AWS is the most popular cloud service provider partly due to its global data center network. The distribution enables organizations to configure their workloads to meet the needs of their global clients.
The thing is AWS Regions charge different rates for almost everything, from compute and storage to data backup and retrieval services. And these cost variances can add up quickly.
To help you prevent surprise costs from multi-region deployments, here’s your guide to how AWS Regions affect your cloud bill.
What Are AWS Regions?
AWS Regions are distinct geographical areas Amazon Web Services (AWS) uses to host data centers globally. Each AWS Region lets you, an AWS customer, deploy applications and data in locations that meet your specific needs, including compliance and regulatory requirements.
Each Region is isolated to ensure data sovereignty, making it easier for organizations to comply with local data protection laws. Picture this:
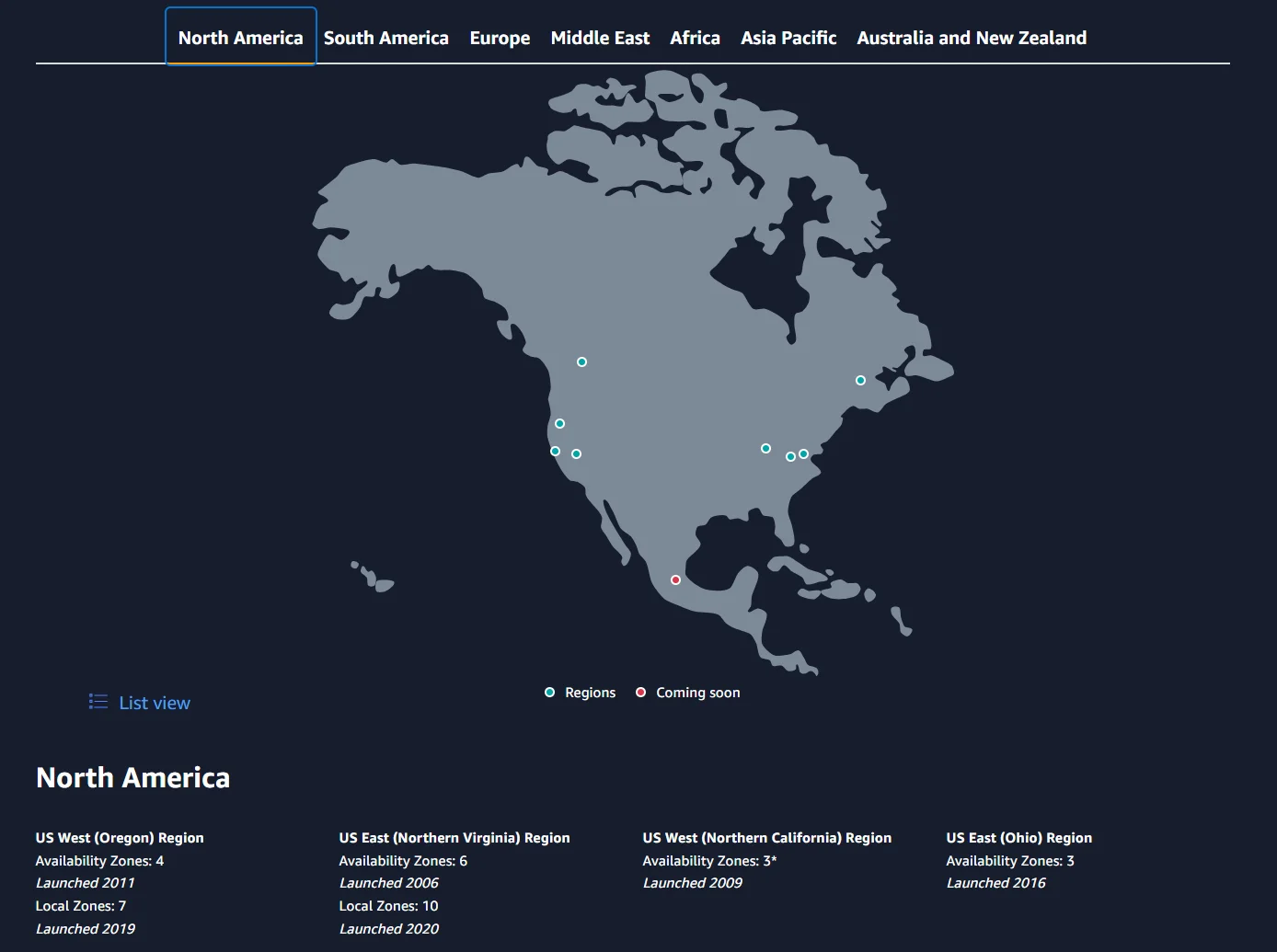
Image: There are currently eight AWS Regions in North America. Also, notice the naming and details of the four example Regions in this image.
