In 2006, Amazon Web Services (AWS) pioneered cloud computing as we know it today. With about 34% of the market share, Amazon Web Services remains the largest cloud infrastructure provider today, followed by Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
AWS is a Cloud Service Provider (CSP). That means AWS builds, maintains, and continually improves multiple data centers worldwide and then rents the computing infrastructure to other companies over the Internet as needed.
For organizations, this is often an effective way to avoid purchasing, installing, maintaining, and upgrading their own data centers, which can be expensive and time-consuming.
In a nutshell, that’s how the cloud works — except there’s no cloud, just lots of third-party data centers and managed IT infrastructure. Here’s what we mean.
What Is A Data Center?
A data center is a physical facility that stores computing machines along with the hardware that supports their operation. This location houses the computing infrastructure IT systems need, like servers, network equipment, and data storage drives.
A modern data center is a physical location that stores your company’s digital data.
An AWS Data Center provides scalable computing power that multiple businesses can access anytime, anywhere over a network. Instead of building and maintaining their own data centers, businesses pay a monthly fee to access this global network of AWS data center infrastructure.
In essence, this is what’s referred to as the Cloud.
AWS provides over 200 services and products. Virtually all AWS data centers support multiple cloud services, including compute, storage, networking, database, enterprise applications, security, analytics, Machine Learning (ML), Artificial Intelligence (AI), mobile, developer tools, the Internet of Things (IoT), and more. In essence, these services support Cloud Computing.
How many data centers does AWS have?
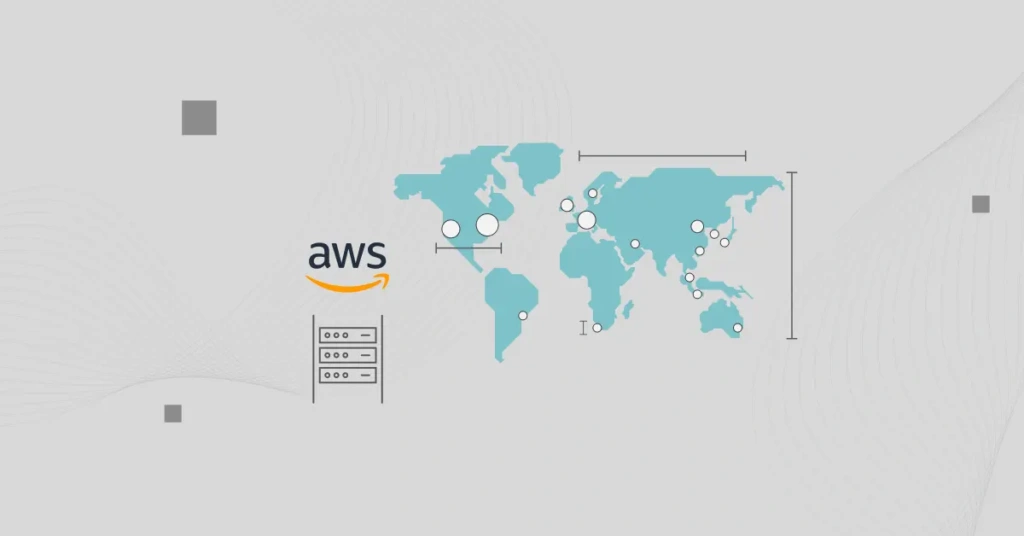
AWS has over 100 data centers worldwide, each with up to 50,000 servers. As of 2014, AWS had over 1.4 million servers in all its data centers.
AWS data centers are spread across 31 AWS Regions, 99 Availability Zones (AZ), 245 countries and territories, over 400 Edge Locations, 34 Local Zones, and 115 Direct Connect Locations. The cloud provider plans to launch another 5 Regions and 15 Availability Zones soon.
You might be wondering what AWS Regions and AZs mean.
What Is An AWS Region?
An AWS Region is a geographic area anywhere in the world where the company has a cluster of data centers. The 31 launched AWS Regions are available in all continents except Antarctica. Most AWS Regions are in North America, Europe, and Southeast Asia.
The North Virginia AWS Region was the first to launch in 2006 and comprises the most Availability Zones to date (six).
What Is An AWS Availability Zone?
An AWS Availability Zone refers to one or more physically separate data centers with independent power and cooling, yet linked logically. This design adds layers of resilience (durability, security, and reliability) to the AWS cloud infrastructure.
