AWS and Azure are considered rivals in the cloud computing industry. Both offer similar services, including cloud storage, computing, container services, databases, and more.
Yet, they have different strengths and weaknesses, which makes them competitors.
Here’s a closer look at AWS vs. Azure to help you find the ideal match.
What Is AWS?
With over 200 services and 102 availability zones across 32 geographic regions, Amazon Web Services (AWS) is one of the top cloud providers globally.
It is best known for its Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) offerings, which include virtual machines, storage, and databases. Three of its primary services support these: Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Simple Storage Service (S3), and Relational Database Service (RDS).
AWS also supports a variety of infrastructure models, including on-premises, private cloud, hybrid cloud, multi-cloud, and more.
Related Reads:
What Is Azure?

Like AWS, Microsoft Azure offers 200 services delivered across IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and edge computing.
However, with 163 availability zones in 79 regions, Azure exceeds AWS in availability zones. It is also recognized as a leader in hybrid cloud solutions and enterprise services.
Related Reads:
AWS Vs. Azure: Market Share Comparison
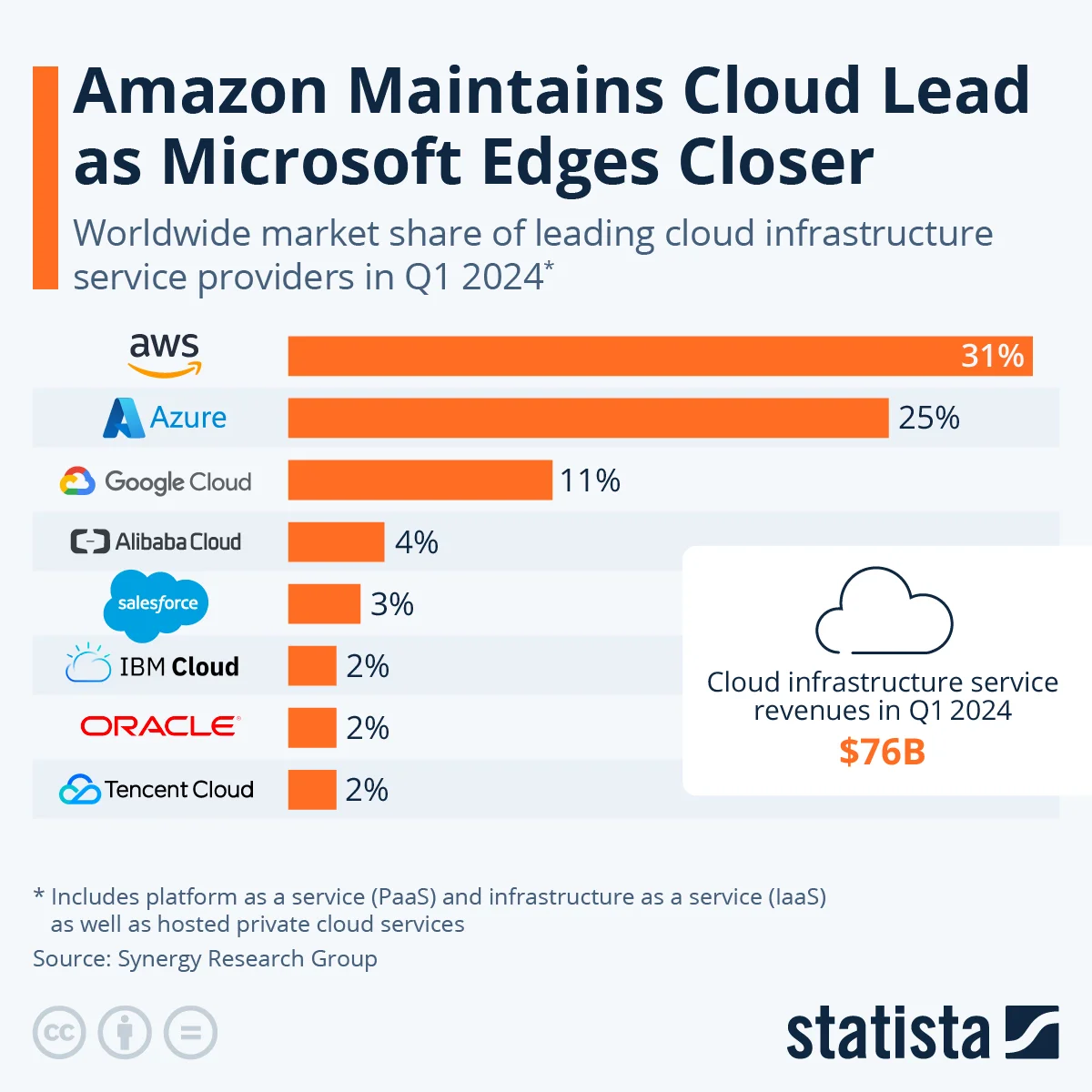
AWS and Azure remain the top players in the cloud infrastructure market. As of Q1 2024, AWS generated $25 billion in revenue, putting it on an annualized run rate of $100 billion. Azure reached $26.7 billion in revenue for the same period, translating to an annual run rate of $107 billion.