AWS’s global infrastructure covers 245 countries and offers 33 Regions, with more in the works. This layout is meant to support flexibility, scalability, and resilience. The Regions are strategically located around the world to provide diverse customers with a range of options for hosting and accessing applications.
For CFOs, the global reach of AWS Regions enables cost optimization by deploying data and applications close to users. This can reduce latency and data transfer costs.
CTOs and software engineers benefit from the architectural flexibility to design robust, high-performing applications that leverage multiple AZs for redundancy and failover capabilities. And this is great for ensuring continuous service availability.
For more information on specific AWS regions, see our AWS data centers guide here.
AWS Regions Vs. AWS Availability Zones Vs. Local Zones
Each AWS Region comprises multiple isolated locations known as Availability Zones (AZs). For example, the US East (Northern Virginia) Region comprises six Availability Zones. AWS currently offers 105 Availability Zones worldwide, with more to come.
These AZs operate independently. However, the AZs can be interconnected within a Region to provide high availability, fault tolerance, and low-latency networking.
Availability Zones are separated by a significant physical distance to mitigate risks from natural disasters, power outages, and other disruptions. This design is meant to improve service availability and reliability.
An AWS Local Zone, meanwhile, is an extension of an AWS Region that places compute, storage, databases, and other AWS services closer to large populations, industries, and IT centers. AWS Local Zones let you deploy applications that require single-digit millisecond latency to end-users in specific geographical areas.
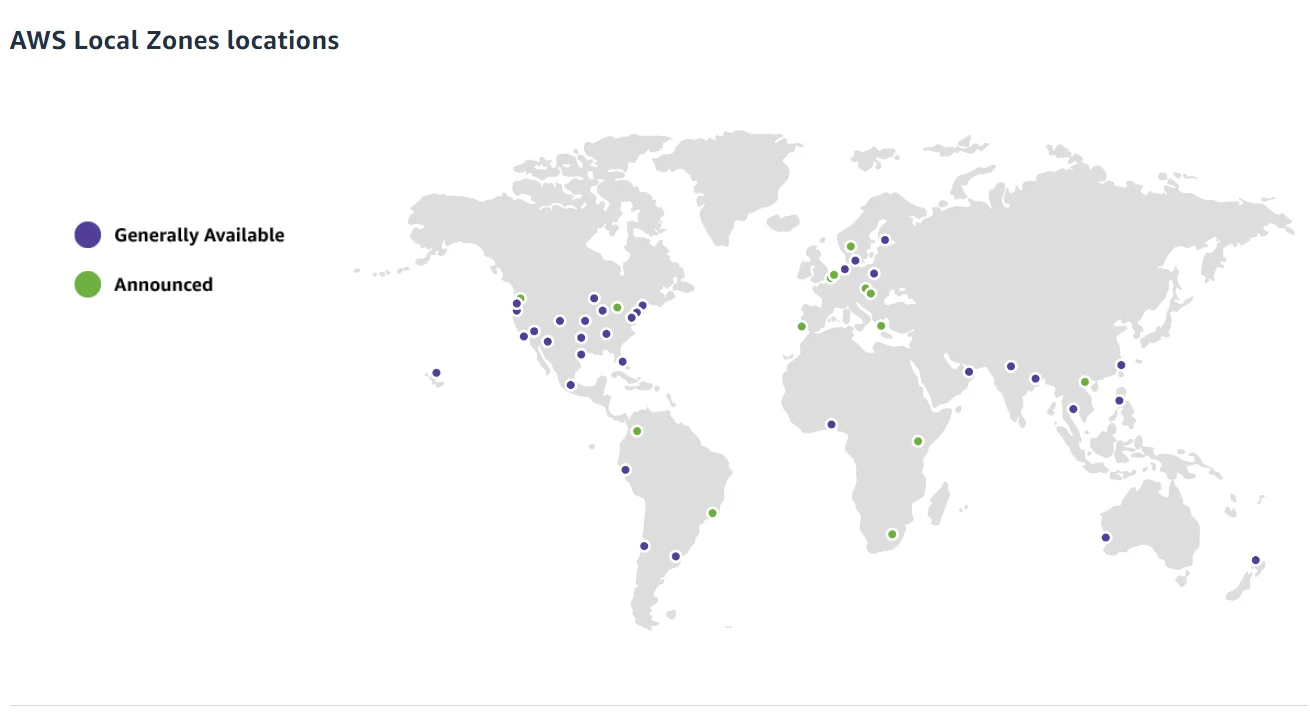
Image: Global distribution of AWS Local Zones
Each of the 41 Local Zones available offers the same AWS services, APIs, and tools available in AWS Regions. But they bring these services closer to end-users. This provides low-latency performance and local data processing.