For example, AWS stores your data in multiple Availability Zones in the same or different AWS Regions, so it remains available even if the primary data center is affected by an outage. This is perfect for backup and disaster recovery purposes.
A single AWS Region comprises multiple autonomous and geographically distinct AZs spread across a geographic area.
What is the difference between an Availability Zone and Local Zone in AWS?
The differences between Availability Zones, Local Zones, Wavelengths, and Outposts are subtle but important.
- AWS Availability Zone – A group of logically connected but geographically separated data centers.
- AWS Local Zone – An extension of an AWS Region where you can run selected services close to your end users or on-premises installations to reduce latency.
- AWS Wavelength – Supports ultra-low-latency mobile edge computing by providing compute, storage, and networking services within 5G networks of communications service providers (CSPs).
- AWS OutPost – Delivers native AWS operating models, services, and infrastructure to virtually any on-premises facility, data center, or co-location space. Provides a consistent hybrid experience across on-premises and AWS cloud services, including APIs and tools.
- AWS Edge Location – A cluster of data centers designed to provide fast access to data from any location by keeping cache copies of that data closest to the end user. They include AWS Local Zones, Regional Edge Caches, and Edge lkocations
- AWS Regional Edge Caches – These are AWS CloudFront (the low-latency content delivery network (CDN) service) locations in close proximity to your viewers — anywhere in the world. These are positioned between your origin server and related POPs, which are the global edge locations serving content directly to your viewers.
Speaking of positioning, here are details about where AWS has data centers across the globe.
Where Are AWS Data Centers Located And Why?
AWS provides data centers in the geographic regions of North America (US and Canada), Europe (Germany, UK, France, Ireland, Sweden, Italy, Switzerland, and Spain), Asia Pacific (China, Japan, India, Indonesia, and Singapore), Middle East (Bahrain, UAE, and Israel), Africa (South Africa), South America (Brazil), and Australia/New Zealand.
There are multiple edge locations and regional edge caches at each location.
In addition, each AWS Region or AZ in any of these locations offers a different price for compute, storage, networking, and other AWS services.
For that reason, you’ll want to be attentive when deciding where to deploy your applications on the AWS cloud. For example, the US East (Ohio) Region tends to offer the lowest AWS service prices.
Here are the AWS data center locations in terms of AWS Regions and Availability Zones.
North American locations
AWS has 7 AWS Regions, 25 Availability Zones, 21 edge locations, 16 Local Zones, and 4 Regional Edge Caches in the North American continent. Each Region offers:
|
AWS Regions |
Availability Zones |
AWS Local Zones |
|
US East (Northern Virginia) Region |
6 |
10 |
|
US East (Ohio) Region |
3 |
|
|
GovCloud (US East) Region |
3 |
|
|
US West (Oregon) Region |
4 |
7 |
|
US West (Northern California) Region |
3 |
|
|
GovCloud (US West) Region |
3 |
|
|
Canada (Central) Region |
3 |
|
Europe locations
In Europe, AWS offers 8 AWS Regions, 24 Availability Zones, 30 edge locations, and 3 Regional Edge Caches:
|
AWS Regions in Europe |
Availability Zones |
|
Europe (Ireland) Region |
3 |
|
Europe (Frankurt) Region |
3 |
|
Europe (London) Region |
3 |
|
Europe (Paris) Region |
3 |
|
Europe (Stockholm) Region |
3 |
|
Europe (Zurich) Region |
3 |
|
Europe (Spain) Region |
3 |
|
Europe (Milan) Region |
3 |
Asia Pacific locations
AWS has 10 AWS Regions, 32 Availability Zones, 20 edge locations, and 4 Regional Edge Caches:
|
AWS Regions in Asia Pacific |
Availability Zones |
|
Asia Pacific (Singapore) Region |
3 |
|
Asia Pacific (Tokyo) Region |
4 |
|
Asia Pacific (Osaka) Region |
3 |
|
Asia Pacific (Hong Kong) Region |
3 |
|
Asia Pacific (Ningxia) Region |
3 |
|
Asia Pacific (Beijing) Region |
3 |
|
Asia Pacific (Hyderabad) Region |
3 |
|
Asia Pacific (Mumbai) Region |
3 |
|
Asia Pacific (Jakarta) Region |
3 |
|
Asia Pacific (Seoul) Region |
4 |
Middle East locations
In the Middle East, AWS currently provides 2 AWS Regions, 6 Availability Zones, and 4 edge locations. The edge locations are in Dubai, Tel Aviv, Manama, and Fujairah.
