Whether you’re growing rapidly and need to expand your infrastructure or demand has slowed and you need to scale down, AWS Auto Scaling can help. While manual scaling is time-intensive and costly, auto scaling is an automated process that adjusts capacity for predictable performance and costs.
Auto scaling can help you optimize how your application is used and reduce wastage and optimize cloud spend. While the learning curve may be high, auto scaling has many benefits which you can further enhance through load balancing.
To help you better understand auto scaling and its benefits, this article will cover AWS Auto Scaling in full detail. We’ll cover exactly what AWS Auto Scaling is, how it works, its benefits, disadvantages, and more.
What Is AWS Auto Scaling?
AWS Auto Scaling is a service that assists organizations in supervising AWS-based software and cloud infrastructure. The service automatically adjusts capacity to maintain steady, predictable performance at the lowest possible cost.
AWS Auto Scaling can increase and/or decrease the capacity of AWS services to optimize costs. The service will monitor all scalable cloud services and resources related to a user’s applications. These resources may include:
- Aurora DB clusters and replicas
- Elastic Compute Cloud Auto Scaling Groups
- EC2 Spot Fleets
- Elastic Container Service (ECS) components
- Amazon Elastic Container Service
- DynamoDB global secondary indexes and tables
However, the best way to understand auto scaling is through Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) service. EC2 provides virtual servers or compute instances that you can use to host your application(s). These virtual servers are known as EC2 instances.
An organization may have multiple instances with different specifications. Throughout the rest of this guide, we’ll focus on Amazon Auto Scaling from an EC2 context, to make the topic simpler to understand.
How Does AWS Auto Scaling Work?
Elasticity (or elastic computing) is one of the cloud’s greatest attributes. Auto scaling facilitates elasticity by automatically adding resources to meet new workload demand and reducing them when demand decreases.
In the case of EC2, AWS will elastically scale your EC2 instances by launching new ones and terminating old unhealthy ones. You can use Amazon Auto Scaling to configure a certain number of instances using a set of defined scaling policies.
If an EC2 instance status-check fails, AWS Auto Scaling will replace the instance. This helps you develop more resilient applications. However, this isn’t the only way auto scaling works.
Auto scaling also utilizes performance-based metrics that are sent to CloudWatch. For instance, you might set performance metrics based on CPU thresholds. If CPU usage reaches a certain defined percentage, CloudWatch will notify AWS Auto Scaling. The auto scaling service will respond by launching an extra instance to handle the pressure and add more capacity.
This is how auto scaling works at a very basic level. However, it also works very well with elastic load balancing. For instance, clients can connect to Amazon’s load balancer, which will distribute them to your EC2 instances. If an EC2 instance fails, the load balancer will re-route the connection to the next available healthy EC2 instance.
AWS Auto Scaling will be notified during this process and will terminate the instance and launch a new one.
Configuring AWS Auto Scaling
When we configure EC2 auto scaling, there are two ways in which we can define the behavior of the instances that are launched. We can either use Launch Configurations or Launch Templates.
With a Launch Configuration, you must specify the Amazon Machine Image (AMI) and the instance type that you want to use. For instance, you can have a Linux 2 AMI type with a T3 micro instance type. Other configurable properties include the role, type of monitoring, tenancy, storage, security groups, IP Address Type, etc.
Thus, we can define these details in the launch configuration, and the auto scaling group will use it to initiate your instances. One thing that should be noted about Launch Configurations is that you cannot edit them after they are saved.
This means that if you want to modify your Launch Configuration settings, you’ll need to define a new one and update your auto scaling group to use it.
Launch Templates are a newer alternative to Launch Configurations. While they’re very similar, they have a few additional features. For instance, they allow you to:
- Have multiple versions of a template
- Edit your launch templates (you can’t edit saved Launch Configuration)
- Use dedicated hosts
- Use a combination of Spot and On-demand instances
- Define more advanced settings such as shutdown behavior, termination protection, placement groups, etc.
When To Use AWS Auto Scaling
Understanding when to use AWS Auto Scaling is crucial for maximizing its benefits and maintaining cost efficiency in cloud operations. Here are a few instances in which it is advantageous.
Cost optimization
AWS Auto Scaling benefits companies aiming to cut down their cloud costs. You pay for only the resources you require, increasing capacity when demand rises and decreasing it when demand falls. This flexible adaptation prevents over-provisioning and under-utilization of resources.
Pipelines for Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
The amount of work in CI/CD pipelines can vary greatly. This depends on the volume of code changes, builds, and deployments happening at the same time. AWS Auto Scaling can automatically change the resources for the CI/CD pipeline to ensure that builds and deployments are completed promptly without the need for manual interference. This results in quicker development cycles and speedier time-to-market for new features and fixes.