Think of AWS Regions as entire cities.
Within each city (Region), there are several neighborhoods (Availability Zones). Each AZ has its own utilities and infrastructure to ensure that if one neighborhood faces an issue, the others remain unaffected.
AWS Local Zones are like suburbs just outside the city, providing essential services and amenities closer to specific groups of residents. This reduces travel time (latency) and improves convenience for locals.
The extensive data center distribution makes AWS the largest of the top cloud service providers today.
How Does AWS Region Availability Work?
AWS Region availability refers to the reliability and resilience of services within a specific AWS Region.
An AWS Region has multiple Availability Zones. Each AZ is an isolated data center with independent power, cooling, and networking. These AZs are strategically located to prevent simultaneous failures but close enough to offer low-latency connections for high-availability applications.
Even if one AZ experiences an issue, the others will continue to operate, minimizing downtime. This setup ensures your business achieves a higher level of fault tolerance and disaster recovery.
It’s all well thought out, but how does this affect your AWS bill?
AWS Pricing By Region: How AWS Regions Affect Costs (And How To Optimize Them)
The AWS Region influences several cost factors. The main ones are the cost of data transfer, storage, compute (instance pricing), and backups/disaster recovery. To optimize your AWS costs, you need to understand how AWS Regions affect them.
Here’s how.
1. How an AWS Region affects compute (instance) pricing
The cost of running virtual machines (AWS instances) differs between Regions based on demand, infrastructure costs, and local market conditions. This variance is especially apparent in Amazon EC2 instance pricing.
Amazon EC2 provides scalable compute capacity. The service also provides a variety of AWS instance types (CPU, RAM, storage, and networking configurations) to suit diverse needs.