|
AWS Regions in The Middle East |
Availability Zones |
|
Middle East (Bahrain) Region |
3 |
|
Middle East (UAE) Region |
3 |
Australian and New Zealand locations
The cloud provider has 2 Regions, 6 Availability Zones, 5 edge Locations (including Auckland, New Zealand), and 1 Regional edge cache (Sydney) here.
|
AWS Regions in Australia and New Zealand |
Availability Zones |
|
Australia (Sydney) Region |
3 |
|
Australia (Melbourne) Region |
3 |
Africa locations
There is one AWS Region in Africa, the Africa (Cape Town) Region with 3 Availability Zones. In addition, there are 3 edge locations in Africa: two in Cape Town and Johannesburg, South Africa, and one in Nairobi, Kenya.
South American locations
The only AWS Region in South America is Brazil; the South America (Sao Paulo) Region. It offers three availability zones. Yet there are 5 edge locations across the continent in Rio de Janeiro and Sao Paulo (Brazil), Buenos Aires (Argentina), Bogota (Colombia), and Santiago (Chile).
AWS Data Center Sustainability Initiatives
AWS is committed to reducing its environmental impact through several initiatives aimed at energy efficiency and sustainability:
- Plans to power all data centers with 100% renewable energy by 2025
- Uses solar and wind farms to generate renewable power
- Invests in advanced cooling technology to lower energy consumption
- Develops water stewardship programs to minimize water usage
- Recycles electronic waste from decommissioned servers
- Partners with governments to promote sustainability
- Implements carbon-reduction strategies in its supply chain
- Supports circular economy efforts to extend the lifecycle of hardware
- Provides customers with tools to track and reduce their carbon footprints
- Innovates in energy storage to increase renewable energy use during peak demand
AWS Data Centers Vs. The Competition
When compared to Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), AWS leads in size and reach:
- AWS: With over 100 data centers across 31 regions and 99 Availability Zones, AWS is the largest cloud provider. It offers a wide range of services from computing to AI, serving a global customer base.
- Azure: Azure has 65+ regions and is popular for its integration with Microsoft products. It’s known for hybrid cloud solutions with Azure Stack, enabling businesses to extend their on-premises systems to the cloud.
- GCP: Google Cloud operates 38 regions focusing on data analytics, machine learning, and high-performance computing. It excels in AI services but has a smaller footprint than AWS and Azure.
Over To You
AWS plans to expand its data center network to support the growing demand for cloud computing as more organizations migrate to the cloud.
But here’s the thing.
AWS infrastructure costs can be difficult to track, analyze, and act on. This is especially true if workloads or applications are running in different regions, availability zones, etc. The most common culprits behind surprise AWS bills are data transfer charges and complex multi-cloud pricing.
With CloudZero’s all-in-one cloud cost platform, you won’t have to worry
CloudZero enables you to view, understand, and control cloud costs with precision. Unlike any other tool, CloudZero provides granular, context-rich, and instantly actionable cost intelligence. This includes costs per customer, project, feature, team, environment, and more.