Development and testing environments
Auto scaling is useful in production settings. It also offers great advantages in development and testing environments. Development teams regularly have to conduct tests that demand varying amounts of resources in different stages. AWS Auto Scaling can automatically allocate and eliminate resources as required. This ensures that development environments are efficiently priced and responsive to the team’s requirements.
Batch processing jobs
AWS Auto Scaling is also valuable for batch processing jobs with varying resource needs. Activities like analyzing data, creating reports, and performing extensive calculations demand large computational power temporarily. Auto scaling allocates necessary resources for job performance and then reduces them afterward. This approach enhances resource use and reduces costs.
High and variable traffic
During peak times, certain online platforms experience sudden increases in the number of users. AWS Auto Scaling can increase resources when there is high demand to ensure optimal performance and decrease them when there is low demand to cut down on costs.
Expansion of geographical area
AWS Auto Scaling can help organizations handle the spiking demand from new users when they enter new geographic areas. Setting up auto scaling policies in many regions ensures that their applications have consistent performance and availability worldwide.
Maintaining application availability
AWS Auto Scaling is crucial for applications that need to maintain high availability. Auto scaling ensures that your application stays accessible and responsive. It does this by automatically getting rid of unhealthy instances and keeping the preferred capacity even when hardware fails or other issues occur.
Auto Scaling Benefits And Disadvantages
Advantages of AWS Auto Scaling
AWS Auto Scaling has numerous benefits. These include:
- Improved fault tolerance – AWS Auto Scaling allows you to monitor your applications. It can help you terminate any corrupted instances and automatically launch new ones.
- Improved cost management – Scaling is done automatically through a set of threshold parameters. You can scale up or down depending on your organization’s requirements. This allows you to save money on personnel and equipment. It also gives you a centralized position to view all your scaling costs.
- Reliability – Since scaling is done automatically, it’s incredibly efficient and reliable. Furthermore, whenever scaling is initiated, AWS will send notifications to your phone or email address.
Disadvantages of AWS Auto Scaling
Nothing is perfect. However, it would seem that AWS Auto Scaling has very few disadvantages. These include:
- Increased development complexity – Integrating auto scaling of any type may make code updates, deployments, and configurations more complicated. You’ll need a separate service to synchronize your code changes. In addition to this, if your application saves user input, it may be harder to capture and manage persistent data such as logs.
- Complicated setup – Setting up AWS Auto Scaling can be challenging. It may require hours of training and a bit of troubleshooting. Amazon could remedy this by making its graphical user interface more intuitive and user-friendly.
- Limited across region functionality – Adding and working with regions and availability zones can be quite complex and isn’t handled with much nuance. Amazon could provide users with more refined options to help organizations running multi-region applications with different usage scopes.
What Is An AWS Auto Scaling Group?
AWS Auto Scaling Groups are an integral part of the scaling process. In the case of EC2, they manage how instances are scaled using Launch Configurations and/or Launch templates. They scale out, scale in, and ensure that there are a minimum and maximum number of instances running. They’re also responsible for automatically registering new instances to the load balancer.
In essence, the Auto Scaling Group (ASG) is a collection of EC2 instances. Thus, the size of the ASG is dependent on the capacity or the number of instances you’ve configured for the group.
ASGs are free. You don’t pay for them, only the EC2 instances that are spun up and spun down.
Load Balancing Vs. Auto Scaling
What is load balancing?
High-traffic applications and websites can serve thousands of users internationally each day. Load balancing describes the process of distributing workload evenly across multiple servers. A load balance sends requests to servers that can efficiently handle them to optimize speed and performance while preventing downtime.
For a long time, load balancers existed in the form of hardware in private data centers. However, thanks to the popularization of the cloud, load balancers have evolved. You may hear them referred to as application delivery controllers (ADCs).
They now provide additional capabilities such as security, acceleration, and authentication. In the context of Amazon EC2, a load balancer will distribute traffic among EC2 instances. The load balancer will spread a load across multiple downstream instances while exposing only a single point of access (DNS) to your application. Additionally, the load balancer will perform regular health checks on instances to ensure they are working correctly.
Amazon’s Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) can also provide SSL termination for your websites. This means that it will handle the termination and encryption of the connection between the client and your website. The ELB will also separate public traffic from private traffic and help you maintain permissions across regions.
How does load balancing work with auto scaling?
Load balancing isn’t an alternative to auto scaling. In fact, it can help facilitate efficient auto scaling when the two work in unison. While load balancing will re-route connections from unhealthy instances, it still needs new instances to route connections to.
Thus, auto scaling will initiate these new instances, and your load balancing will attach connections to them. That’s why having both AWS Elastic Load Balancing along with AWS Auto Scaling is worthwhile.
AWS Auto Scaling Policy Types
Auto Scaling uses various policy types to manage and improve resource scaling.
Below are the primary categories:
Target tracking scaling policies
These policies automatically change the instance count to meet a desired utilization level for a specific metric, like CPU usage or request count per target.