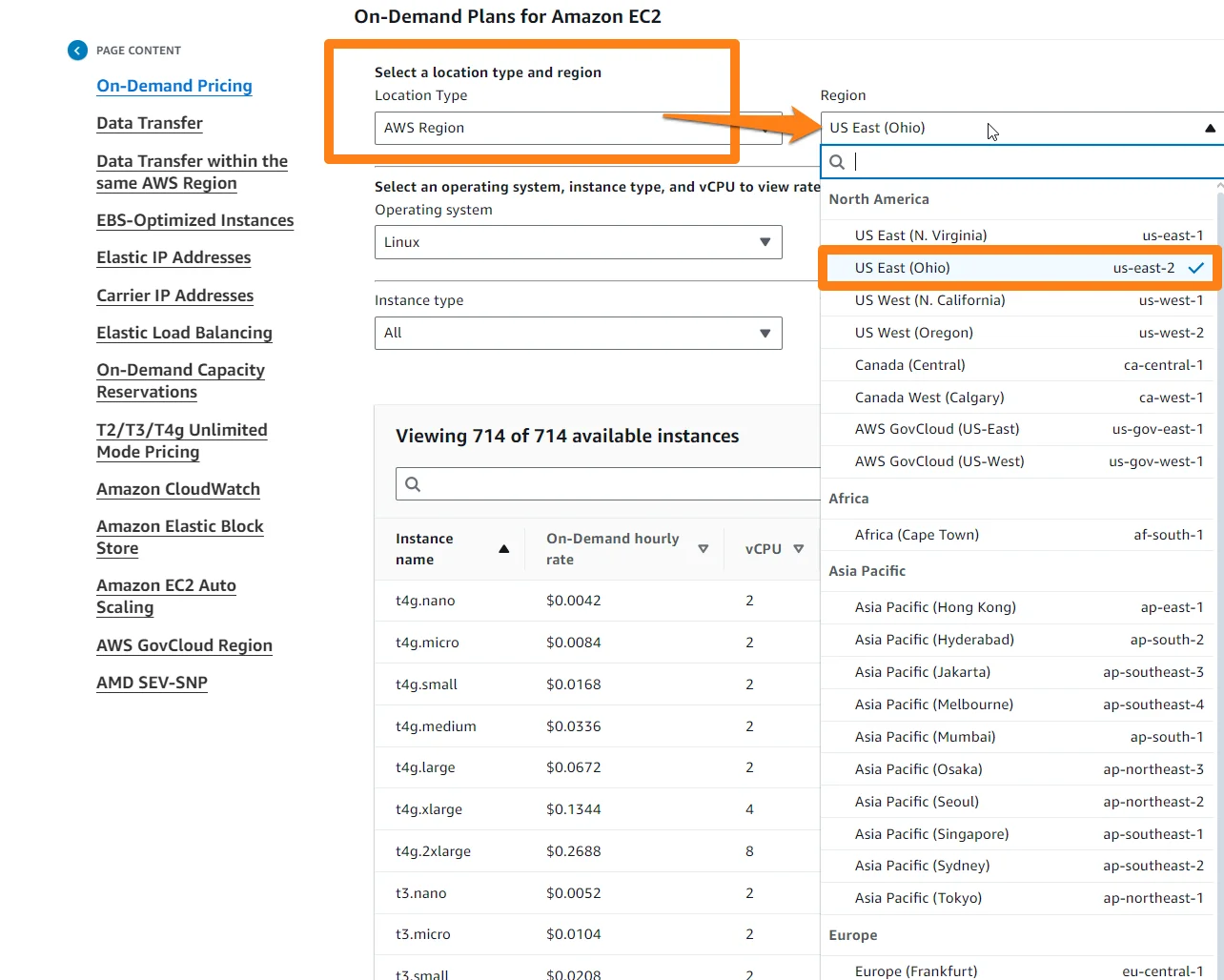
Here’s an example. In the US East (Ohio) region, a t4g.large instance with 2vCPU, 8GiB memory, and EBS-only storage costs $0.0672 per hour. An instance type of similar size in the South America (Sao Paulo) region costs $0.1072. This is due to different regional infrastructure costs and demand levels.
In fact, Ohio is still cheaper than running the same instance in the US West (North California) region, which costs $0.08/hour. For a 30-day month, if both instance configurations run eight hours a day, the Ohio region would be cheaper by $3.072 per instance per month.
Running in a Region with lower instance prices can have a significant impact on operational costs. It’s true for startups with limited resources and corporations with lots of instances.
That means choosing the right region is a crucial decision to make. That’s also because there is more to consider than instance costs.
You need to also consider networking, storage, and other infrastructure components as well. Besides, you should take into account the region’s latency, bandwidth, and other performance-related factors.
2. How an AWS Region affects data transfer charges (data egress fees)
AWS charges for data transfers between its platform and the internet (egress) and between its services such as Amazon S3 storage to Amazon EC2 instances. Data transfer costs also vary by Region and depend on the amount of data moving in and out of AWS.
Imagine a video streaming service that needs to deliver high-definition content to users worldwide. Sending this data from a Region far from the users will be more expensive due to higher data transfer fees.
Take transferring data from a server in Tokyo to users in New York, for example. It will cost more due to distance and bandwidth requirements than transferring data locally within Tokyo.
In some cases, AWS services charge to move data one way, but not the other. Meanwhile, transferring data between EC2 instances in different availability zones incurs different costs.