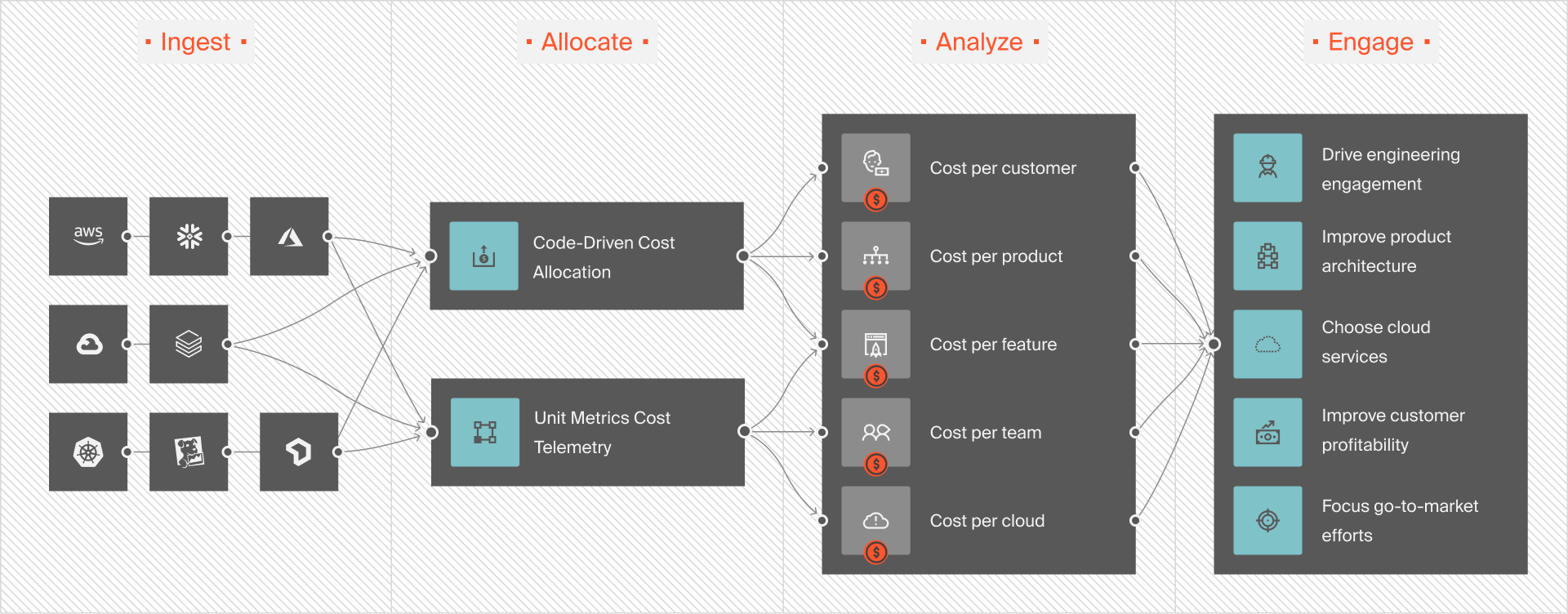
CloudZero also enables you to analyze and control your AWS, Azure, and GCP costs alongside your Kubernetes, Snowflake, Databricks, Datadog, MongoDB, and New Relic costs. It’s truly a single pane of glass for all your cloud costs, complete with 100% cost allocation, shared cost visibility, and even real-time cost anomaly detection and alerting.
Click here to take a tour of CloudZero or  to experience CloudZero for yourself (and see how companies like Drift are saving $2.4 million in annual AWS spend, so you can too).
to experience CloudZero for yourself (and see how companies like Drift are saving $2.4 million in annual AWS spend, so you can too).
AWS Data Center FAQs
Who builds AWS data centers?
AWS data centers are built and maintained by Amazon Web Services (AWS). AWS designs, constructs, and operates these data centers, ensuring security, performance, and scalability.
How many data centers does AWS have today, and where are they located?
AWS has over 100 data centers globally, covering 31 AWS Regions, 99 Availability Zones, over 400 edge locations/local zones, and 245 countries and territories. AWS provides data centers in North America (US and Canada), Europe (Germany, UK, France, Ireland, Sweden, Italy, Switzerland, and Spain), Asia Pacific (China, Japan, India, Indonesia, and Singapore), Middle East (Bahrain, UAE, and Israel), Africa (South Africa), South America (Brazil), and Australia/New Zealand.
How many Availability Zones does AWS offer?
AWS currently has 99 Availability Zones with plans to launch more.
How many data centers are in an AWS Availability Zone?
An AWS Availability Zone consists of one or more data centers that are physically separated but logically connected. The number of data centers per Availability Zone varies but typically includes multiple facilities to ensure redundancy and resilience.
How many servers does AWS have?
As of 2014, AWS had over 1.4 million servers across its data centers. Each data center could comprise up to 50,000 servers.
What are AWS Edge locations?
AWS Edge locations are data centers that cache content closer to end users, enabling faster data delivery. These locations support services like AWS CloudFront, providing low-latency access to data across the globe.
What is the difference between a data center and the cloud?
The cloud is a distributed network of remote servers accessible on an as-needed basis over the Internet, while a data center is a centralized physical location for storing, processing, and distributing data.
Also, while owning a data center requires you to manage your own infrastructure, the cloud service provider manages the infrastructure on your behalf in the cloud.