In June 2024, Amazon hit an astounding $2 trillion valuation, joining the elite ranks of companies like Alphabet, Apple, Microsoft, and Nvidia. This growth was largely driven by the success of its cloud computing division, Amazon Web Services (AWS), which holds one-third of the global cloud market share. That equals the combined market share of Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud!
But who are AWS’s biggest contributors to this success? With 2.38 million organizations relying on AWS, the list includes industry giants and innovative startups.
In this post, we explore some of the leading enterprises leveraging AWS. We will also help you understand how to manage and optimize AWS spending with a cost intelligence approach. After all, you don’t want to overspend on making AWS richer while you just, well, spend.
But first, where did it all start?
The Growth Of AWS To This Point
Amazon introduced AWS in 2006 to enable businesses to access on-demand computing power, storage, and other IT resources through the Internet. Its first services were AWS Simple Storage Service (S3) and EC2, which provide storage and compute power, respectively.
As demand for cloud services grew, AWS rapidly expanded its portfolio and now offers over 200 services.
Global regions and availability zones
AWS operates in 32 global regions and has over 102 availability zones. Each AWS region consists of at least two or more availability zones. These zones are isolated data centers with independent power, networking, and cooling. They ensure redundancy fault tolerance and improve availability.
Geographical spread
AWS operates across six continents with data centers strategically placed to serve a global customer base. In North America, AWS has regions in the U.S. and Canada. South America is served through São Paulo, Brazil. In Europe, AWS has regions in countries like Germany and Ireland. Africa is covered by a region in Cape Town, South Africa.
AWS also serves Asia-Pacific with data centers in Australia, Japan, and Singapore. It also has an expanding presence in the Middle East.
Total servers and compute power
AWS’s infrastructure comprises over 1.5 million servers across its data centers. Its compute power is immense, spanning hundreds of thousands of instances globally. With custom Graviton processors, GPU options for AI, and scalable infrastructure, AWS supports varied workloads — from everyday applications to high-performance computing. Its flexibility, advanced silicon, and regional spread enable rapid scaling for intensive tasks such as machine learning and large data processing.
Now, let’s look at the global leaders who trust AWS with their operations.
Top AWS Customers
Here are businesses driving AWS’s success.
Netflix
With over 269 million paid subscribers worldwide and an annual revenue of $36.3 billion as of 2024, Netflix remains the most successful streaming platform. It’s no surprise that it’s also AWS’s highest spender. Estimates suggest that the company spends hundreds of millions annually on AWS services.
What AWS services does Netflix pay for?
Netflix uses various AWS services to support its streaming operation and deliver smooth, high-quality experiences for viewers. Amazon EC2 provides the computing power behind Netflix’s essential operations. These include video processing, recommendation algorithms, and handling high traffic volumes.
Amazon S3 serves as Netflix’s main storage for its extensive media library. It ensures global accessibility and secure storage of content. Beyond S3, Netflix also uses Open Connect, a custom CDN that caches popular shows locally for faster streaming. For infrequent content, Netflix turns to Amazon Glacier for cost savings.
Amazon Kinesis processes real-time data to improve user experience. It helps Netflix personalize recommendations and optimize its platform’s performance.
Netflix also relies on AWS Lambda for serverless functions to manage backend tasks. It also leverages Amazon CloudFront to reduce streaming delays by serving content from locations.
Here is a comprehensive guide on how much Netflix spends on AWS and how it monitors and measures AWS costs.
Twitch
Amazon’s live-streaming platform, Twitch, follows Netflix as a top AWS spender. With around 31 million daily users and millions of paid subscribers, Twitch relies on AWS’s scalability to handle real-time streaming demands. It is also estimated to spend millions on AWS services.
AWS services utilized by Twitch include:
- Amazon EC2: Provides scalable compute power to manage global live streams smoothly.
- AWS Lambda: Supports serverless functions, which are essential for handling real-time interactions during streams.