When transferring data within the US and Canada, it costs $0.01 per GB in each direction (transfer data in and out) of various services, including Amazon EC2, Relational Database Service (RDS), and Redshift. When the transfer is across Regions, AWS typically charges $0.02 per GB on top of egress fees (Amazon EC2 to the internet charges). It costs more if you are in other regions, such as $0.08 per GB in Asia Pacific (Seoul).
Consider this:
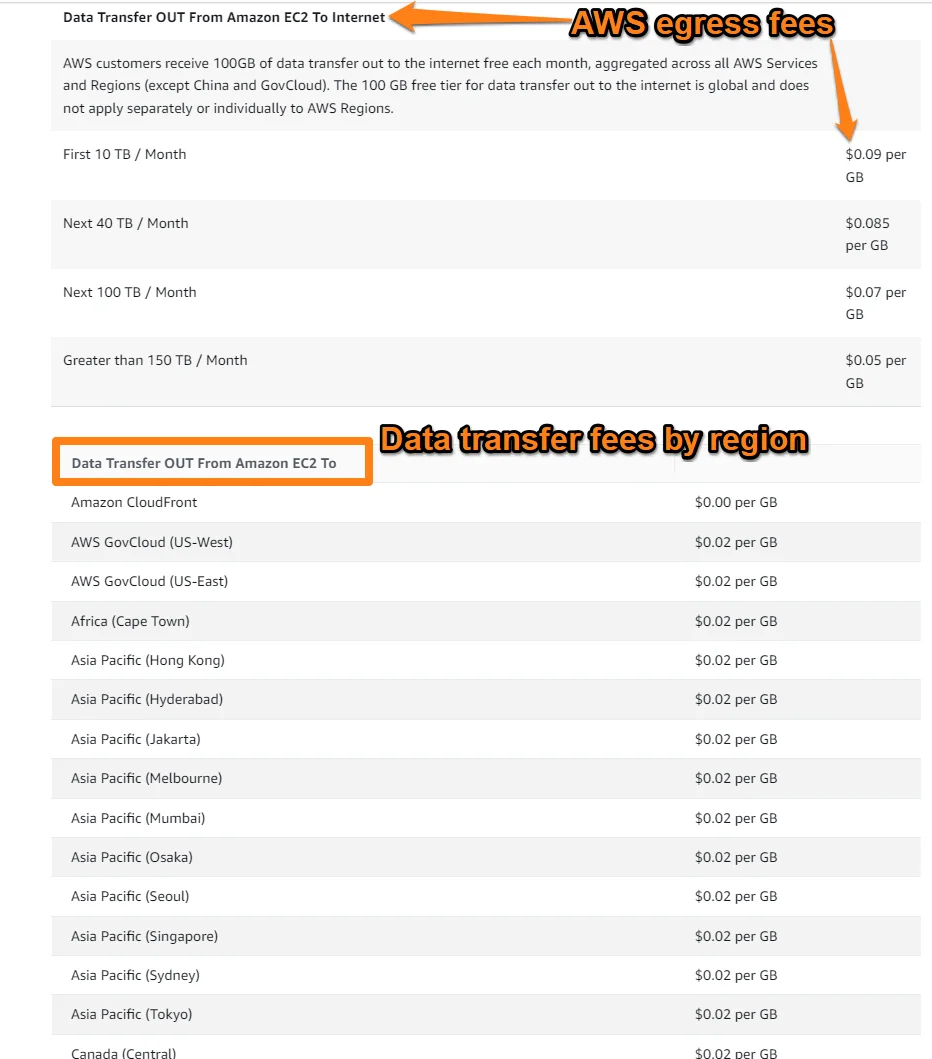
Image: Amazon EC2 pricing
Besides, running in the same region can reduce latency, which is beneficial to applications that rely heavily on real-time interactions.
We cover how AWS data transfer pricing works here. The guide includes tips to optimize your data transfer costs when using AWS across multiple regions, so check it out.
3. How an AWS Region affects data storage costs
AWS cloud storage offers different pricing for different regions across factors such as storage type and class, retrieval frequency, and provisioned throughput requirement. Check out our no-BS guide to Amazon S3 pricing here for a deeper breakdown.
Likewise, moving data between Amazon S3 instances across different Regions costs the same as Amazon EC2. For example, from a US East (Ohio) region, it costs $0.02 per GB to move data out from S3 to other regions.