Step scaling policies
A step scaling policy modifies capacity using a series of scaling adjustments. The adjustments change based on the extent of the alarm breach.
Simple scaling policies
These policies increase or decrease a set amount of instances when a specific metric hits a specified threshold.
Scheduled scaling policies
These are scaling policies that are planned at specific times or days of the week in order to manage resources.
Understanding Your AWS Costs
Above, we explored what AWS auto scaling is and how it works with AWS Elastic Load Balancing. Understanding how services like these work and integrating them into your organization can help you optimize costs and save time.
Being able to make informed cost and engineering decisions like this, though, first start by having complete visibility into your cloud spend. This is where a cloud cost intelligence platform, like CloudZero, can help.
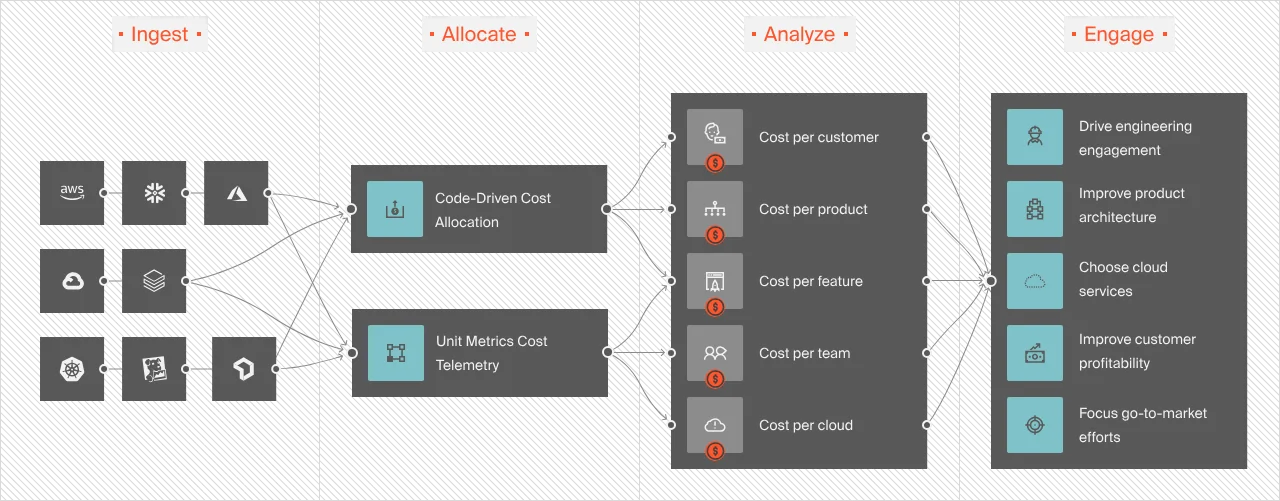
CloudZero provides visibility into your cloud costs, enabling engineering teams to drill into cost data from a high level down to the individual components that drive their cloud spend — and see exactly what AWS services cost them the most and why.
With detailed cloud cost intelligence, organizations can make informed product, engineering, and business decisions.  to see how CloudZero can put your engineering team in control of cloud spend.
to see how CloudZero can put your engineering team in control of cloud spend.
AWS Auto Scaling FAQs
What are the benefits of using AWS Auto Scaling?
AWS Auto Scaling offers enhanced fault tolerance, cost optimization, and application reliability. It automatically adapts resource capacity, decreasing the need for manual involvement. This guarantees that applications operate smoothly, optimize costs, and utilize resources effectively.
How do I configure AWS Auto Scaling?
Users can set up preferences either with Launch Configurations or Launch Templates. Launch Configurations are more straightforward but less adaptable. Launch Templates offer more features. These include version control and the option to use different instance types. You can configure scaling policies such as custom CloudWatch alarms, network traffic, and CPU usage.
How does AWS Auto Scaling help with cost management?
AWS Auto Scaling adjusts resource capacity automatically in response to real time usage. You will only be charged for the resources you need at any moment. This reduces extra usage and maximizes cost-efficiency in the cloud.
Can AWS Auto Scaling be used across multiple regions?
AWS Auto Scaling is efficient in a single region. However, managing it across several regions becomes complicated. This necessitates thorough planning and configuration to consistently maintain performance and cost efficiency.
How does Elastic Load Balancing work with AWS Auto Scaling?
Elastic Load Balancing distributes incoming traffic among various instances. When paired with AWS Auto Scaling, it ensures that traffic is directed to healthy instances. It also adds or removes instances as needed.
How does CloudZero integrate with AWS Auto Scaling?
CloudZero offers insight into cloud costs related to Auto Scaling. It assists in monitoring costs immediately and aligns them by business metrics such as cost per customer, product, and feature. This incorporation ensures effective cost management and optimization throughout your cloud infrastructure.