Together, they control over 55% of the global cloud services market, with AWS holding 31% and Azure close behind at 24%.
Future projections
Global cloud spending is expected to exceed $1 trillion by 2028. This will be driven by the need for AI, cloud-native architectures, and scalable infrastructure.
Both AWS and Azure will maintain their leadership. But Azure is projected to experience more aggressive growth, driven by its robust enterprise adoption and the expansion of Microsoft’s Intelligent Cloud business.
Key Factors To Consider When Choosing Between AWS And Azure
The choice between AWS and Azure is entirely based on your organizational needs.
- Integration with existing tools. Azure’s integration with Active Directory and other Microsoft products makes it a preferred choice for enterprises that use Microsoft products. AWS, however, is more platform-agnostic and integrates well with a wide range of third-party tools and services.
- Hybrid cloud solutions. Azure leads in hybrid cloud capabilities. With services like Azure Stack, businesses can extend their on-premises infrastructure to the cloud, maintaining flexibility between private and public clouds. AWS has Outposts, but Azure’s hybrid capabilities are often seen as more mature and comprehensive.
- Pricing model. AWS and Azure both use pay-as-you-go pricing, with additional savings for long-term commitments. However, due to its broader range of services, AWS’s pricing can be more complex. Azure tends to offer more straightforward pricing, especially for Windows-based workloads.
- AI and Machine Learning. Both platforms offer robust AI services. AWS’s SageMaker, however, stands out for building, training, and deploying machine learning models. Azure’s AI Bot Service and Azure Machine Learning are ideal for enterprises focused on Microsoft-centric AI solutions.
- Networking and security. AWS offers more networking features, such as VPC and Direct Connect. It is best suited for organizations that require low-latency performance across different regions. Azure provides network services like ExpressRoute, but AWS generally offers more robust networking capabilities.
AWS vs. Azure quick comparison
Here is a snapshot comparison of AWS and Azure.
Criteria | AWS | Azure |
Number of data centers (regions) | 32 regions, 102 availability | 44 regions, 163 availability |
Number of services provided | Over 200 services | Over 200 services |
Pricing model | Pay-as-you-go, Savings Plans | Pay-as-you-go, Reserved Instances |
Storage service | S3, EBS, Glacier | Blob Storage, Azure |
Database services | Aurora, RDS, DynamoDB | Cosmos DB, SQL Database |
Developer tools | AWS CodePipeline, CodeDeploy | Azure DevOps, GitHub |
Hybrid cloud support | AWS Outposts | Azure Arc, Azure Stack |
Monitoring services | CloudWatch | Azure Monitor |
AI functionality | Amazon SageMaker | Azure Machine Learning |
Compute services | EC2, Lambda | Virtual Machines, Functions |
Integrations | Extensive third-party integrations | Deep integration with the Microsoft ecosystem |
Migration services | AWS Migration Hub | Azure Migrate |
Azure Vs. AWS: Computation Power Compared
Compute powers the processing and running of applications and workloads in the cloud.