But it costs $0.147 per GB if you are in Africa (Cape Town) and $0.08 in the Asia Pacific (Seoul) region.
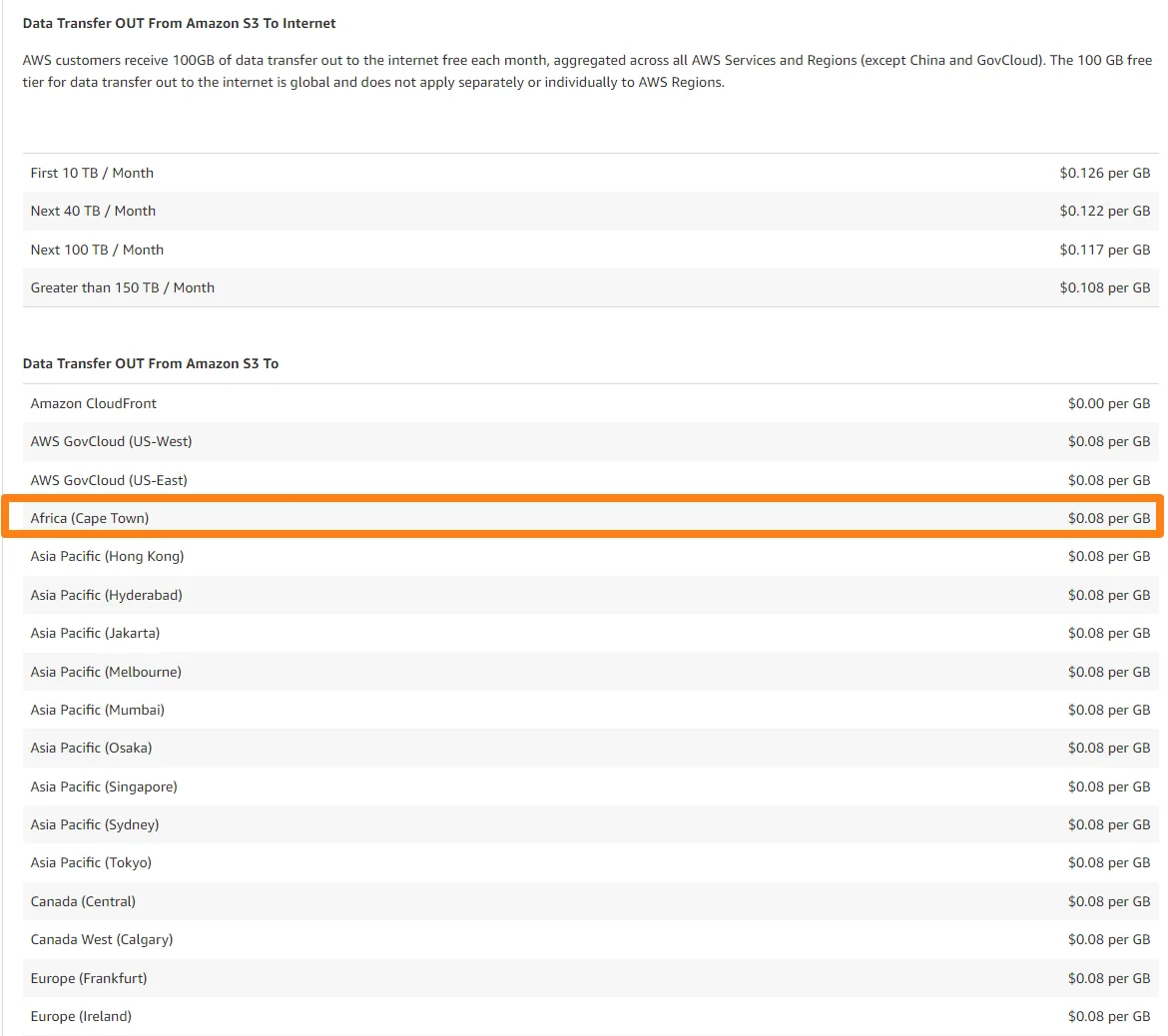
There are also other options, such as Amazon S3 multi-region access points.