- Amazon IVS (Interactive Video Service): Utilizes Twitch’s video infrastructure for low-latency, interactive video streaming.
- Amazon CloudFront: Ensures low latency and reliable content delivery.
LinkedIn is also a prominent AWS client, spending around $13 million monthly on AWS infrastructure. This substantial investment supports LinkedIn’s high-volume networking, job postings, and content-sharing needs, as the platform manages millions of user interactions daily.
LinkedIn utilizes EC2 for scalable compute resources and AWS S3 for secure data storage. It also relies on Amazon RDS for database management, AWS Lambda for serverless automation, and AWS CloudFront for efficient content delivery.
How other big names use AWS:
- Meta leverages AWS for AI research, PyTorch optimization, and third-party integrations. Platforms like Instagram also use AWS infrastructure.
- Turner Broadcasting uses AWS for streaming content and real-time data analytics, which is critical for sports and news delivery.
- X (Twitter) uses AWS for data storage, content delivery, and platform stability during high-traffic events.
- BBC relies on AWS for video streaming, content management, and secure storage for global media delivery.
- Baidu utilizes AWS for data-intensive AI, search, and autonomous driving technologies tasks.
- ESPN employs AWS for low-latency, high-definition streaming, especially live sports events.
- Adobe: AWS powers Adobe’s cloud-based creative and analytics tools.
- NASA: AWS supports NASA’s data storage and analysis needs for space missions.
- CIA relies on AWS for secure cloud computing, focusing on data storage and analysis.
- Samsung uses AWS for IoT management, device analytics, and data-driven improvements.
Why enterprises use AWS
AWS’s early launch gave it a head start in refining and expanding its offerings. Its services cover everything from compute, storage, AI, machine learning, and more, with extensive integration and customization options. This maturity brings reliability that’s hard for competitors to match.
Other AWS advantages that often tip the scales for enterprises include:
- Global coverage. AWS spans more availability zones and regions than most cloud providers. This helps businesses reach users faster and keeps operations resilient.
- Robust partner network. AWS’s Marketplace and third-party integrations ensure businesses can find tailored, reliable solutions for their industry needs.
- High compliance standards. AWS meets strict regulatory requirements like HIPAA, SOC, and PCI, with specialized options like AWS GovCloud. These support many industries, from healthcare to government and more.
What’s Next: How To Control, Manage, And Optimize AWS Costs
AWS has become a favorite among organizations for its flexibility and scalability. Yet, it is also a budgeting headache for most. This pain point is so common that about 60% of companies exceed their cloud budgets simply due to insufficient cost controls.
AWS does provide cost management tools such as Cost Explorer and Budgets, which help identify usage patterns and set alerts. However, these tools often fall short in larger, complex environments. This limitation often leads to cloud waste, where resources like unused instances continue to rack up costs.
As a result, many organizations turn to third-party tools for improved visibility and control over cloud spending.