Both AWS and Azure offer a range of compute options, but there are differences in their approaches.
Compute service | AWS | Azure |
Virtual Machines | Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) with customizable instances supporting Linux, Windows, macOS | Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) excel with integration for Windows-based environments |
Serverless computing, also known as Function as a Service (FaaS) | AWS Lambda automatically scales based on workload and runs code without provisioning servers | Azure Functions, similar to Lambda, with deeper integration with Event Grid and Logic Apps |
Containers | AWS ECS, EKS for managing containerized applications | Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) for orchestrating containers |
Edge computing | AWS Wavelength, integrated with 5G | Azure Stack Edge for running compute functions closer to data sources |
High-performance computing (HPC) | EC2 P4d instances optimized for ML and AI workloads | HBv3 VMs with InfiniBand for HPC workloads in industries like financial services |
Bare metal servers | AWS Bare Metal Instances for direct access to physical servers | Azure Bare Metal Servers for high-performance workloads |
Related Reads:
Cloud Storage Options For AWS And Azure
Storage is the second most in-demand service after compute in cloud computing. A significant portion of cloud providers’ revenue comes from storage. This is due to the increasing use of data, especially for backups, data lakes, and analytics.
AWS and Azure offer various cloud storage options, from object, block, and file to archival.
Object storage
Object storage is ideal for storing large amounts of unstructured data such as images, videos, and backups.
Amazon S3 is one of the most popular AWS services, known for its durability, scalability, and flexibility. It offers different storage classes for archiving, such as Standard, Infrequent Access, and Glacier, helping users manage costs based on how often data is accessed.
Azure Blob Storage provides similar tiers — Hot, Cool, and Archive — enabling users to adjust costs based on data access frequency.
AWS S3 has, however, been around longer and is considered more mature and feature-rich.
Block storage
Block storage is used for mission-critical applications such as databases and virtual machines. Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) provides persistent block storage for EC2 instances. It is known for its high-performance SSD-backed options for demanding applications.
Azure Managed Disks are the main block storage options for Azure VMs. For performance requirements, Azure also provides Standard HDD, Premium SSD, and Ultra Disk options.
Both EBS and Azure Managed Disks support scalability and resilience. However, Azure’s Ultra Disks offer more granular control over IOPS and throughput.
File storage
File storage organizes data in a hierarchical system using files and folders. It is ideal for unstructured data that need shared or direct access.
Amazon Elastic File System ( EFS) is a fully managed, scalable service that supports scalable file storage for shared file systems and Linux-based workloads.
Azure Files supports both Linux and Windows workloads. It also offers Azure File Sync, which enables users to synchronize their on-premises data with Azure storage for hybrid cloud environments.
Archival storage
AWS offers Amazon Glacier and Glacier Deep Archive for long-term archival, both low-cost options for infrequently accessed data. Azure Archive Storage provides similar low-cost solutions for large volumes of inactive data.
AWS Vs. Azure For Databases
Both AWS and Azure offer a robust selection of databases for every type of application.
Relational databases
Relational databases are critical for applications that need structured data with defined relationships. Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) supports multiple database engines, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, SQL Server, and Amazon Aurora.
Azure’s equivalent is Azure SQL Database, a fully managed relational database service based on SQL Server. It integrates with other Microsoft services and provides smooth scaling, automatic backups, and high availability.
Note: Azure also offers Azure Database for MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MariaDB, which are ideal for multi-model and cloud-native database applications.
NoSQL databases
NoSQL databases are essential for handling unstructured data or high-performance applications.
Amazon DynamoDB is known for its low latency and scalability and is commonly used for web applications, gaming, and IoT workloads. It also supports both document and key-value data models, offering developers flexibility.
Azure counters with Azure Cosmos DB, a globally distributed, multi-model database service. Cosmos DB supports key-value, document, graph, and column-family data models. Its low-latency performance and global distribution are crucial for applications that demand data availability across multiple regions.
In-memory databases
In-memory databases are crucial for use cases requiring extremely low-latency access to data.