Meanwhile, here’s another cost factor that closely relates to regional pricing for AWS storage.
4. How an AWS Region affects backups and disaster recovery costs
The region you are backing your data from affects how much you pay for the service. In addition, using multi-region redundancy and disaster recovery solutions can increase costs. For example, mirroring databases across multiple Regions assures you of high availability and fault tolerance. But it also doubles your storage and operational expenses.
For backups, AWS offers a variety of services. These include Amazon S3 for storing backup data, AWS Backup for managing and automating backup tasks, and Amazon RDS snapshots for database backups.
The services offer high durability and availability, replicating data across multiple Availability Zones (AZs) within a Region.
For disaster recovery (DR), strategies include multi-region deployments. It also includes services such as AWS Elastic Disaster Recovery (DRS), which replicate applications and data to a different AWS Region.
Options like S3 One Zone-Infrequent Access store data in a single Availability Zone. This reduces costs but sacrifices redundancy. Yet, choosing S3 One Zone-IA can cut redundancy costs for less critical data compared to standard multi-AZ storage.
AWS DR architectures range from simple backup and restore solutions to more complex, real-time failover systems. You can also tailor the options to suit your budget, complexity, and data size.
How To Choose The Best AWS Region For Your Needs
There are a variety of factors to consider here, from latency to GDPR. Consider the following:
1. Workload type
Different workloads have varying requirements for compute power, storage, and networking.
Some regions are better suited to specific workloads. For example, machine learning and big data analytics might benefit from regions with advanced hardware like GPU instances. Besides, these workloads are often not sensitive to network latency, so the lowest-cost region is often preferred.
In that case, the US East (Northern Virginia) Region is an example of an excellent match because it offers specialized and high-performance instance types.
2. Latency
Latency refers to the delay in data transfer between the user and the application. Lower latency improves user experience and application performance, especially critical for real-time applications.
For applications that require low latency, such as online gaming or real-time data streaming, you’ll want to choose regions with lower latency despite the cost. The rule of thumb is to avoid regions far from your user base, like choosing a European region for an Asia-focused application.
However, regions with high latency might be just right for workloads such as data processing or storage that do not require low latency.
3. Number of available services
You’ll want to ensure your preferred Region supports all required AWS services for your application. And yes, the range of AWS services available varies by region.
For example, if your application relies on a newer AWS service that is not yet available across all regions, select US West (Oregon).
If your workload relies on older services, you can pick other Regions based on other factors here.
4. Number of Availability Zones
More AZs provide better fault tolerance and higher availability. If that’s what you want, then the Northern Virginia Region offers multiple AZs for mission-critical apps requiring high availability.
For workloads that do not require high availability, deploying in a single Availability Zone within a region can be sufficient.
5. Proximity to your users
This refers to the physical distance between the AWS region and end-users. Proximity reduces latency and improves performance for your end-users, especially where streaming or real-time interactions are required.
For example, if you have a predominantly New York user base, you can choose New York for a US-based retail website to ensure fast load times. Otherwise, you can move further away for cost savings.
6. Data residency and regulatory compliance
Different regions have specific legal and regulatory requirements for data storage and processing.
Take the European regions, for example. Frankfurt would be ideal for storing and processing EU citizens’ data to comply with GDPR.
If your workload is bound by local regulations, choosing a region that complies is crucial. Otherwise, you’ll have legal issues and fines to deal with.
7. Scalability and future growth prospects
In general, regions with higher capacity and expansion plans can better support growing businesses.
For example, the US East (Ohio) may be ideal for a startup expecting rapid growth due to its vast scalability options.
Be sure to evaluate your business’s long-term scalability and growth plans.
8. AWS Region costs
As we’ve seen by now, costs for compute, storage, and data transfer can vary significantly between AWS Regions. You’ll also notice that the US East Regions are generally more affordable than other regions.
Alternatively, consider the US West (Oregon) Region for cost-effective storage solutions for large datasets. And if you can, avoid higher-cost regions if budget constraints are critical.
That said, irrespective of the AWS Region you deploy from, you’ll still need to keep an eye on your AWS costs.
