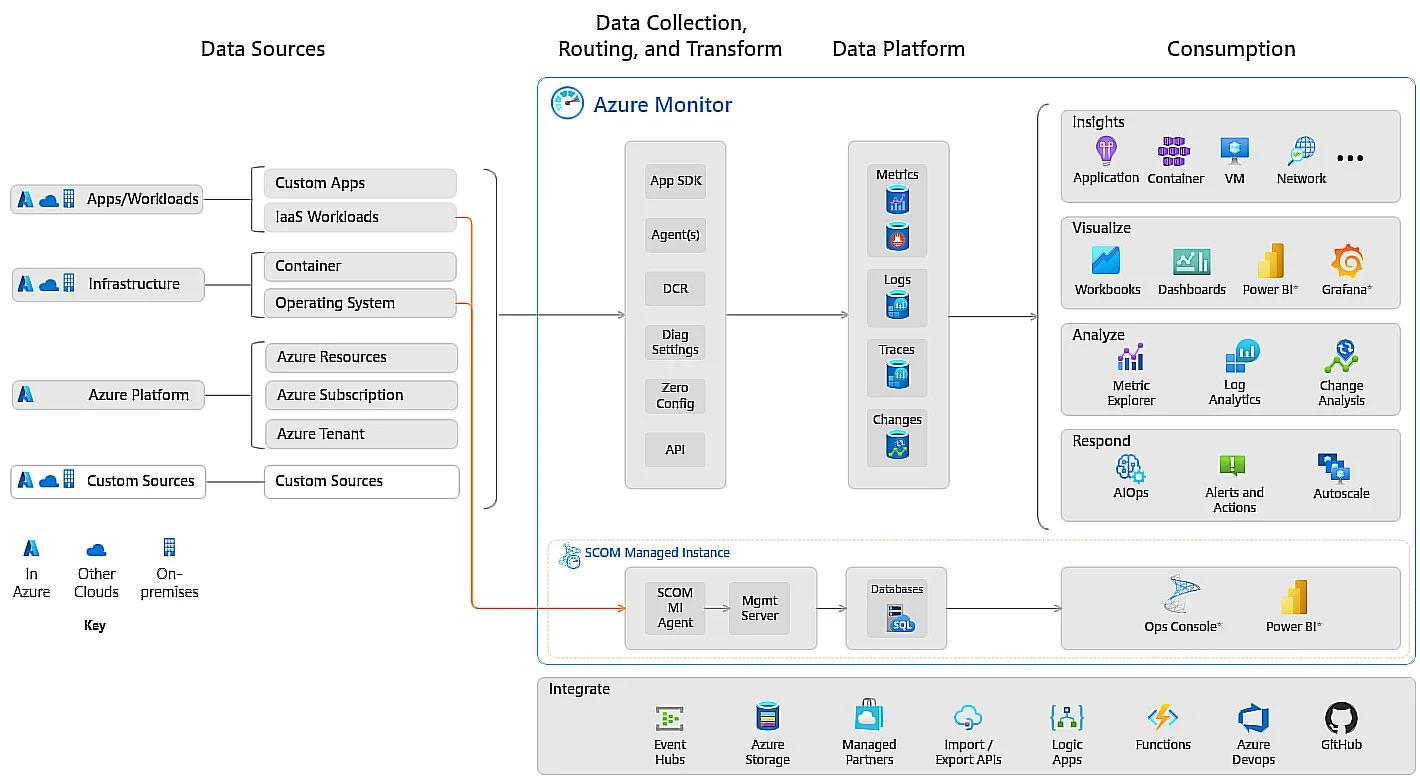
Credit: How Azure Monitor works
Azure Monitor then stores this data where other Microsoft and non-Microsoft tools can access and use it for various analytics jobs.
6. Governance
Governance in IT is the process of creating and maintaining policies, standards, and procedures to ensure that information technology (IT) assets are used and managed per your organizational goals and objectives. Governance is the responsibility of the entire organization, not just the IT department.
In Azure, governance also covers planning your cloud strategies and setting key priorities. You do that primarily through two Azure services:
- Azure Policy – This service lets you set policies, assign them to resources, and manage them. It ensures that those resources meet your corporate standards, such as:
- Deploying resources only to allowed Azure Regions
- Maintaining consistency in the use of taxonomic tags
- Requiring your Azure resources to submit diagnostic logs to a Log Analytics workspace
- Azure Cost Management – Also known as Microsoft Cost Management and Billing, the service helps you track your cloud usage and spending for your Azure and non-Azure resources. You can use it to:
- Analyze and report on costs via the Azure portal, the admin center of Microsoft 365, or externally (by exporting your cost data).
- Proactively monitor costs using budget, anomaly, and scheduled alerts.
- Use cost allocation rules to split your shared costs in Azure.
- Create and organize your Azure subscriptions, enabling you to customize invoices.
- Set up payment options and quickly pay invoices.
- Update your Azure billing information, including legal entity, agreements, and tax information.
That’s about it. Keeping a close eye on these six Azure cloud management areas will help you maintain effective control over your Azure cloud environment.
How To Control Your Azure Cloud Costs The Better Way
Now, you can track your cloud usage and associated costs with native tools such as Azure Cost Management. Yet, most native tools only provide totals and averages — not the specifics you need to identify your per-unit costs in real-time.
Without per-unit costs, it can be difficult to track who, what, or why your costs change. You may struggle to tell exactly what areas to cut to reduce your Azure costs or where to invest more to maximize returns.
CloudZero changes that.
Using CloudZero, you can track your Azure cloud costs for specific people, products, and processes. Picture this:
You can, for example, use CloudZero to:
- Get both a summary and a detailed view of your Azure costs per customer, feature, project, team, and more dimensions (up to 12 dimensions by default + custom metrics).
- Keep track of costs hourly to prevent surprises (most cost tools send reports just once every 24 hours).
- Accurately track the costs of your tagged, untagged, and untaggable resources (as well as the shared resources in multi-tenant architectures)
- Allocate 100% of your Azure spend in hours regardless of how complicated your environment is. Having this cost information at your fingertips ensures you can make data-backed cost calls on demand.
- Be able to analyze Kubernetes costs both in engineering and business metrics, such as cost per pod and cost per customer.
- View and compare your Azure cloud costs alongside your AWS, GCP, Oracle, and platform costs (supports Snowflake, Kubernetes, Databricks, MongoDB, Datadog, New Relic, etc.)
Drift has saved over $4 million using CloudZero. Many CloudZero customers – including Remitly, MalwareBytes, NinjaCat, and ResponseTap – now save 6-10 hours a week managing cloud costs. You can, too.
 to see firsthand how CloudZero isn’t a typical Azure cloud cost optimization platform.
to see firsthand how CloudZero isn’t a typical Azure cloud cost optimization platform.