Amazon ElastiCache supports Redis and Memcached, which are ideal for caching, real-time analytics, and gaming leaderboard applications.
Azure Cache for Redis helps accelerate applications by offering high throughput and low latency. Like ElastiCache, it is also popular in web apps and real-time analytics.
Data warehousing
Databases serve as the foundational storage systems that supply data to data warehouses.
AWS provides Amazon Redshift, which is highly scalable and can handle petabytes of structured and semi-structured data, ideal for big data analytics.
Azure’s answer is Azure Synapse Analytics (formerly SQL Data Warehouse). It also supports massive-scale analytics and integrates tightly with Power BI for reporting.
Both support hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Redshift leverages AWS Outposts for hybrid, but multi-cloud relies on third-party tools. Azure Synapse, with Azure Arc, offers more seamless multi-cloud management across platforms.
Here’s a breakdown of Redshift pricing to help you understand the costs.
Other databases include time-series databases, with AWS Timestream and Azure Data Explorer offering fast, scalable options for time-stamped data. For graph databases, AWS provides Amazon Neptune, while Azure Cosmos DB supports graph models via the Gremlin API.
AWS Vs. Azure: Customer Support And Documentation
Both services feature multiple tiers of customer support to cater to different business needs.
AWS offers four support plans: Basic, Developer, Business, and Enterprise. The Basic plan includes community forum access and limited support. The Enterprise plan provides 24/7 support, a dedicated account manager, and priority response times, ideal for critical workloads.
Similarly, Azure offers Basic, Developer, Standard, and Professional Direct plans. Professional Direct provides 24/7 support, faster response times, and a dedicated Azure team.
Documentation quality
AWS offers detailed documentation, including guides, tutorials, and troubleshooting for every service. Users can find answers quickly through the AWS Knowledge Center and Forums. The Support API also automates case management.
Azure’s documentation is also well structured. Azure Docs offers integration instructions for Windows Server, SQL Server, and Power BI tools.
Community and learning resources
AWS has a large community, including AWS User Groups, a dedicated subreddit, and courses on platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning. AWS also provides certifications to help professionals upskill in cloud services.
Azure’s community is expanding, with resources like Microsoft Learn, Azure Fridays, and forums like Stack Overflow. Azure also offers certifications such as Azure Fundamentals and Azure Administrator Associate.
Understand, Control, And Optimize AWS And Azure Costs With CloudZero
As you’ve seen, AWS and Azure offer similar services. However, they also face a common challenge — cost management.
You may use AWS, Azure, or both and rely on traditional cost management tools to monitor your spending. Yet, surprise bills still catch you off guard, disrupting your organization’s financial plans and strategy.
Enter CloudZero, the only cost intelligence platform that contextualizes your spending across AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes, Snowflake, and more. The platform helps align teams around critical metrics such as cost per feature, product, and customer. This granular visibility is necessary for improving unit economics.