How To Manage, Control, And Optimize Your AWS Cloud Costs Differently
Choosing just the right AWS Region for each workload you have can be daunting. Often, SaaS companies serve customers across multiple regions, so you’ll have to optimize for multi-region considerations continuously. This can be daunting and tough to maintain.
Additionally, in any AWS Region, you’ll run into “hidden costs” like data transfer fees that you didn’t expect. But you can avoid this. How? Monitor your AWS usage down to hourly unit costs such as Cost per Request, Cost per Daily User, and Cost per Customer.
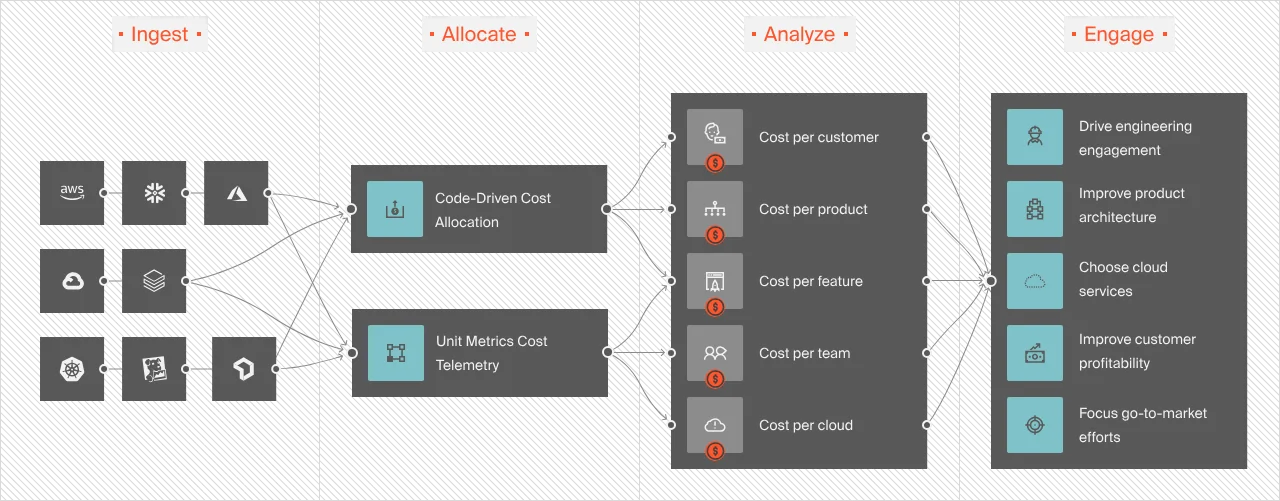
You can then tell which people, products, and processes drive your AWS spend, so you can refine them as needed to reduce costs.
You can also create alerts to detect any unexpected increases to prevent surprise AWS costs.
Moreover, you’ll also want to look out for ways to optimize the performance and cost-efficiency of your applications.
Using a robust AWS cost intelligence platform can also help you estimate your costs in advance for budgeting and forecasting. Yet most AWS cost management tools do not deliver this level of cloud cost intelligence.
And yes, CloudZero can help
With CloudZero, you can:
- Allocate 100% of your cloud costs to understand your true AWS costs in any Region, Availability Zone, or Local Zone
- Easily view and interact with your immediately actionable unit costs, including Cost per Customer, Cost per Environment, and Cost per Feature. This can help you pinpoint exactly where to optimize AWS usage to reduce costs without sacrificing performance.
- Get timely anomaly alerts right in your inbox to identify issues before they become costly problems
- Engineering-Led Optimization empowers your engineers to create cost-effective solutions from the start.
- Create, monitor, and alert on custom budgets for accurate budgeting and forecasting.
Companies like Drift, Remitly, and Shutterstock have all benefited from these and other CloudZero capabilities. Upstart just saved $20 million as well. And don’t just take our word for it. Here is your risk-free chance to see why CloudZero pays for itself in about three months.  to see CloudZero in action for yourself.
to see CloudZero in action for yourself.
AWS Regions FAQs
Which AWS Region should you choose?
Pick the right AWS Region based on your needs, from latency considerations and workload types to regulatory compliance and cost factors.
Which AWS Region is the cheapest?
In most cases, US East regions such as Ohio and Northern Virginia offer the lowest costs of any AWS Region.