Enter CloudZero
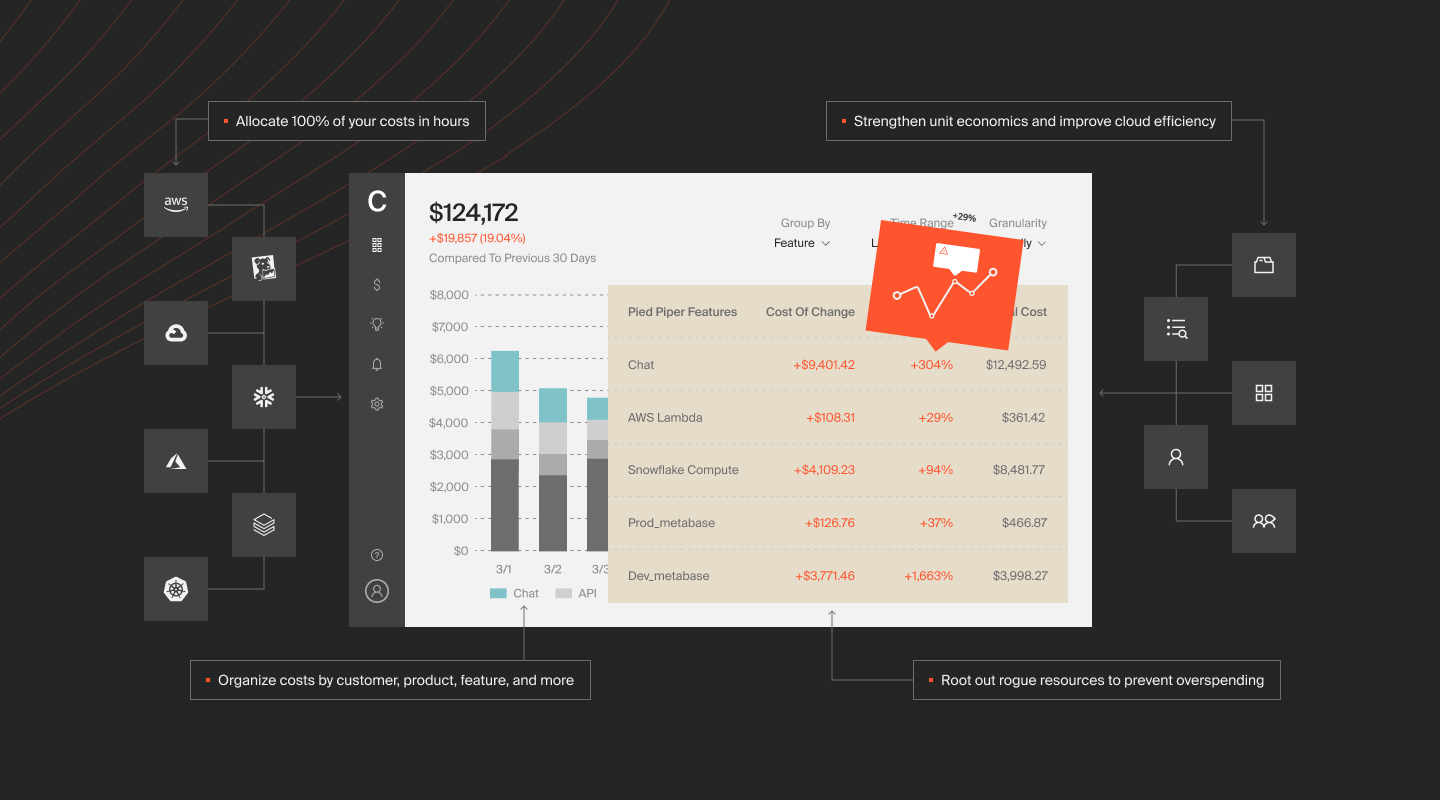
Most traditional AWS cost optimization tools focus on reducing waste and purchasing savings plans. CloudZero is different. It gives engineering teams real-time cost data, enabling them to make smart, profitable decisions.
CloudZero provides the tools engineers need to understand the direct cost impact of their work. Engineering teams can see how their code changes affect AWS costs. They can also link these costs to business metrics, like COGS and cost per customer. This visibility enables teams to make data-driven choices that align cloud spending with overall business.
CloudZero also:
- Automatically detects unusual spend events in real-time, notifying relevant teams to prevent budget surprises and overspending.
- Tracks cost down to the customer level. This enables companies to understand and control the cost-to-revenue balance for each client.
- Integrates with Kubernetes, providing precise cost allocation within clusters. CloudZero ensures accurate billing even for complex containerized environments.
- It ingests data from multiple cloud providers and services and consolidates all spending data into one dashboard for unified cost tracking.
- Supports custom budget creation for any business unit.
- It gives regular budget updates to engineering and finance. This fosters cost awareness and timely adjustments.
- Uses historical data and current trends to predict future cloud costs.
- Breaks costs into fine details such as cost per product feature, team, customer, and more.