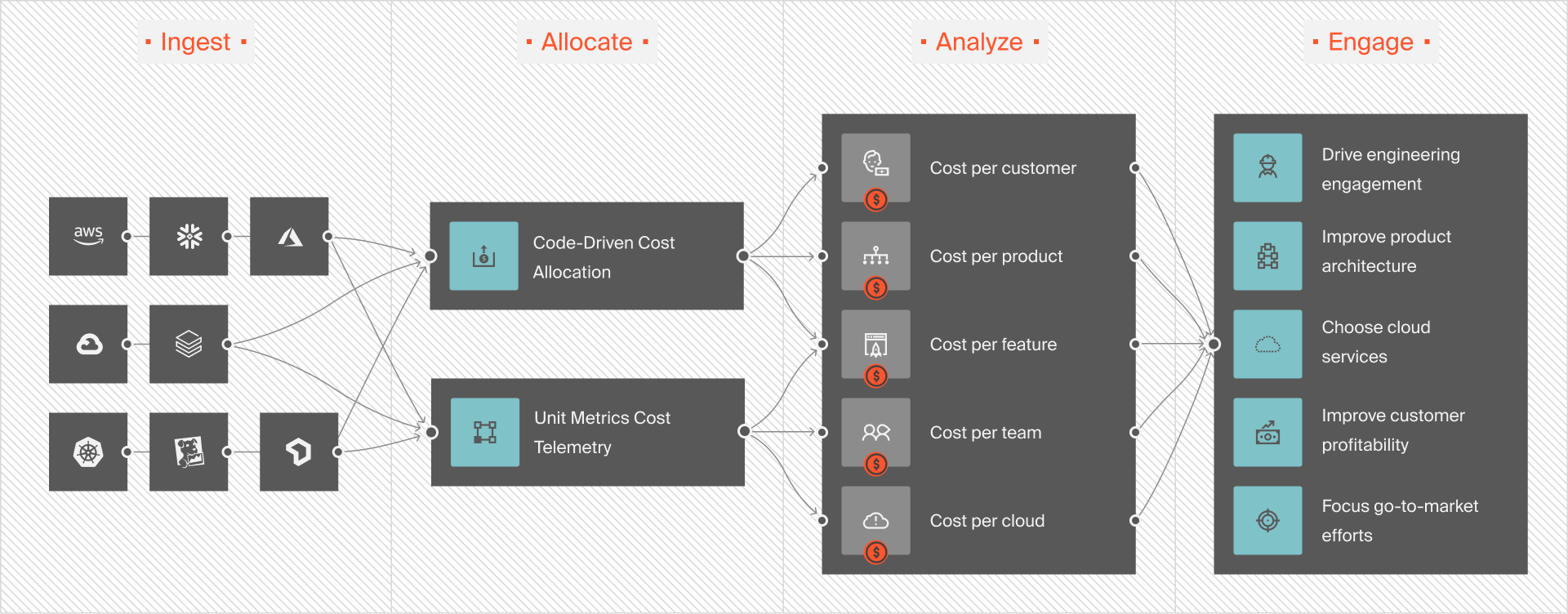
CloudZero’s Cost per Customer feature allows you to identify your most profitable customers. This insight helps your organization customize its services and focus its marketing efforts on the customers who bring the most value.
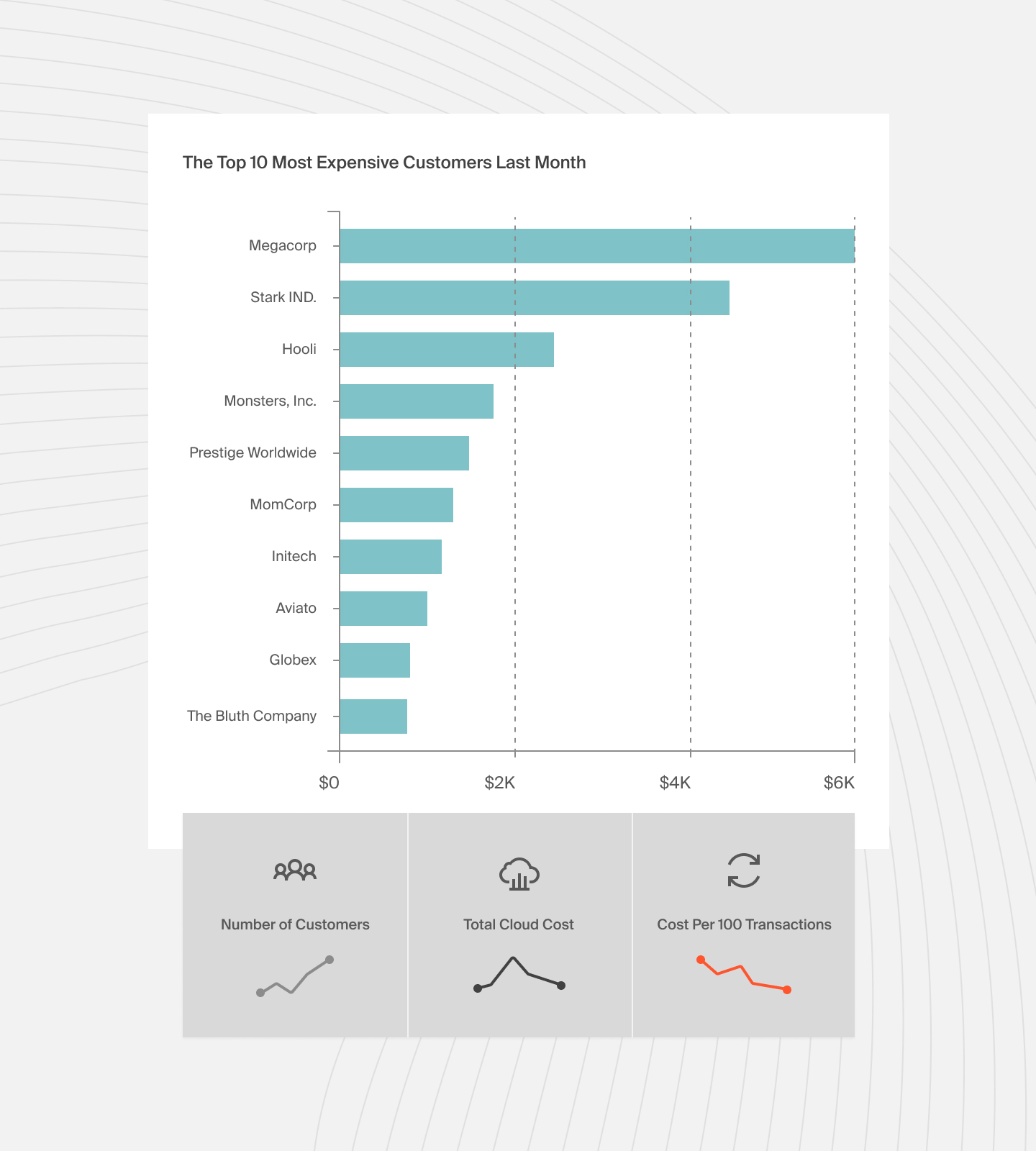
CloudZero also provides hourly cost insights, unlike most platforms that update only after 24 hours or weekly.
With CloudZero, you can:
- Get precise insights into your Kubernetes spending
- Receive real-time alerts for unusual spending
- Integrate spending data from different cloud providers
- Optimize your resource usage for greater cost savings
- Allocate costs based on actual code usage for better accuracy
- Set and manage budgets with real-time tracking capabilities using CloudZero Budget
- Forecast future spending trends to improve financial planning
- Identify and capitalize on areas for cost reduction
Reading about CloudZero is nothing like seeing it in action.  , or head to our customer page and discover how CloudZero is helping companies save millions of dollars on cloud costs.
, or head to our customer page and discover how CloudZero is helping companies save millions of dollars on cloud costs.
AWS Vs. Azure FAQs
What is the difference between AWS and Azure?
AWS is the market leader with over 200 fully-featured services covering compute, storage, and networking. Microsoft Azure also offers over 200 services and is robust in the hybrid cloud.
Which cloud provider has more data centers?
Azure has more global regions, with over 79 regions and 163 availability zones, while AWS has 32 regions and 102 availability zones.
Which is better for hybrid cloud?
Azure is often considered the best for hybrid cloud, thanks to its Azure Stack and Azure Arc. Both services support integration between on-premises infrastructure and the cloud. AWS has Outposts, but Azure leads in this area.
Which is more cost-effective, AWS or Azure?
AWS and Azure both use pay-as-you-go pricing, but Azure is often seen as more cost-effective for Windows-based workloads.
What are the most common uses for AWS and Azure?
AWS is widely used for large-scale enterprise applications, machine learning (via SageMaker), and e-commerce. Azure is popular for businesses using Microsoft products and hybrid cloud environments.
Which is better for AI and machine learning?
Both AWS and Azure offer AI tools. AWS has SageMaker for building and deploying machine learning models. Azure’s AI services and Azure Machine Learning provide many AI solutions.
Is it possible to switch between AWS and Azure?
Yes, cloud migration tools, including AWS Migration Hub and Azure Migrate, facilitate migrations between AWS and Azure.